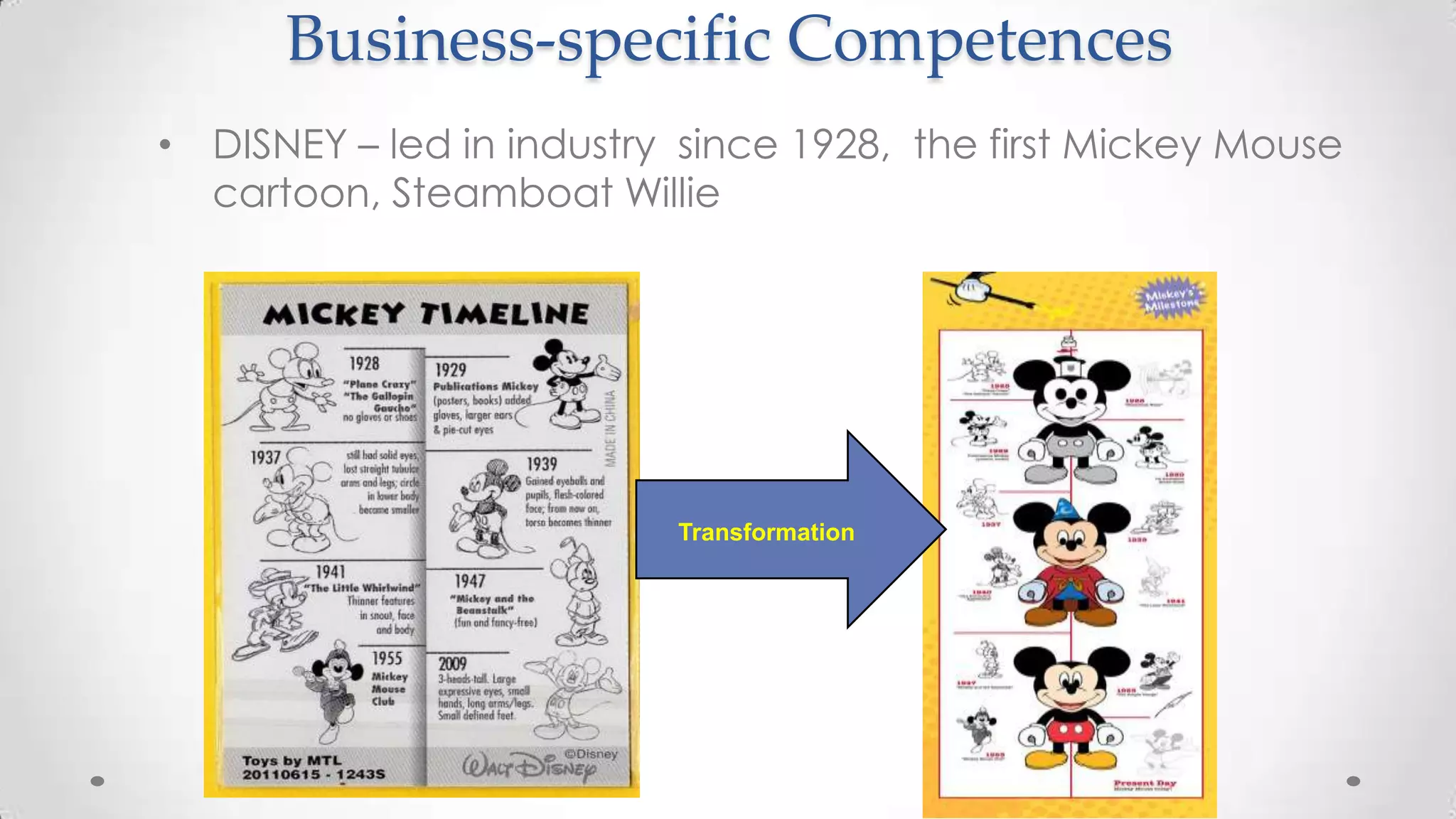
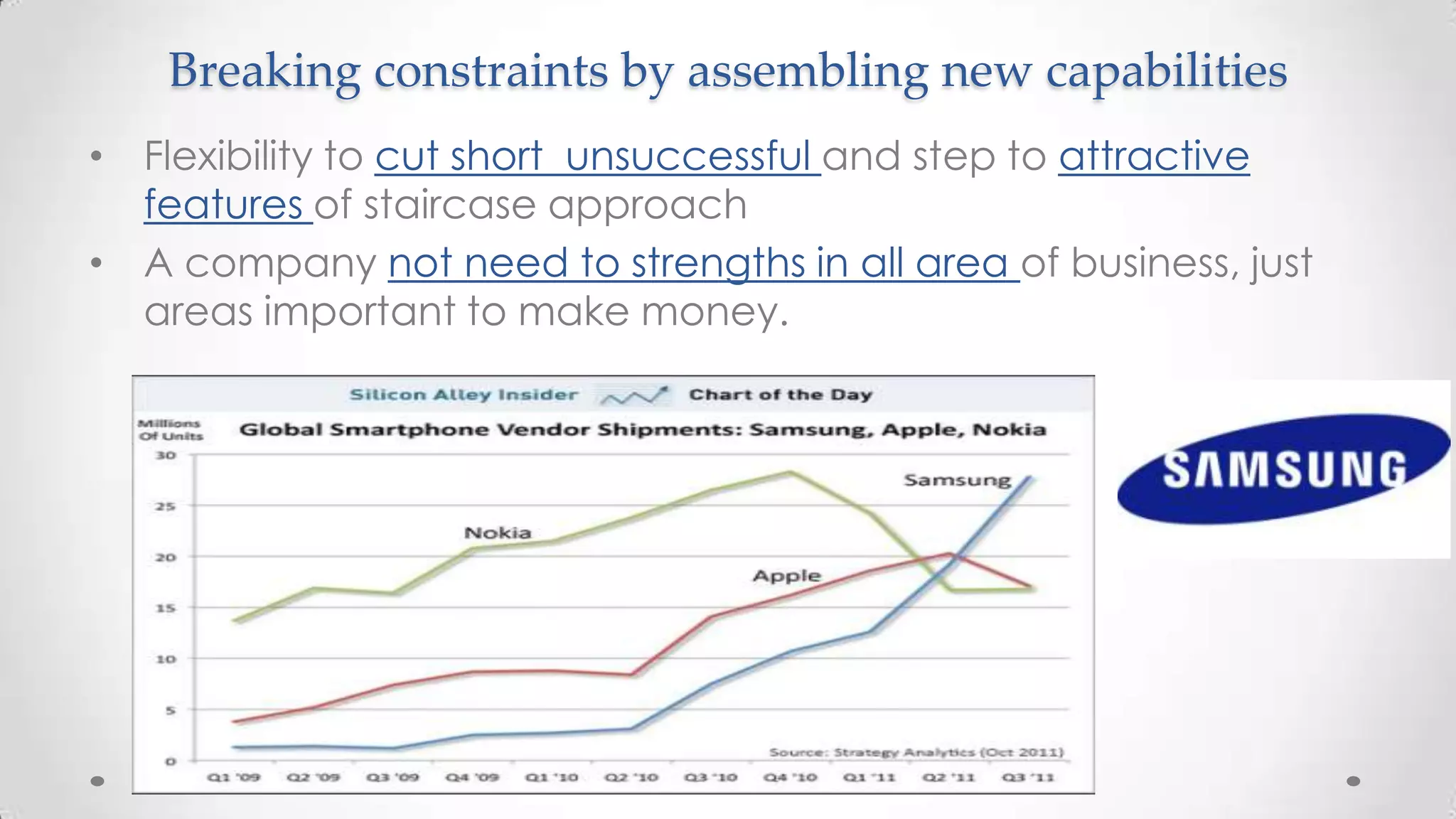
This document discusses strategies for achieving growth through a "staircase" approach with three horizons. It provides examples of how companies like Coca Cola Amatil, Disney, and SAP implemented growth strategies. The key points are:
1. Successful companies plan both short-term tactics and long-term vision within a clear strategy, taking short-term steps to build new skills and seize opportunities.
2. They assemble "platforms" of capabilities including core competencies, growth-enabling skills, privileged assets, and special relationships.
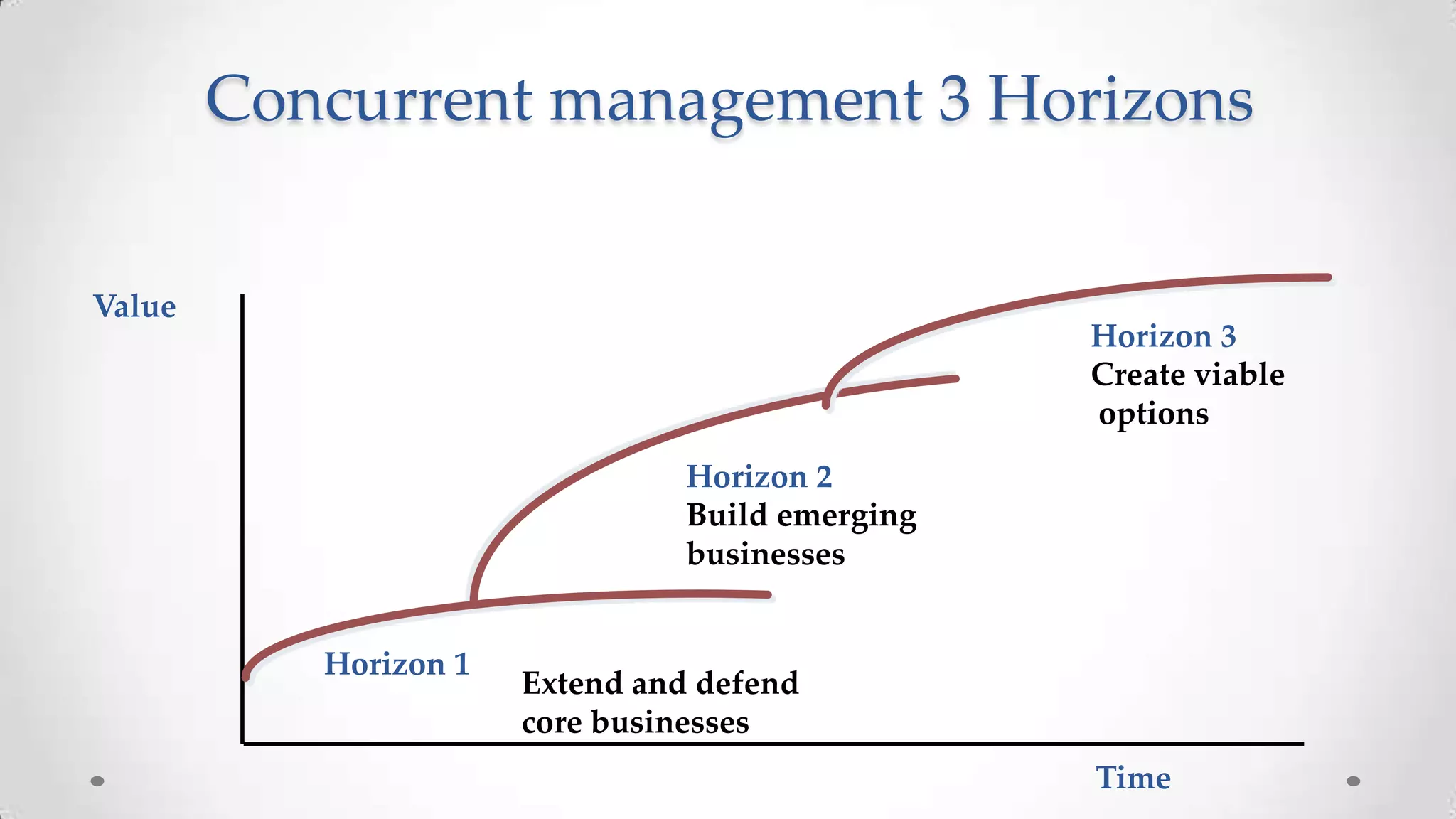
3. Leaders must concurrently manage initiatives across three horizons - extending the core business, building emerging businesses, and creating future options - to achieve sustainable growth over 10