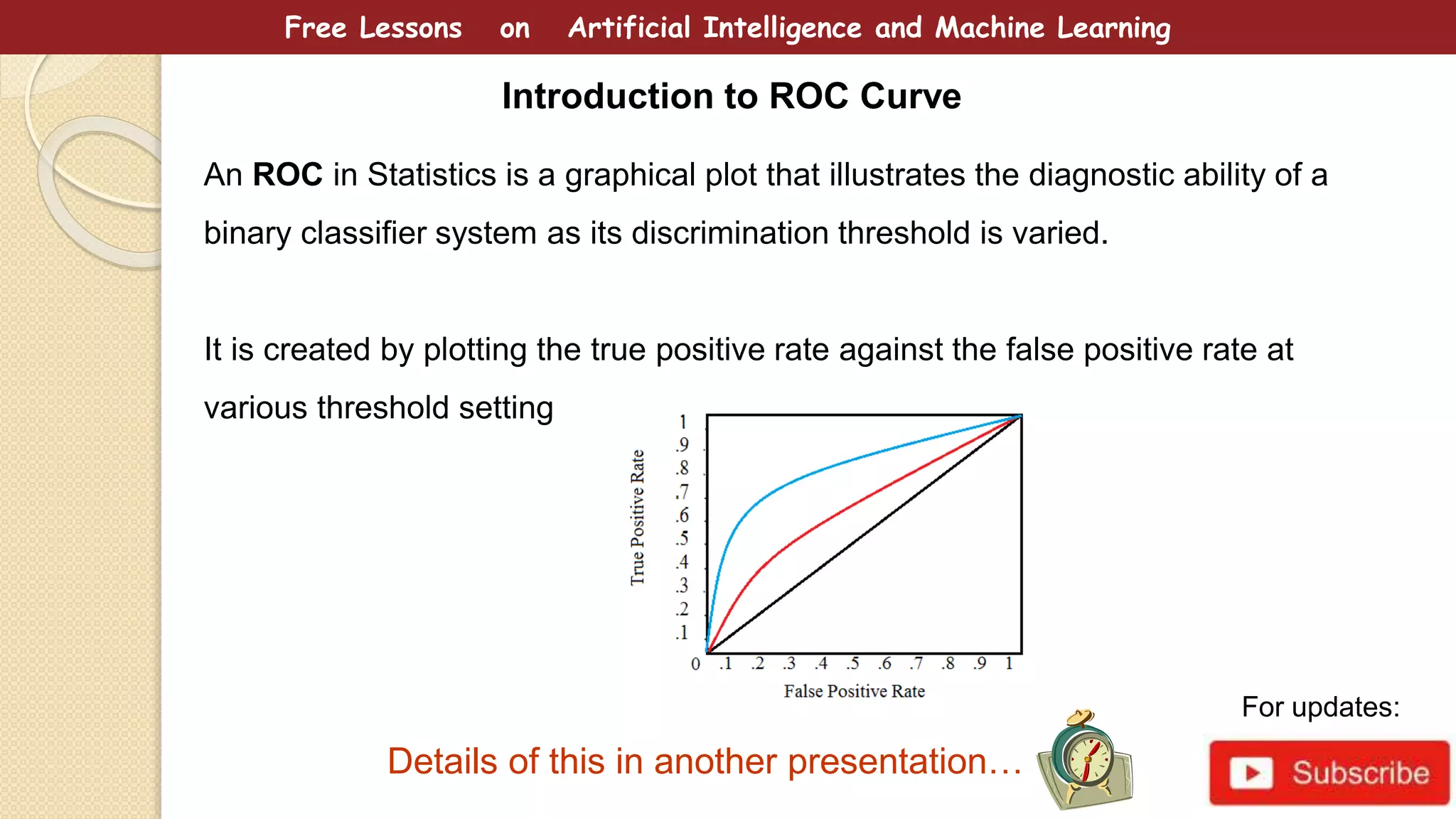
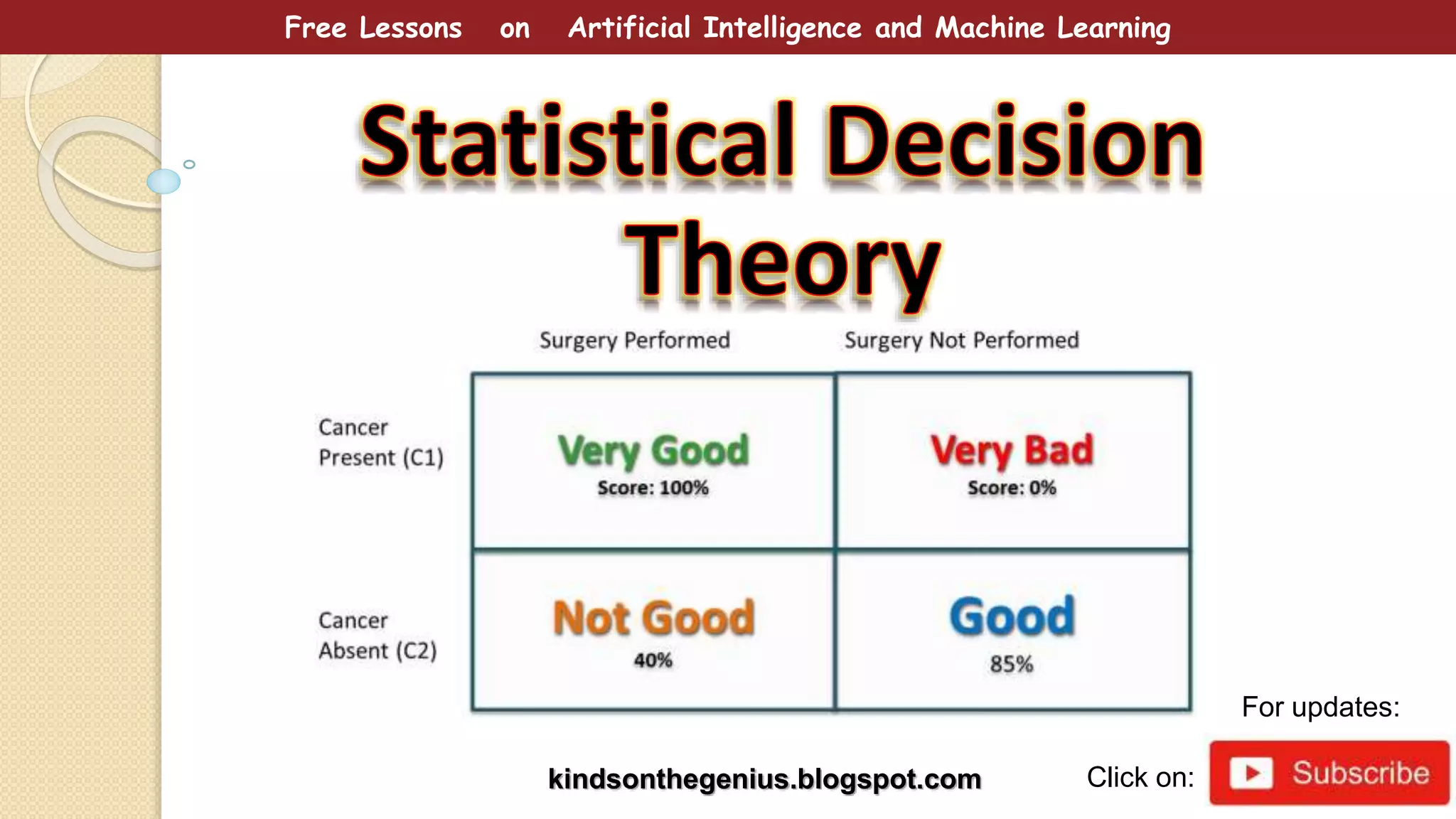
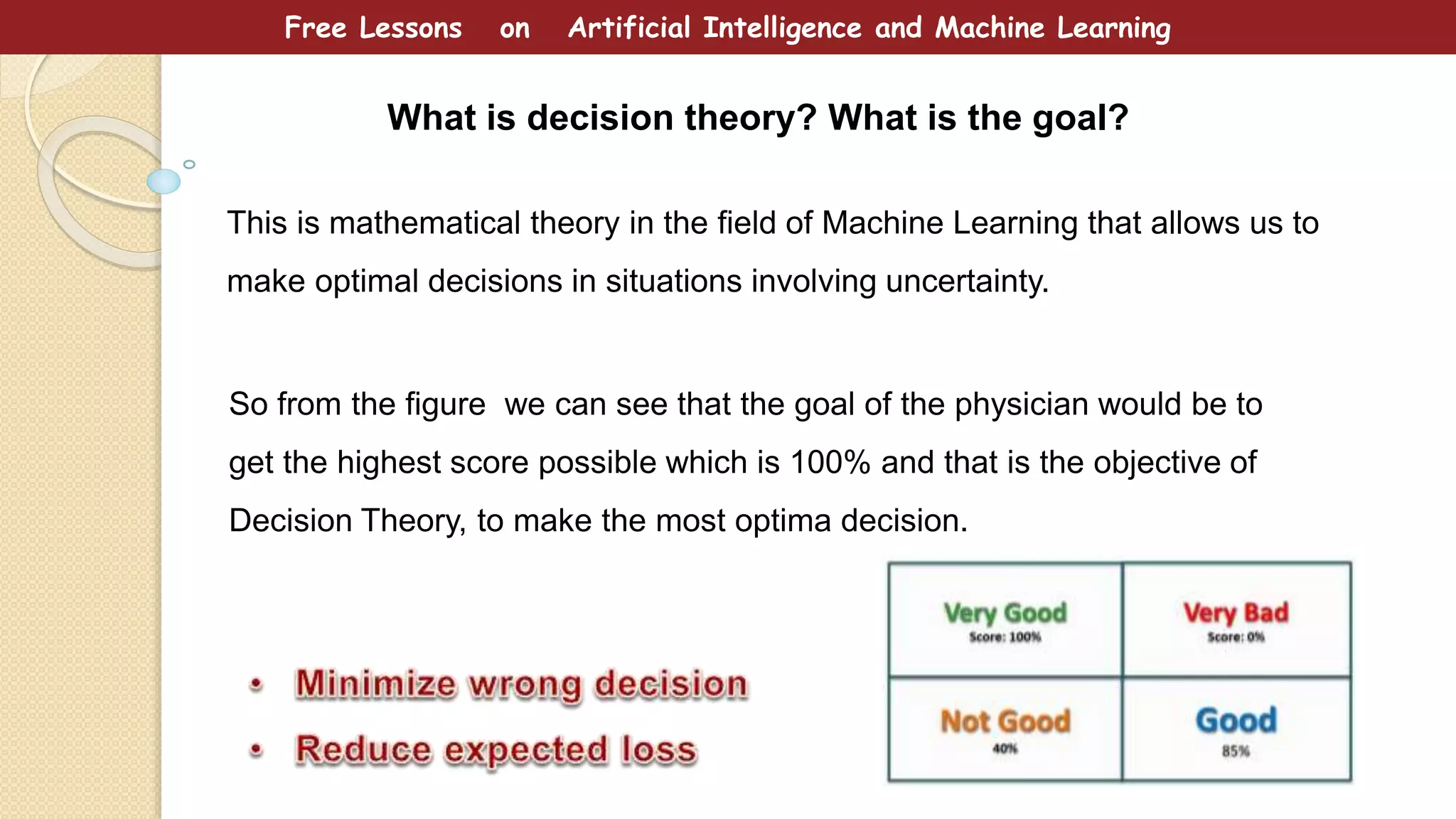
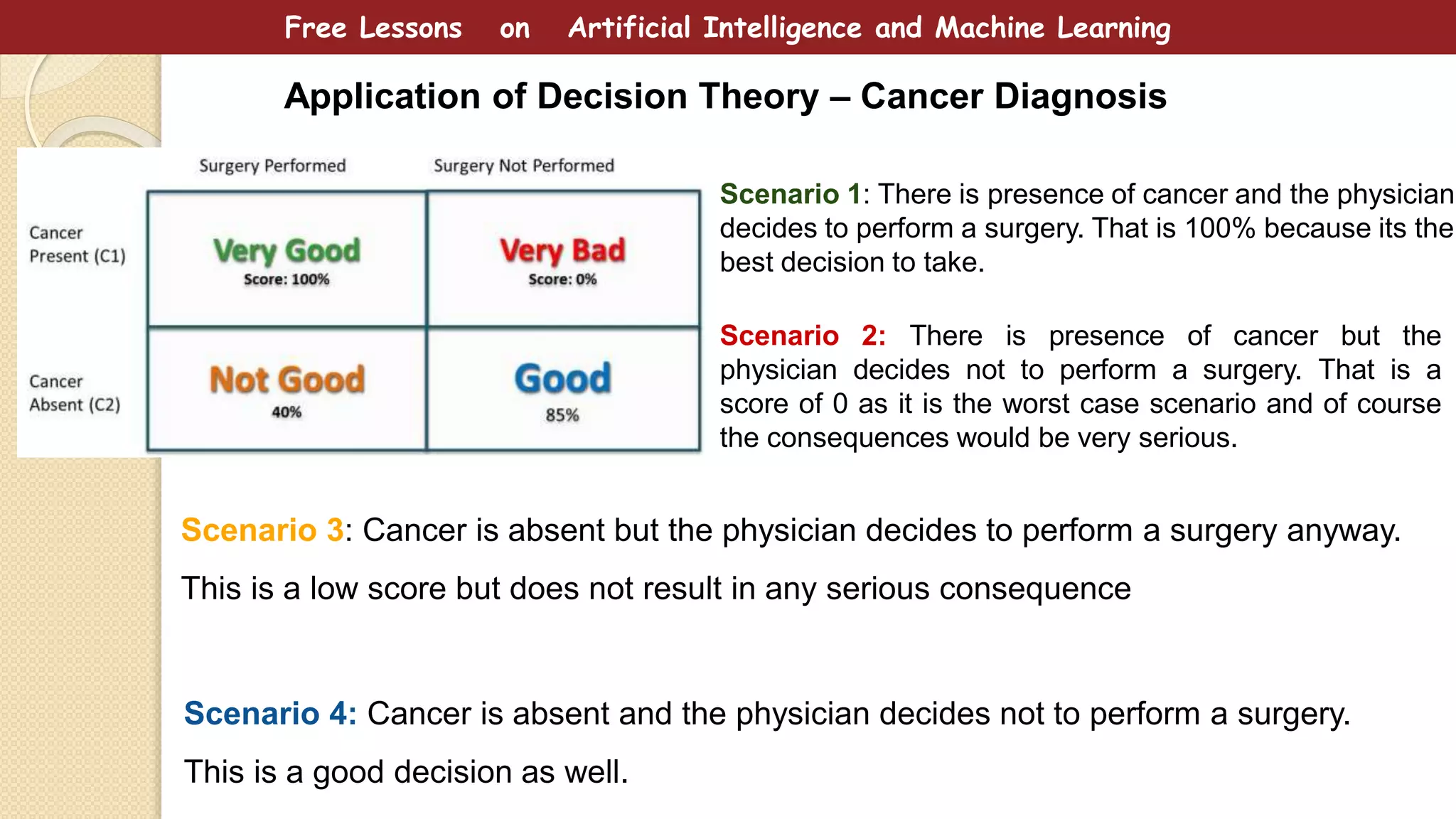
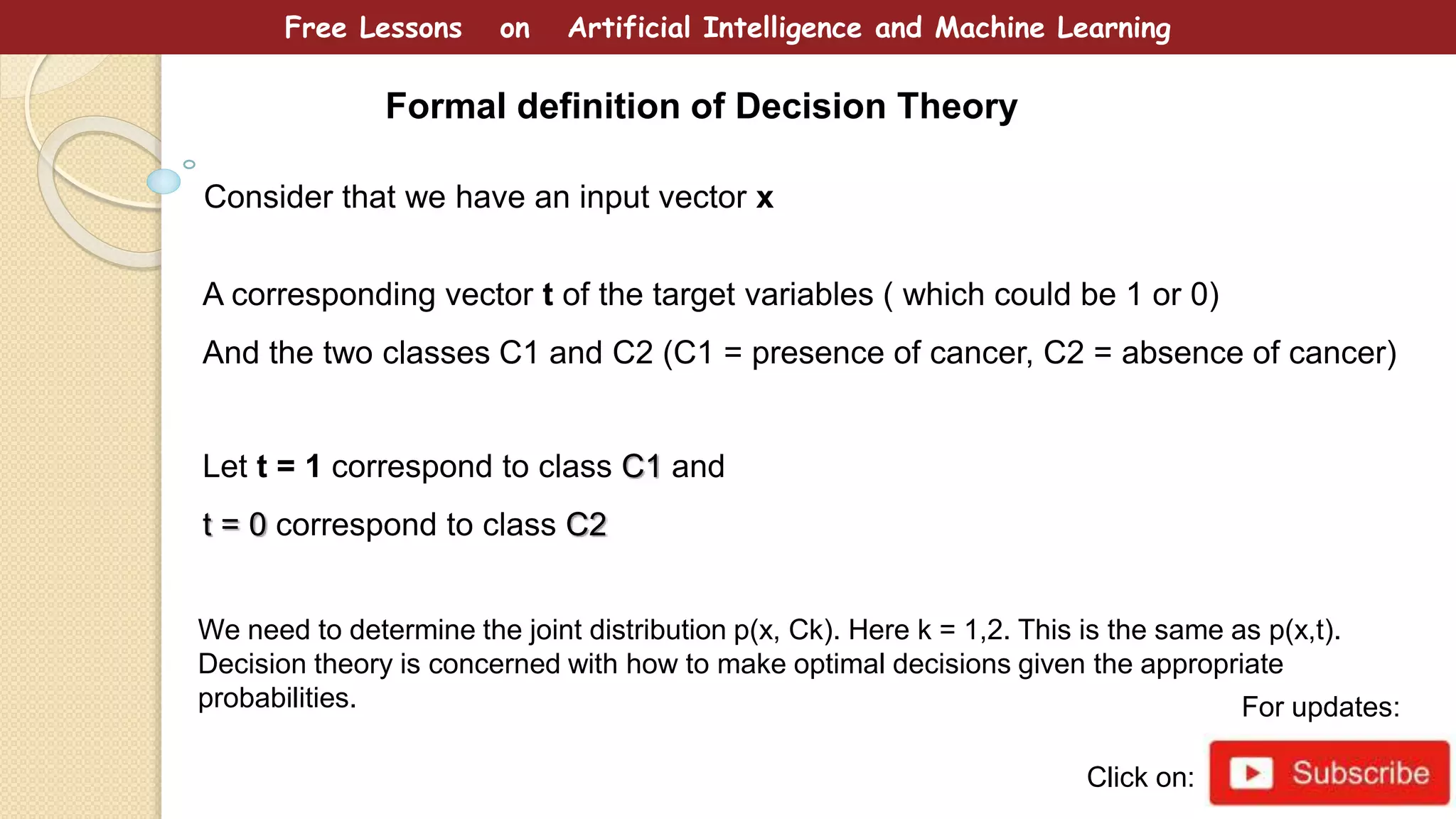
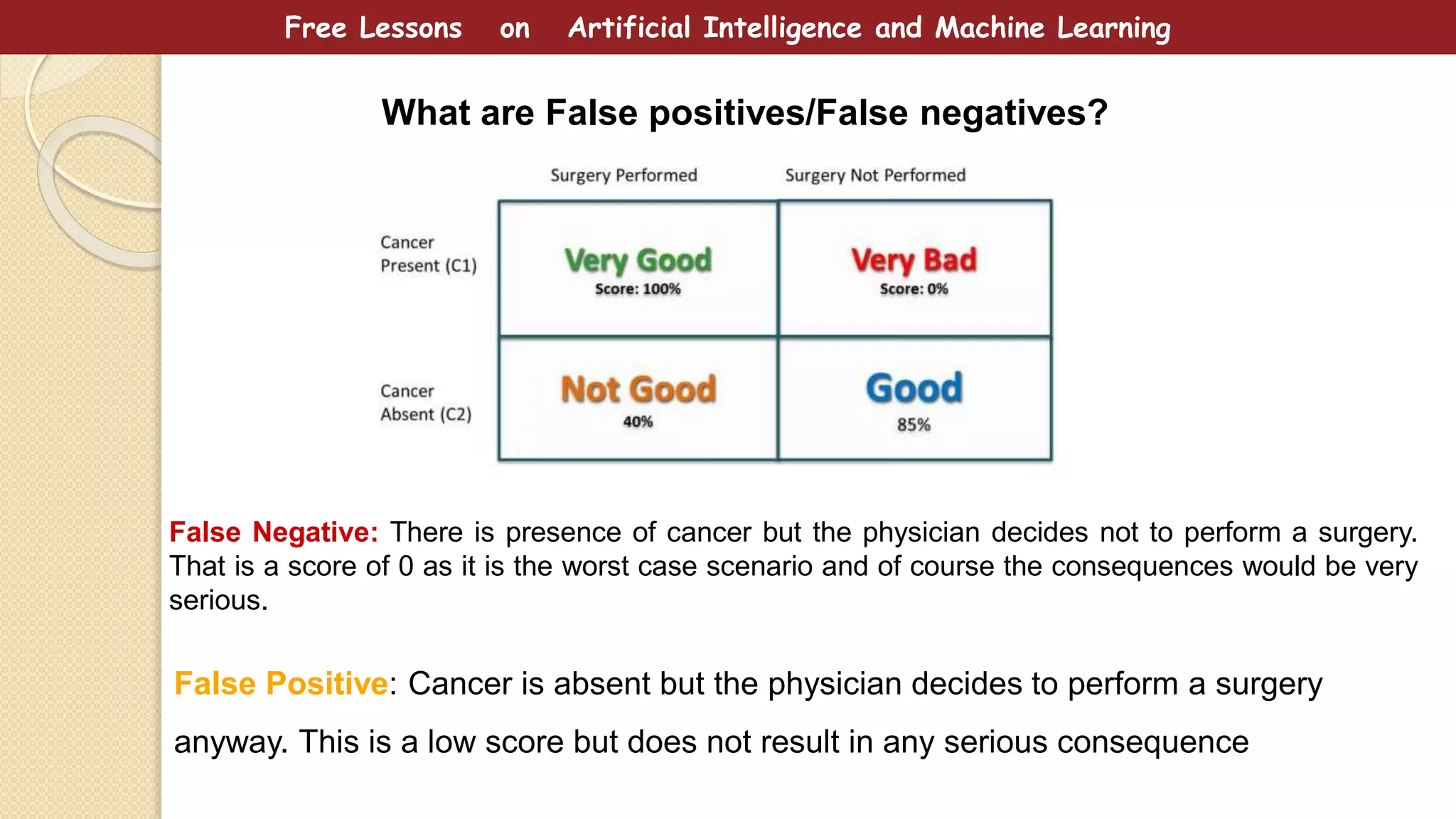
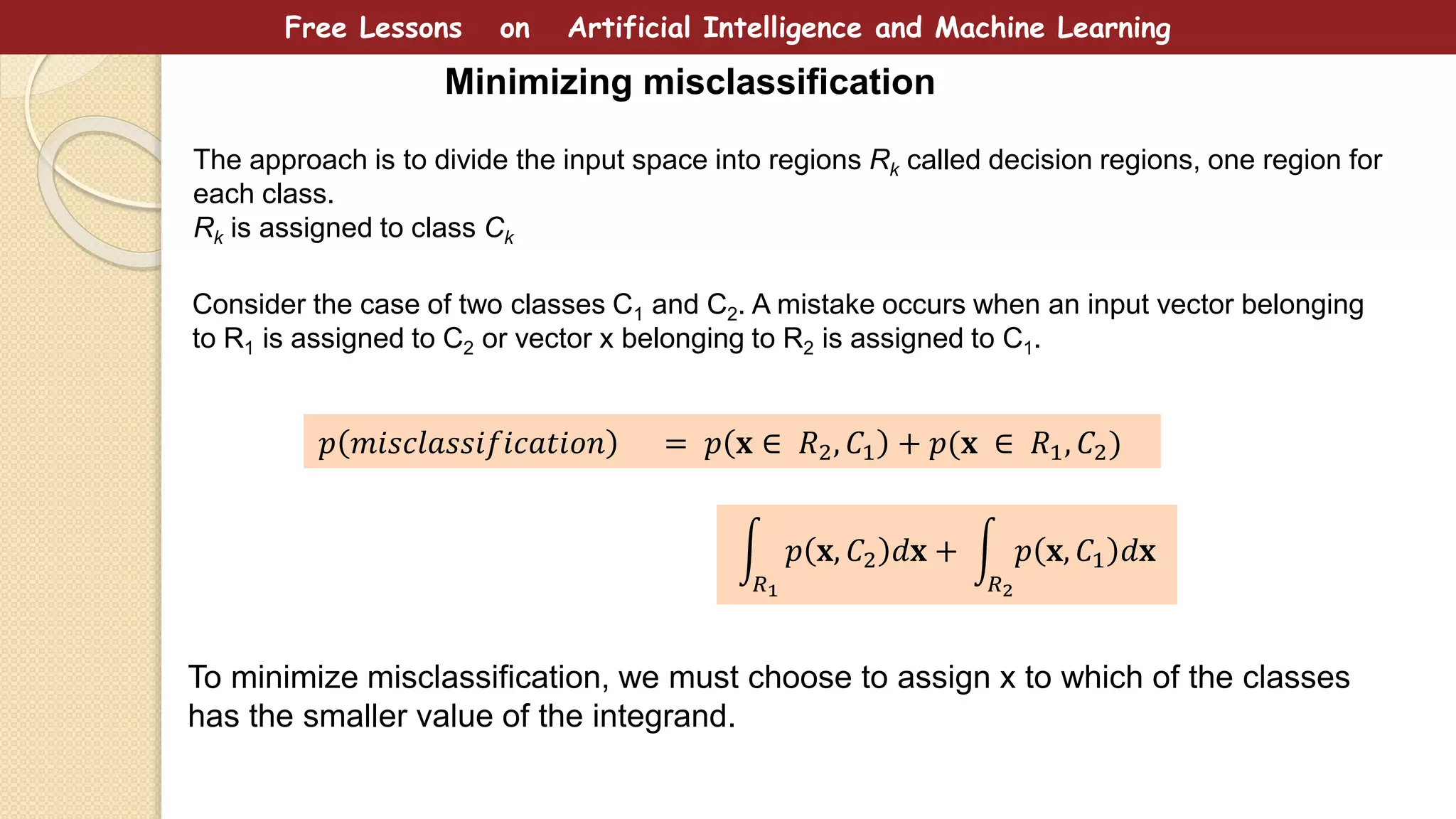
This document provides free lessons on decision theory in the context of artificial intelligence and machine learning, specifically in cancer diagnosis. It covers the concept of decision theory, including scenarios of misclassification, false positives, false negatives, expected loss, and the use of ROC curves for evaluating binary classifiers. The document emphasizes the goal of making optimal decisions under uncertainty using mathematical approaches.

![Free Lessons on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Reducing Expected Loss
The Loss Matrix
The Loss Matrix is a table showing the decision that was taken relative to
the true class
Assuming that for a new value of x, we assign it to class Cj whereas the real correct
class is Ck. It means we have incurred a loss Lkj, which is the k, j element of the loss
matrix.
𝐸[𝐿 ] =
𝑘 𝑗 𝑅 𝑗
𝐿 𝑘𝑗 𝑝(𝐱, 𝐶 𝑘)𝑑𝑥
The average loss function is given by the equation:
The best solution is one that minimizes the average loss function. For a given input
vector x, our uncertainty in the correct class is expressed through the joint
probability distribution p(x, Ck)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticaldecisiontheory-180122125749/75/Basics-of-Statistical-decision-theory-8-2048.jpg)