Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

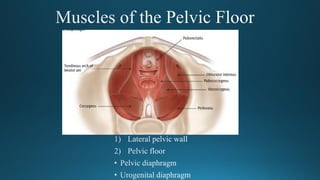
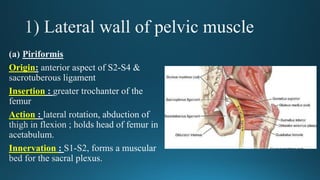
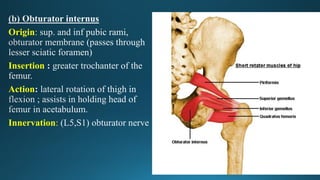
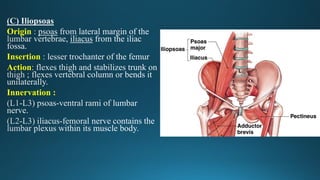
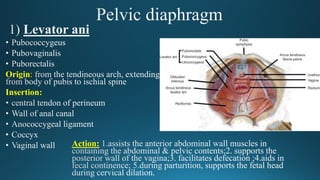
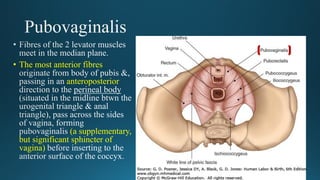
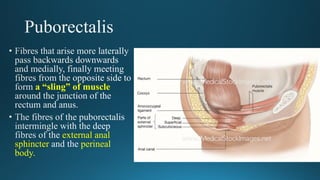
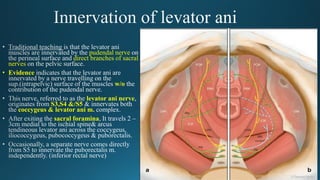
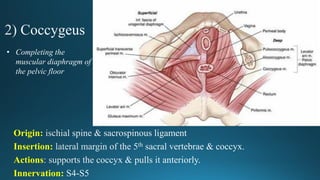
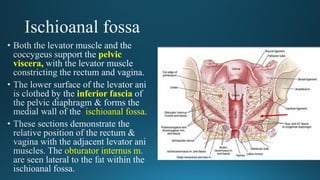
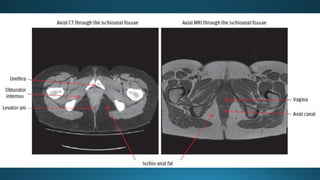

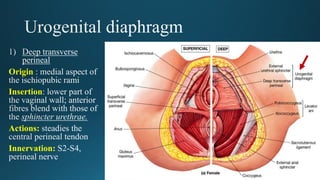
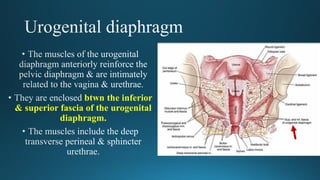
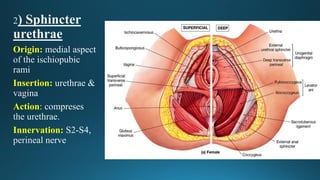

The document reviews the anatomy and imaging of pelvic muscles, specifically in relation to obstetrics and gynecology. It discusses the origin, insertion, action, and innervation of pelvic floor muscles, including the levator ani and external anal sphincter. The text highlights the impact of childbirth on pelvic floor integrity, particularly the risk of rupture and subsequent prolapse.
















