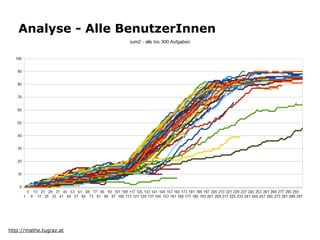
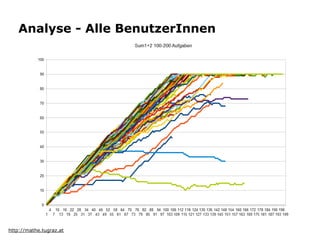
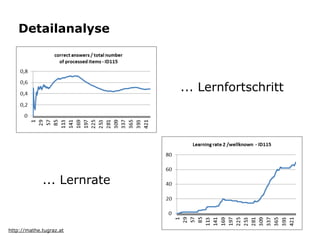
Learning analytics is the interpretation of learner-specific data to improve the individual learning process. It involves collecting traces left by learners and using them to enhance learning. While the potential is difficult to assess given increasing data volumes may reveal new insights, learning analytics aims to discover information, social connections, predict learning, and provide recommendations and feedback to support learners and instructors. Key applications include analyzing performance, modeling students, detecting behaviors, grouping students, and developing courseware.