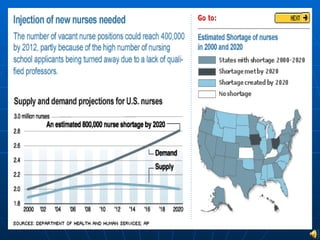
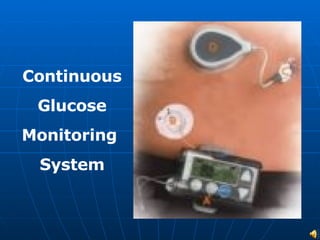
This document discusses quality control in nursing. It covers three main paths to quality control: education, practice, and technology. Regarding education, it discusses the roles of nurse educators and how advancing education benefits both nurses and communities. For practice, it discusses nurse-managed centers and how they can lead to superior patient outcomes. It also discusses the roles and qualifications of case managers. Finally, it discusses how technology can advance the future of nursing, using continuous glucose monitoring as an example. The conclusion reiterates that nurses at all levels, including bedside nurses, case managers, nurse practitioners, and educators, are involved in quality control efforts.