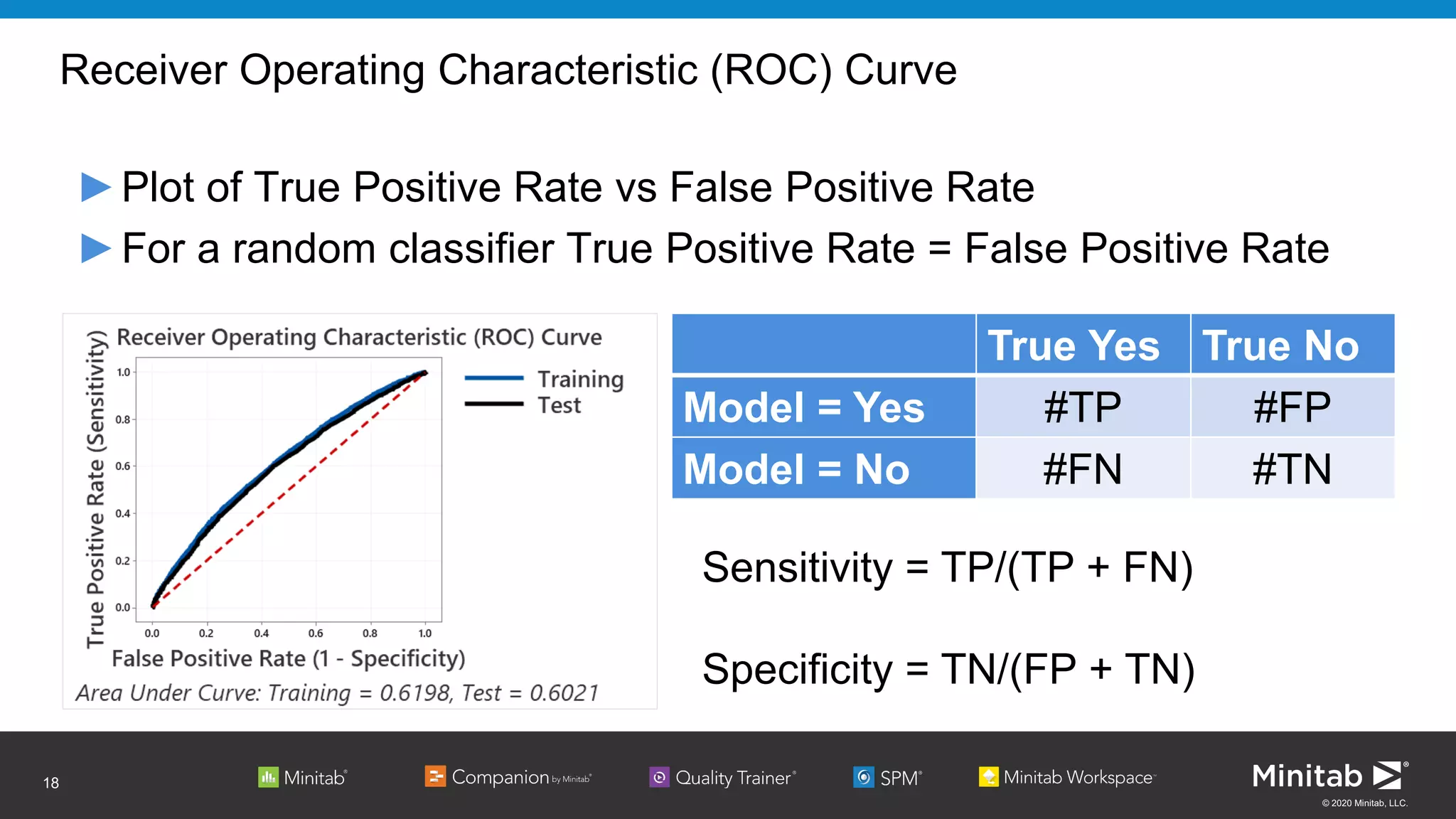
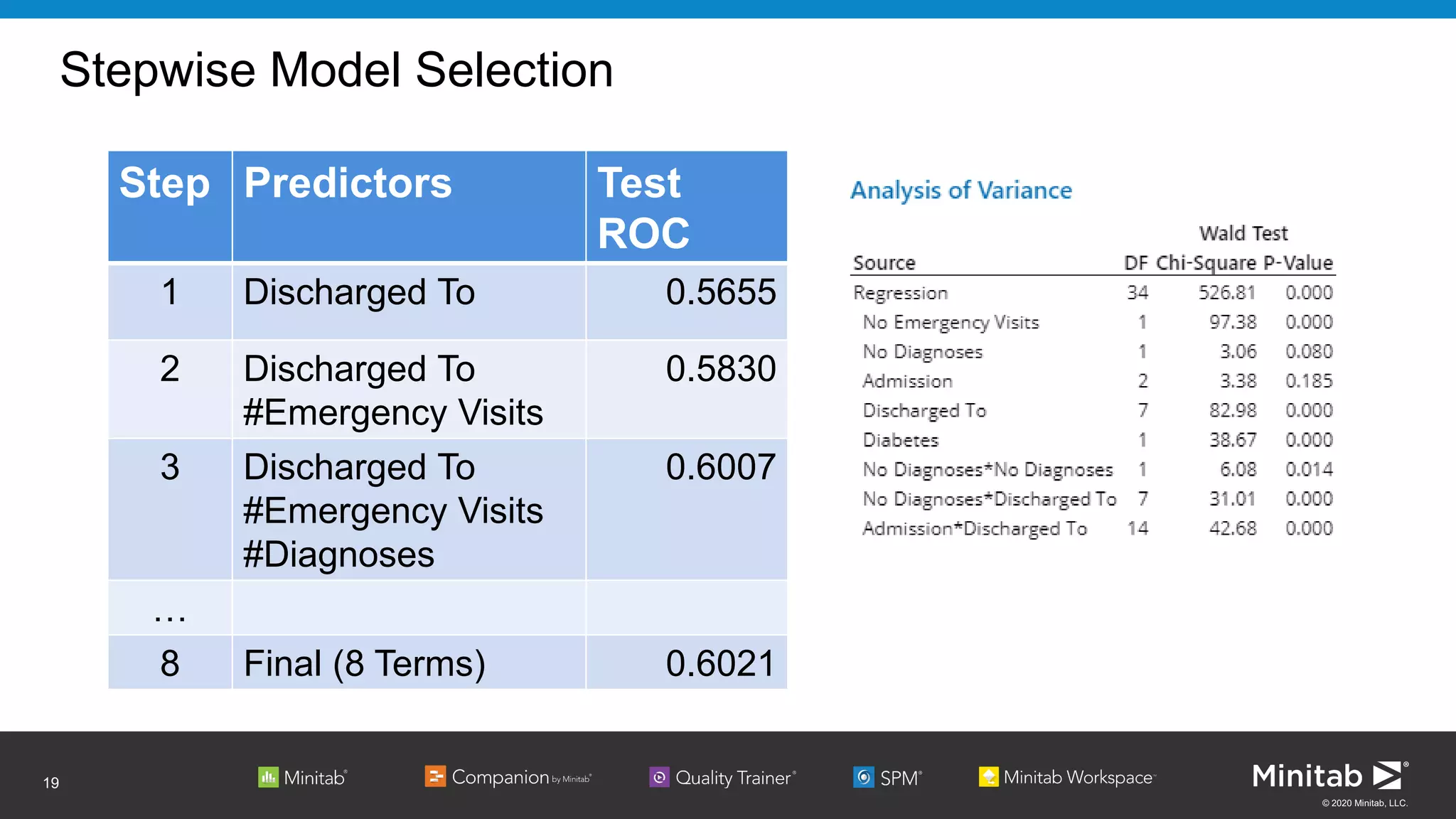
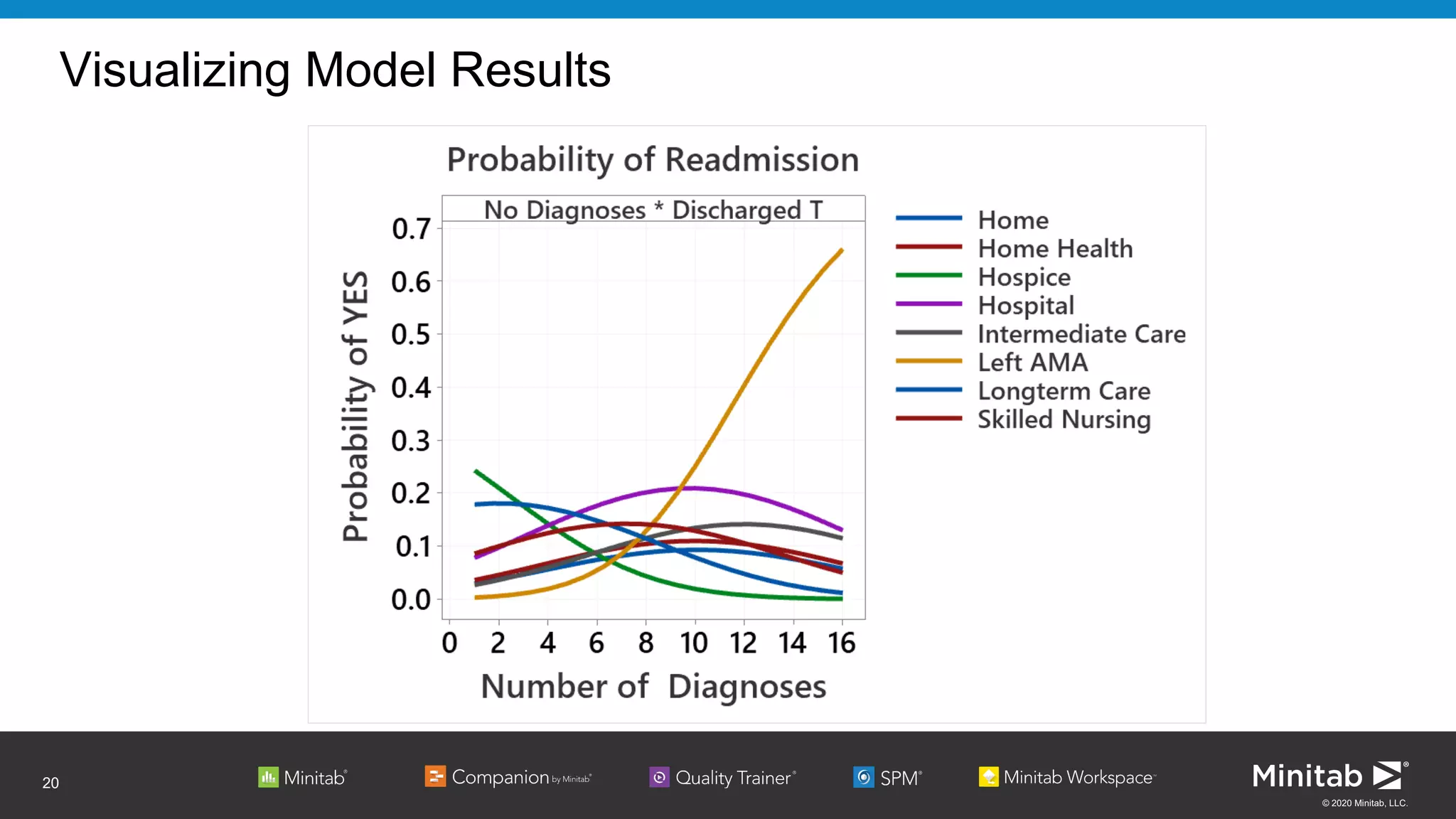
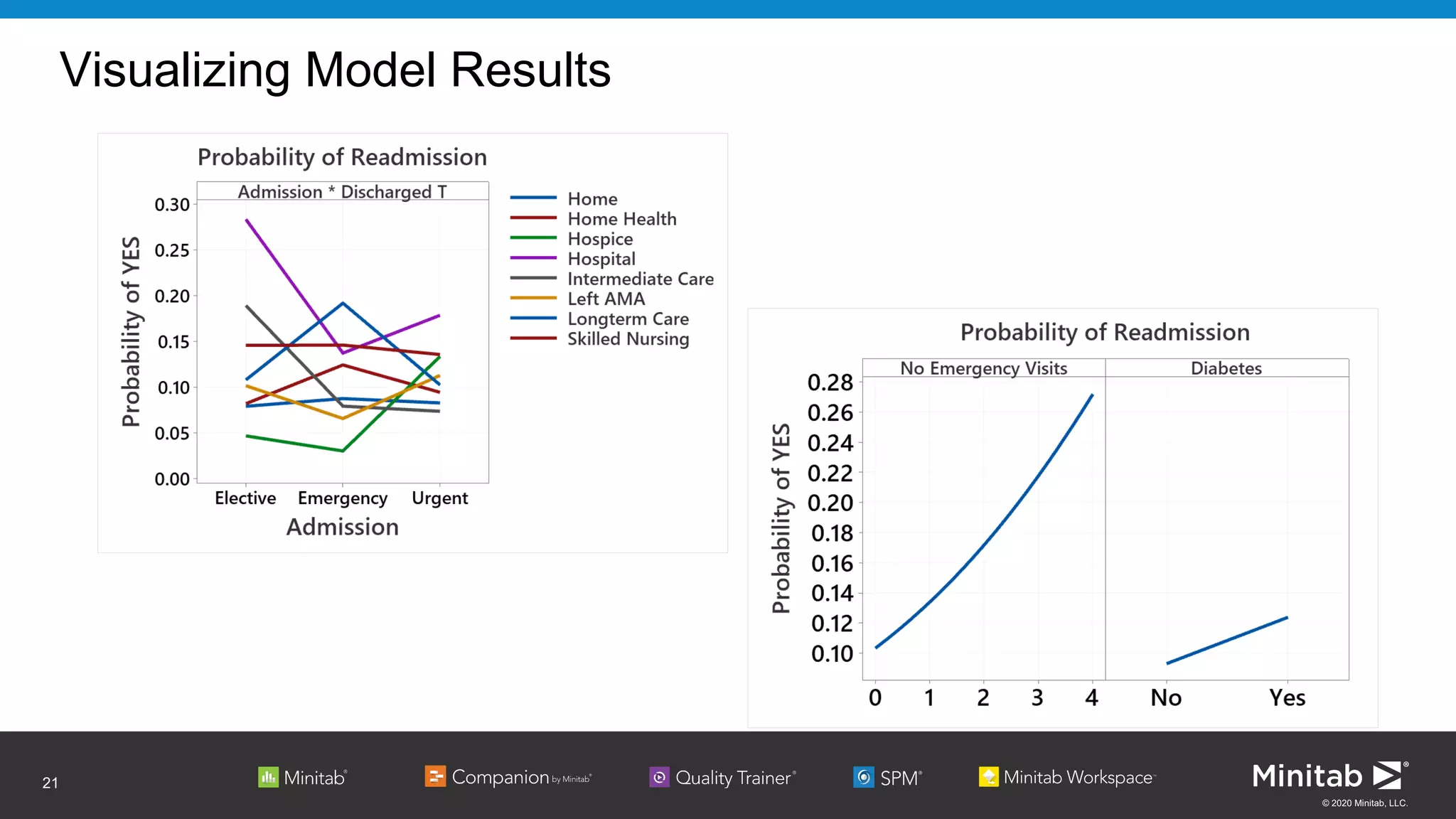
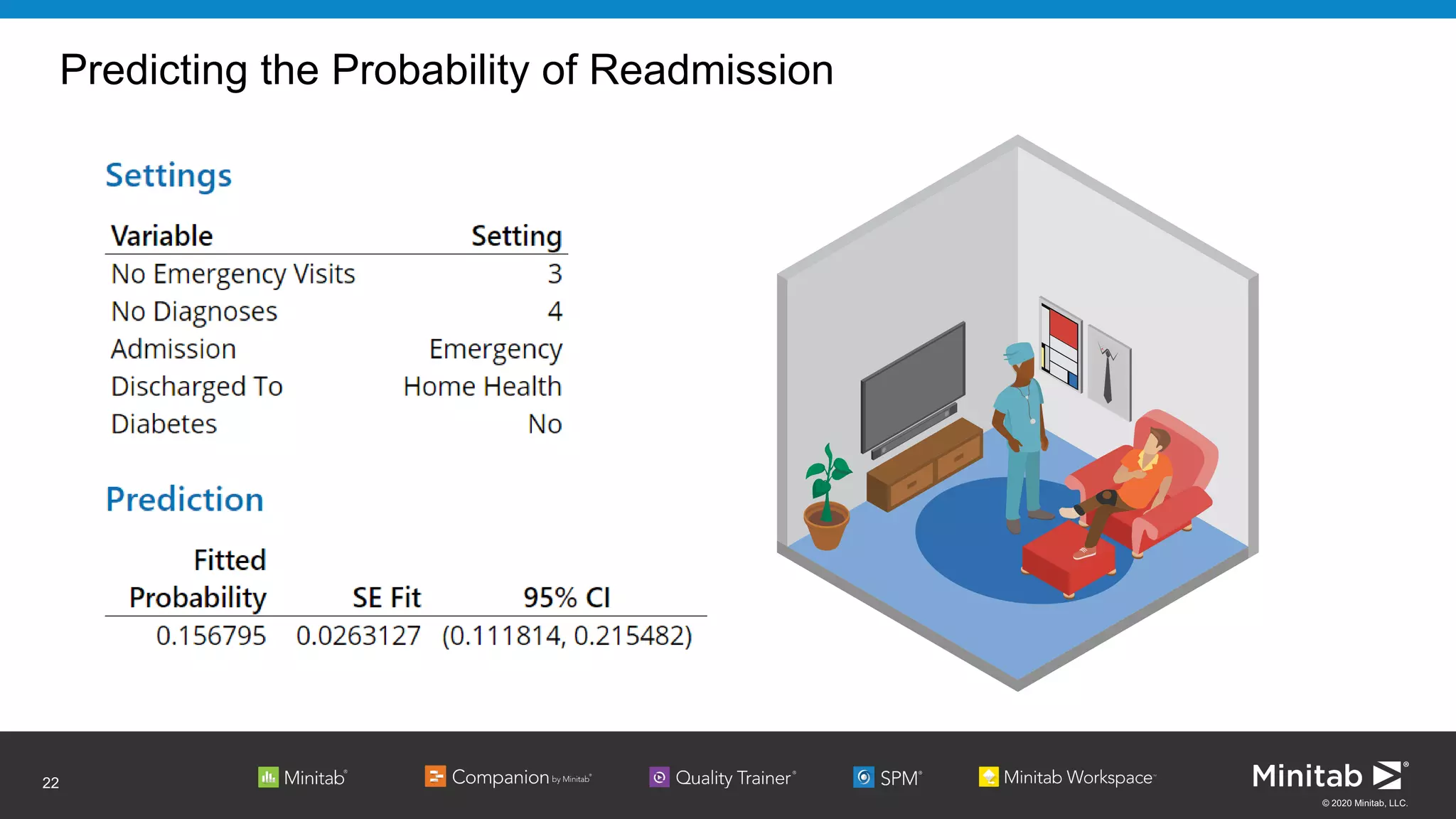
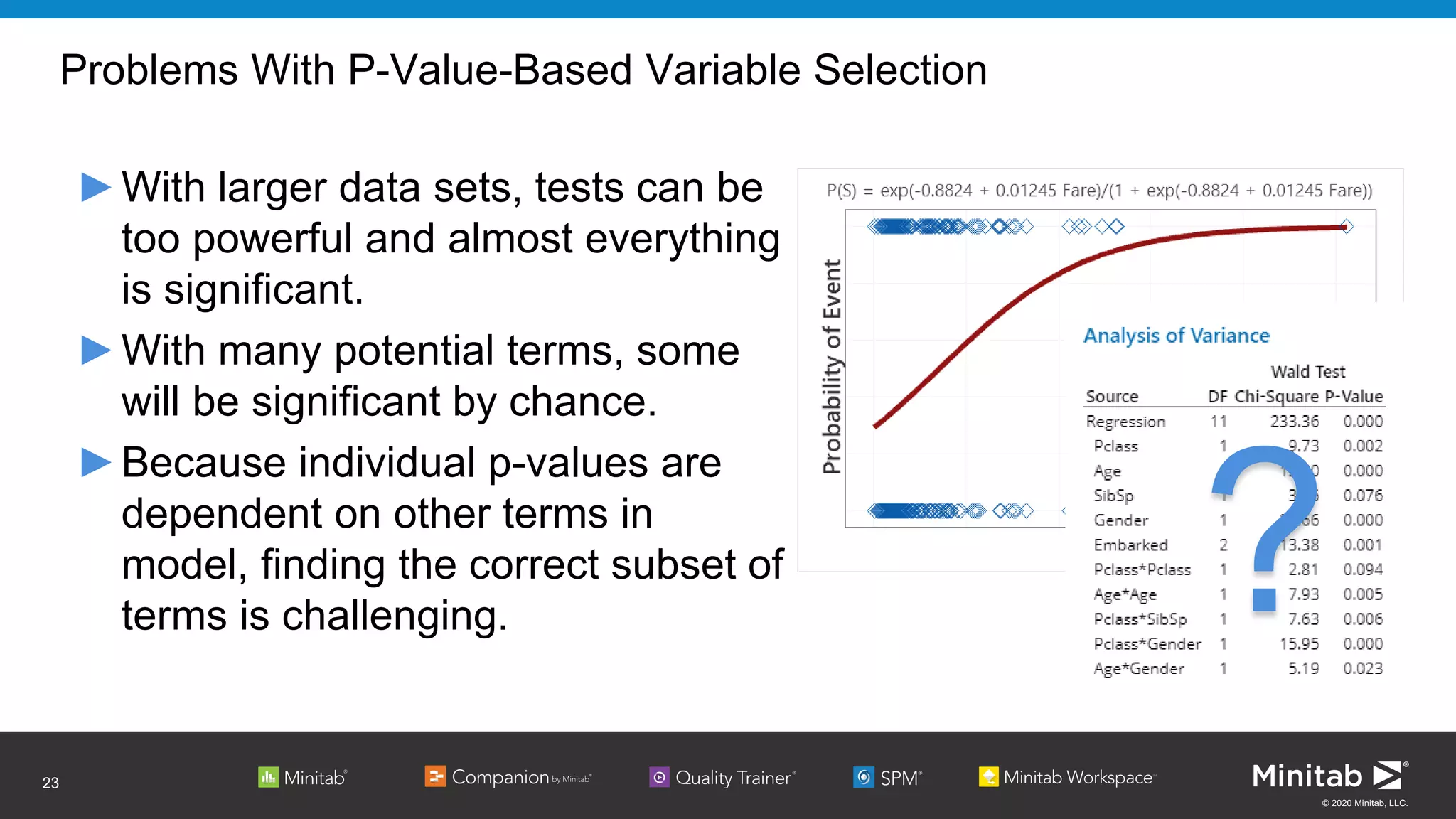
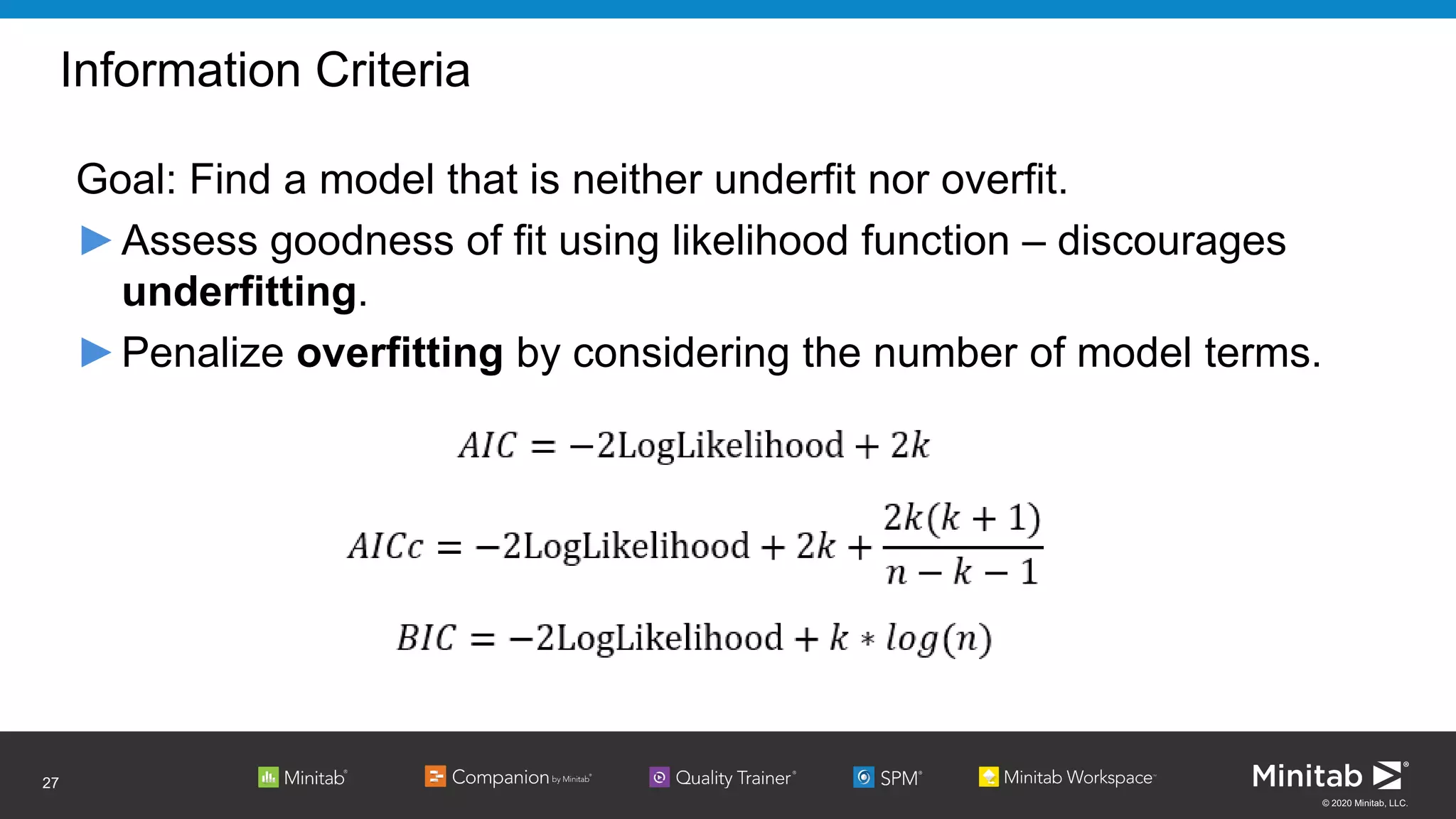
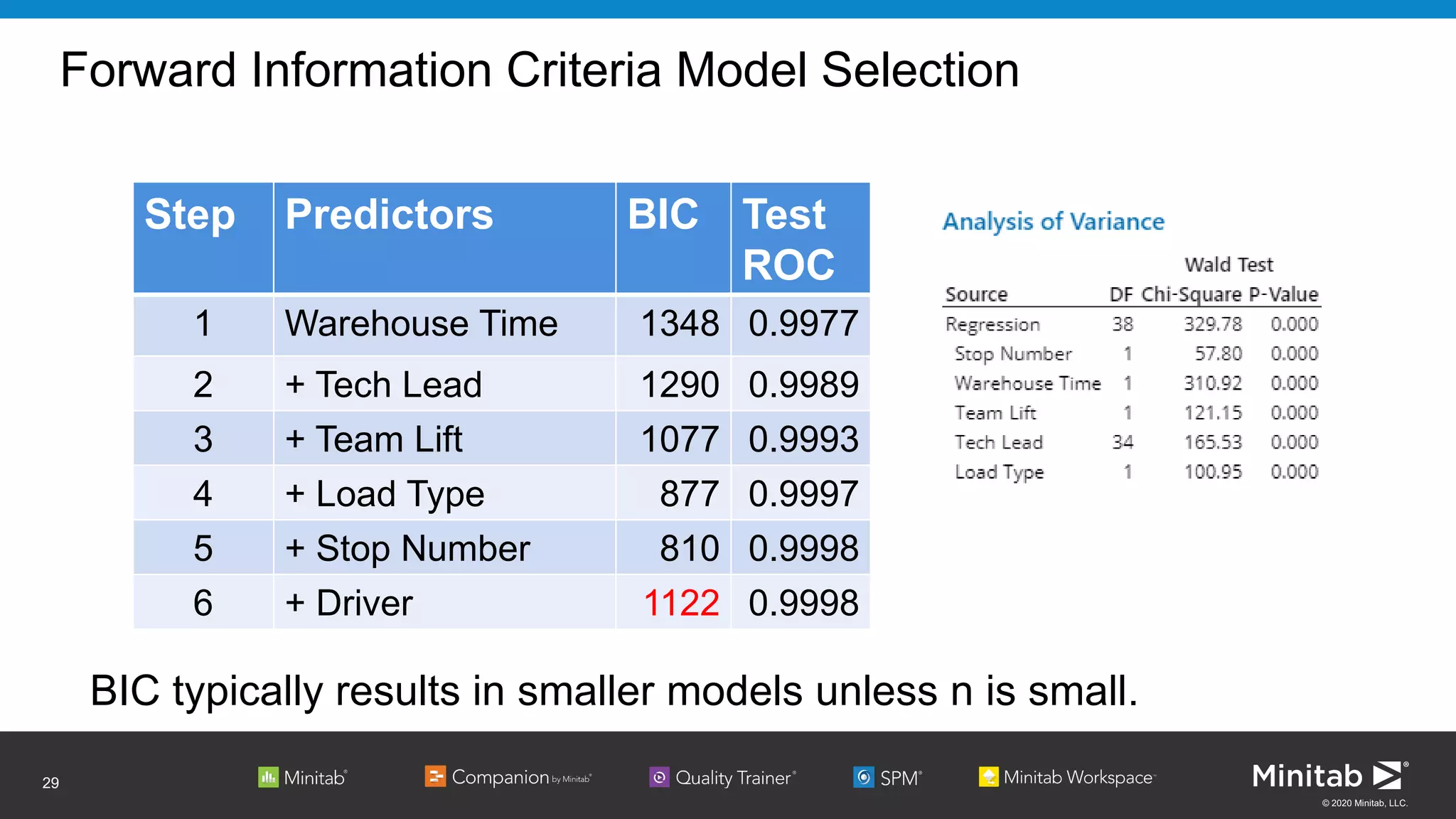
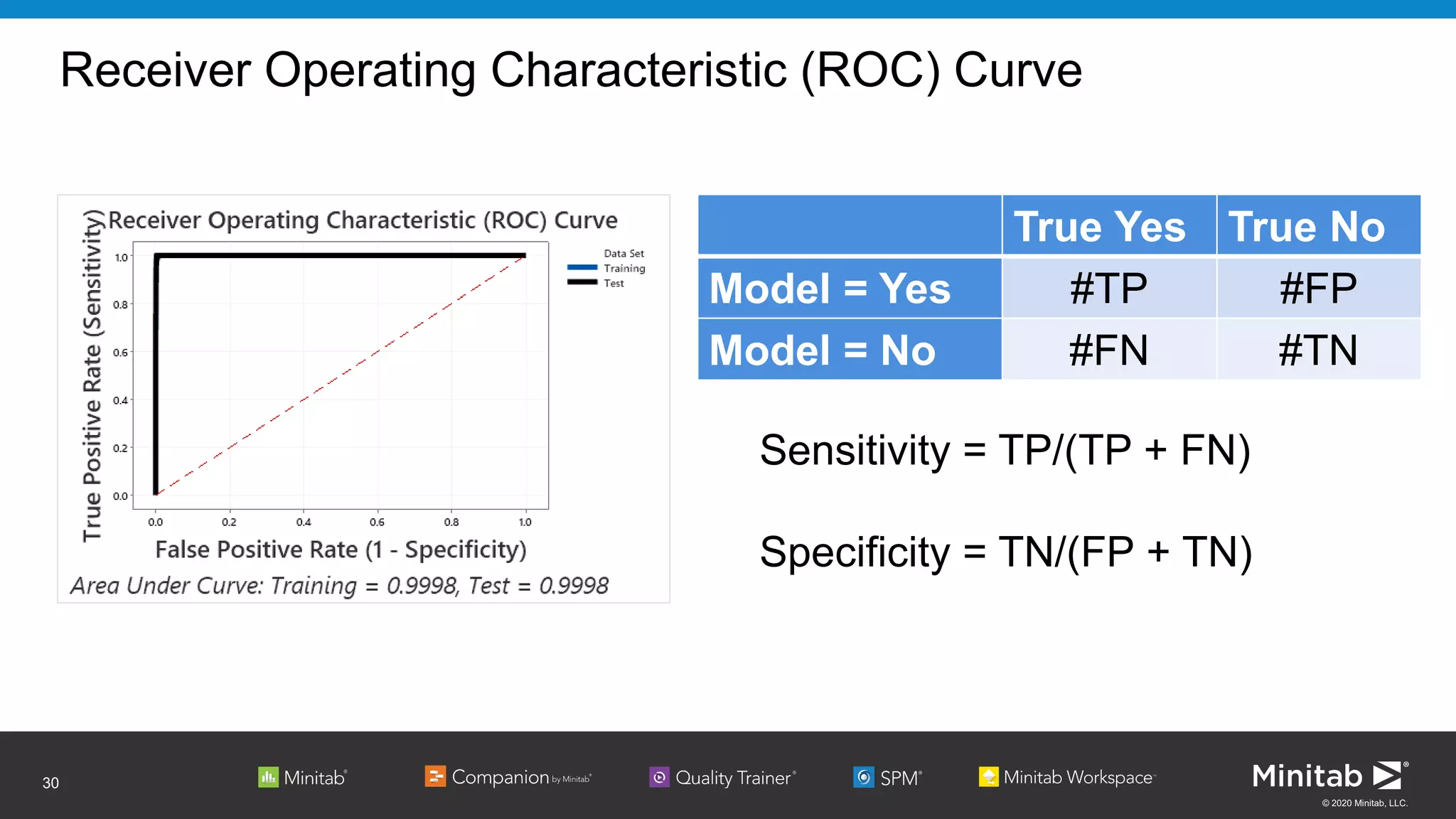
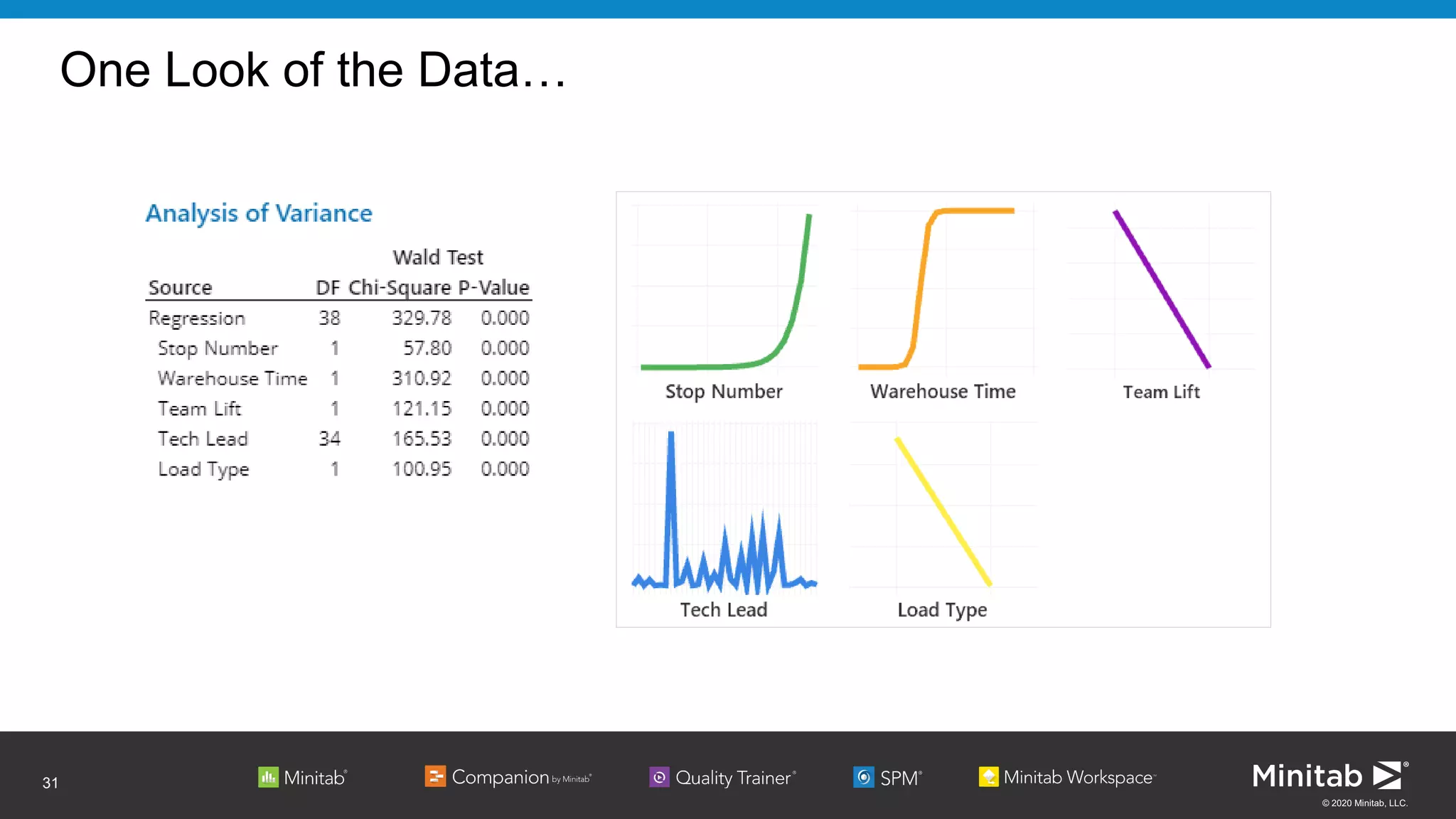
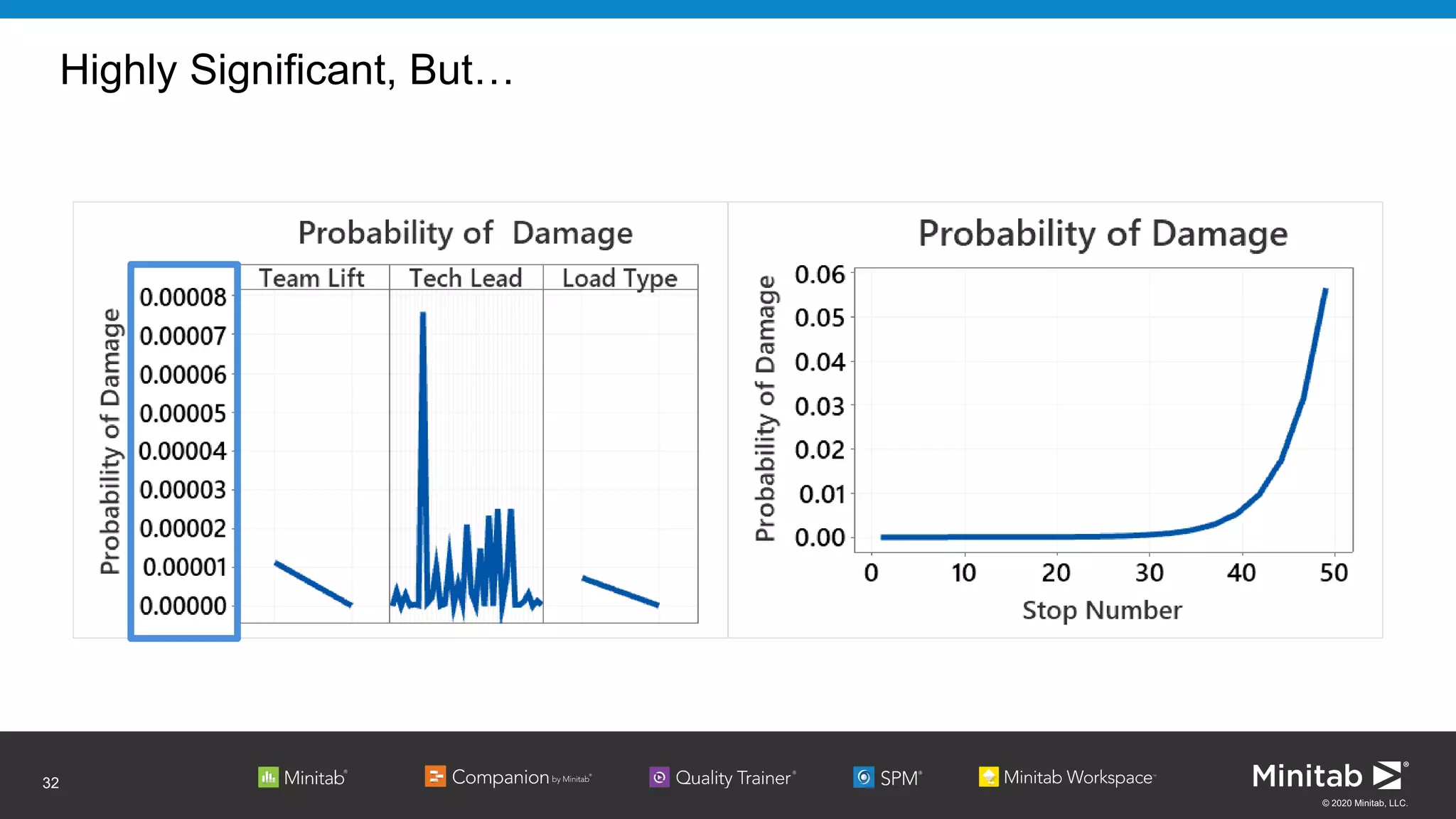
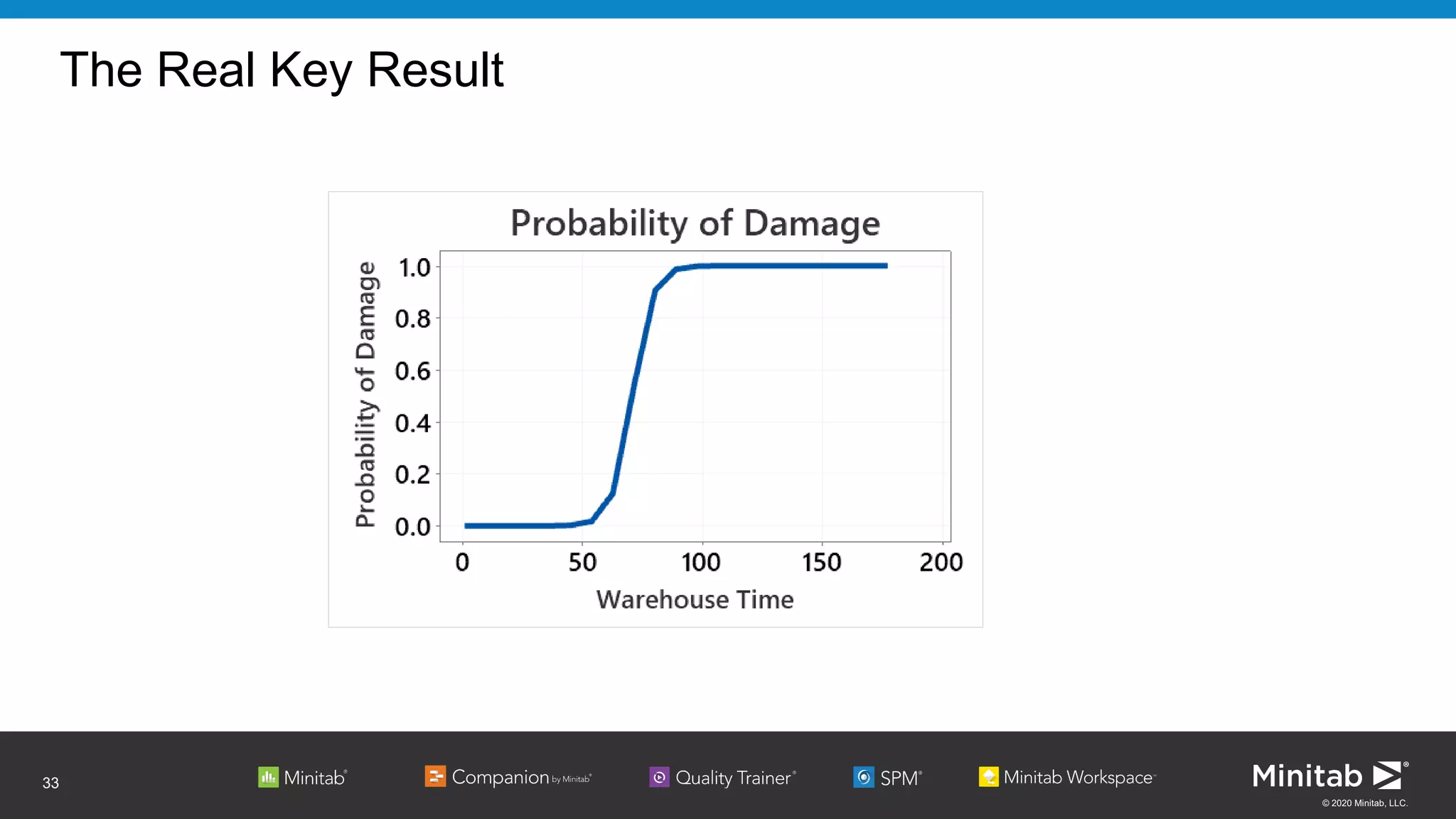
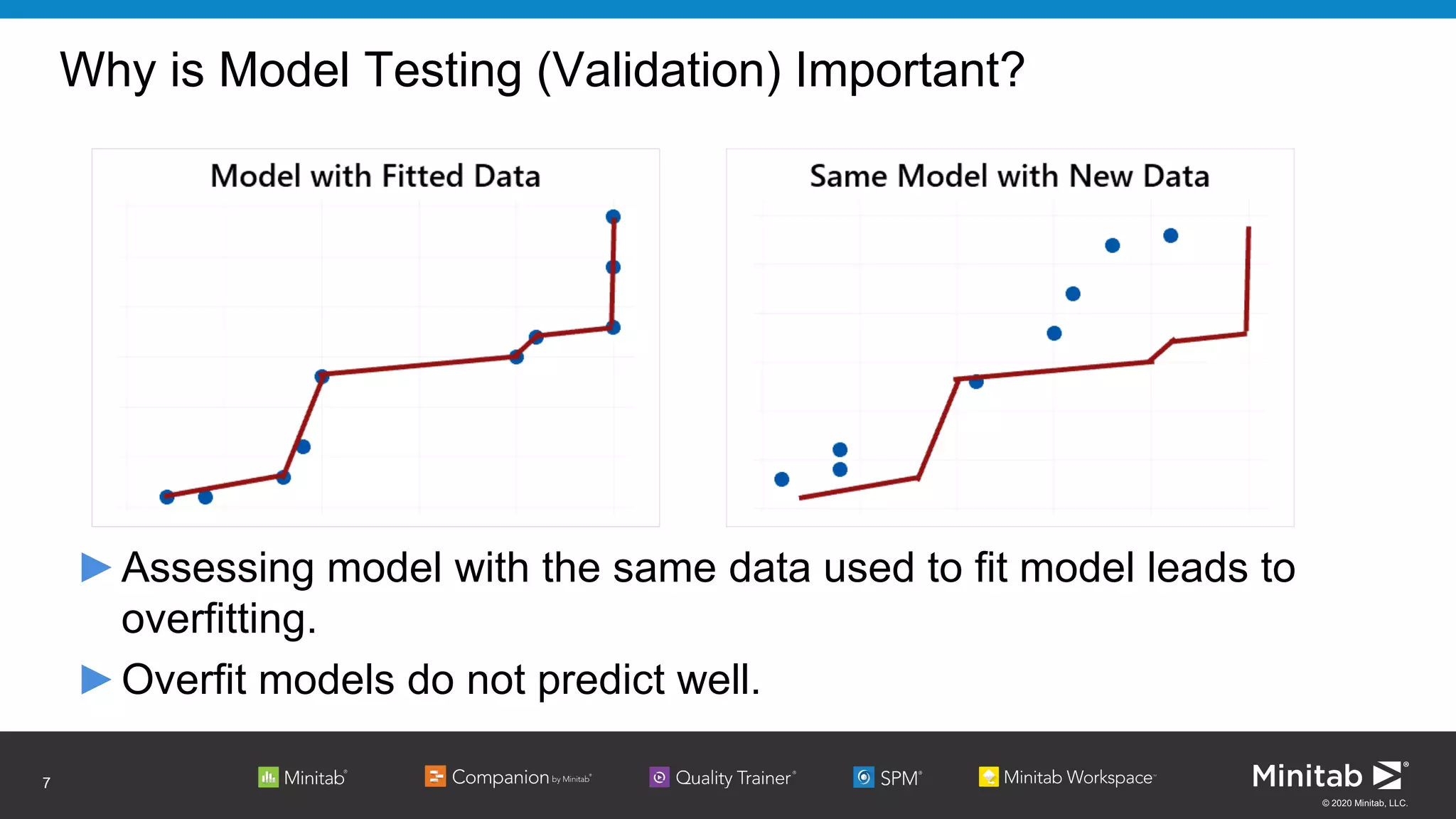
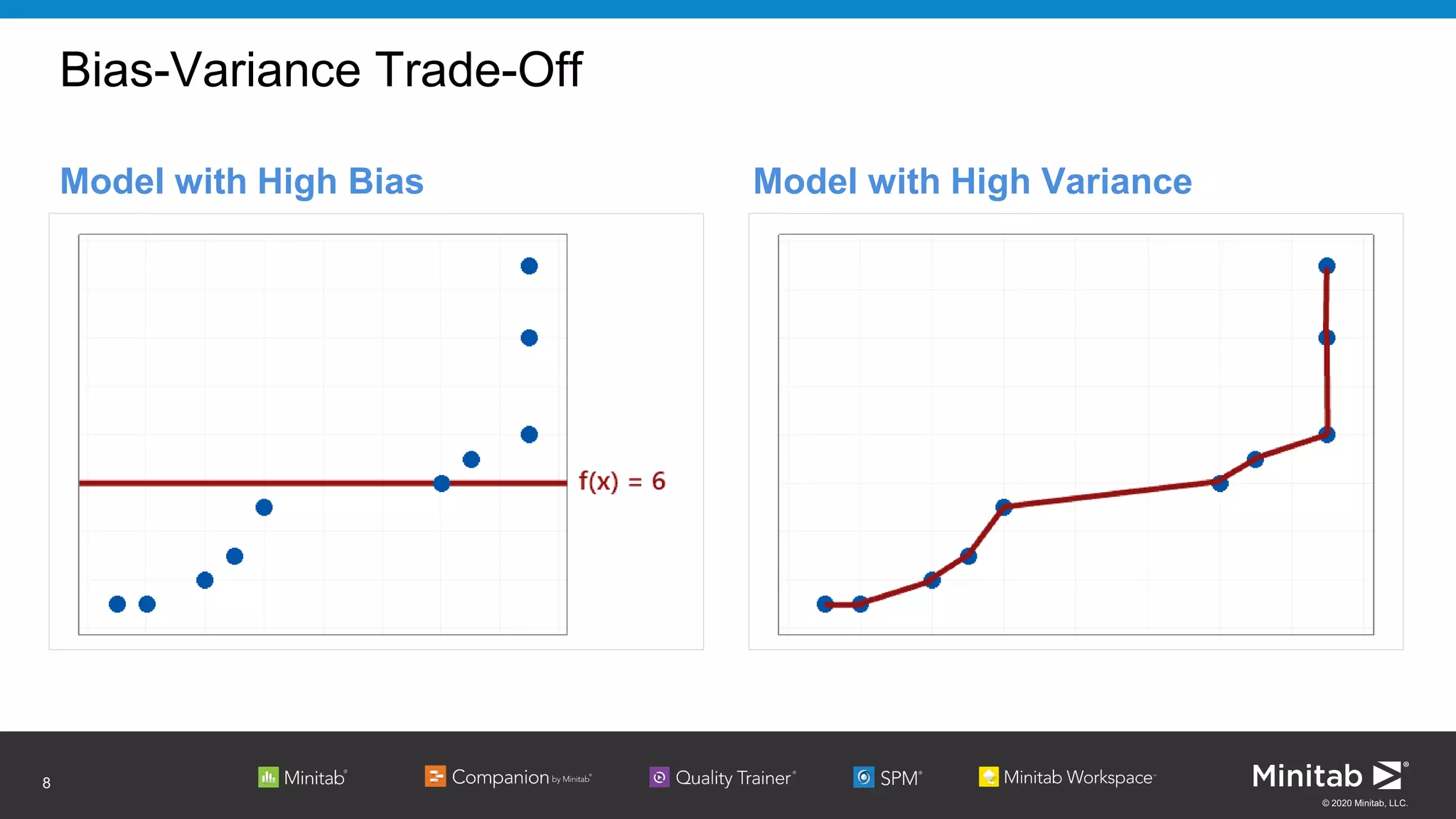
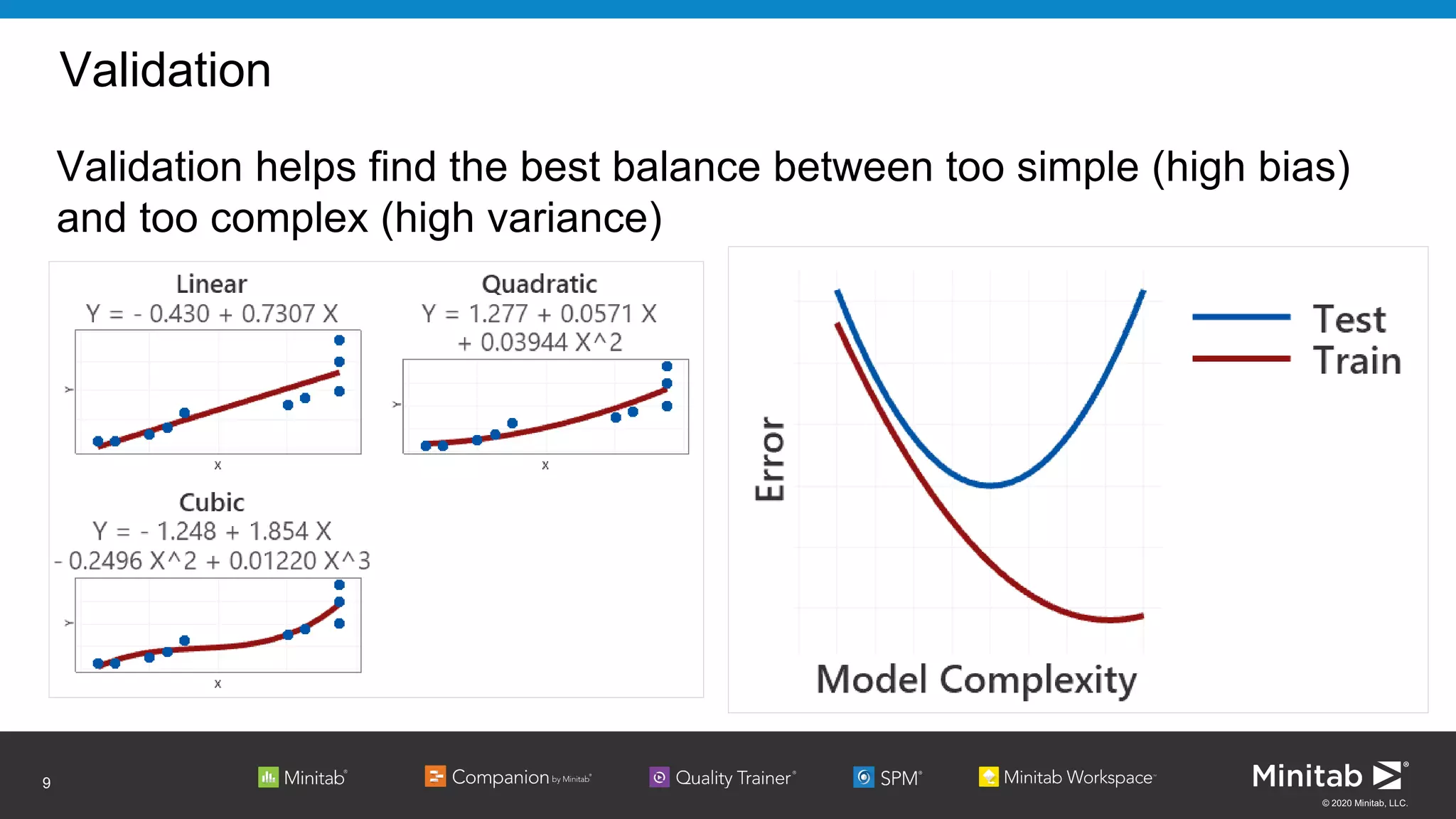
The document discusses the application of binary logistic regression in machine learning, emphasizing model selection techniques such as p-values, ROC curves, and information criteria. It highlights the importance of model validation to avoid overfitting and provides examples, including healthcare predictions and manufacturing defect analysis. Additionally, it addresses challenges in variable selection and model comparison strategies, aiming for models that balance complexity and performance.
![© 2020 Minitab, LLC.
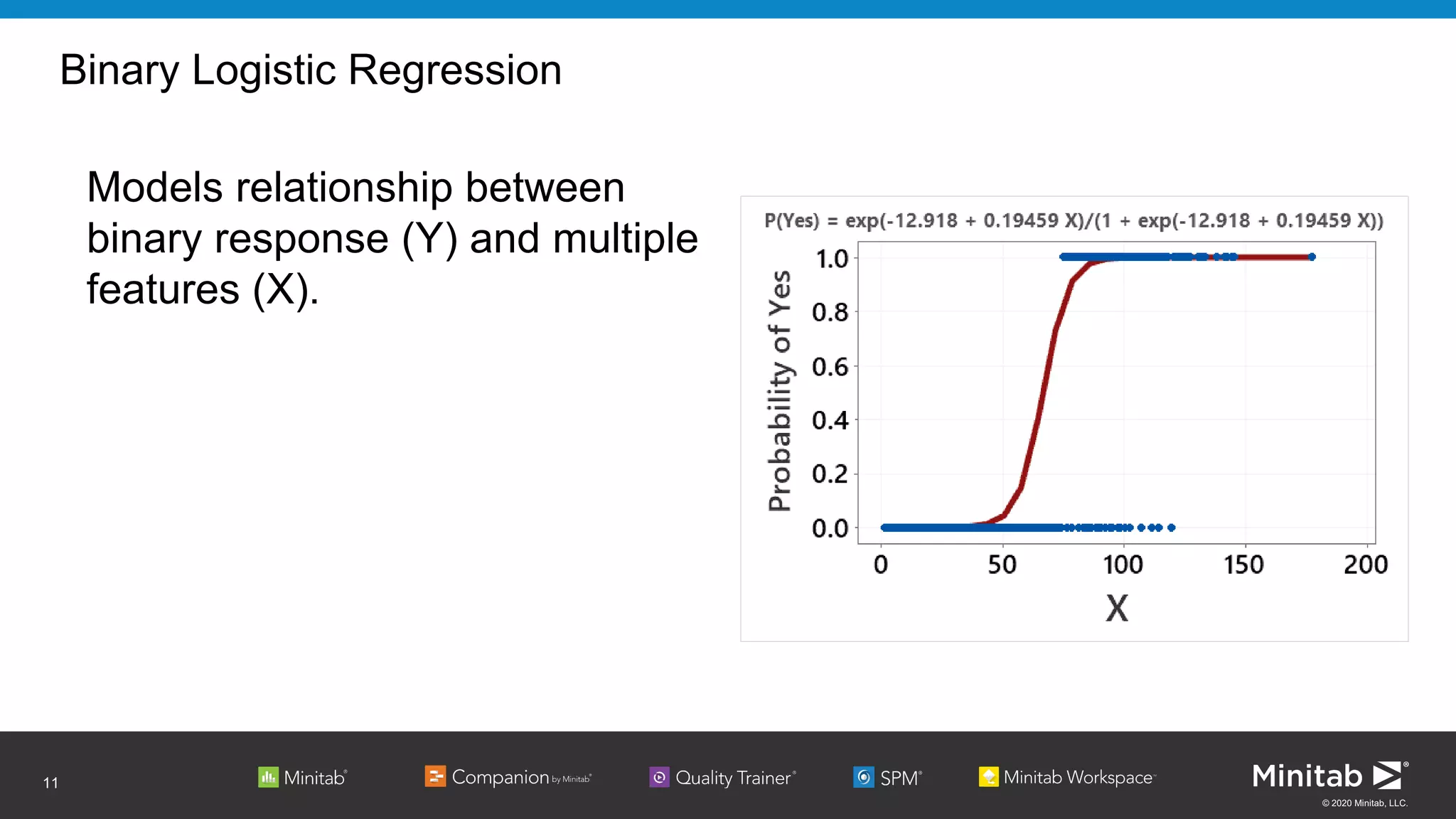
Binary Logistic Regression
12
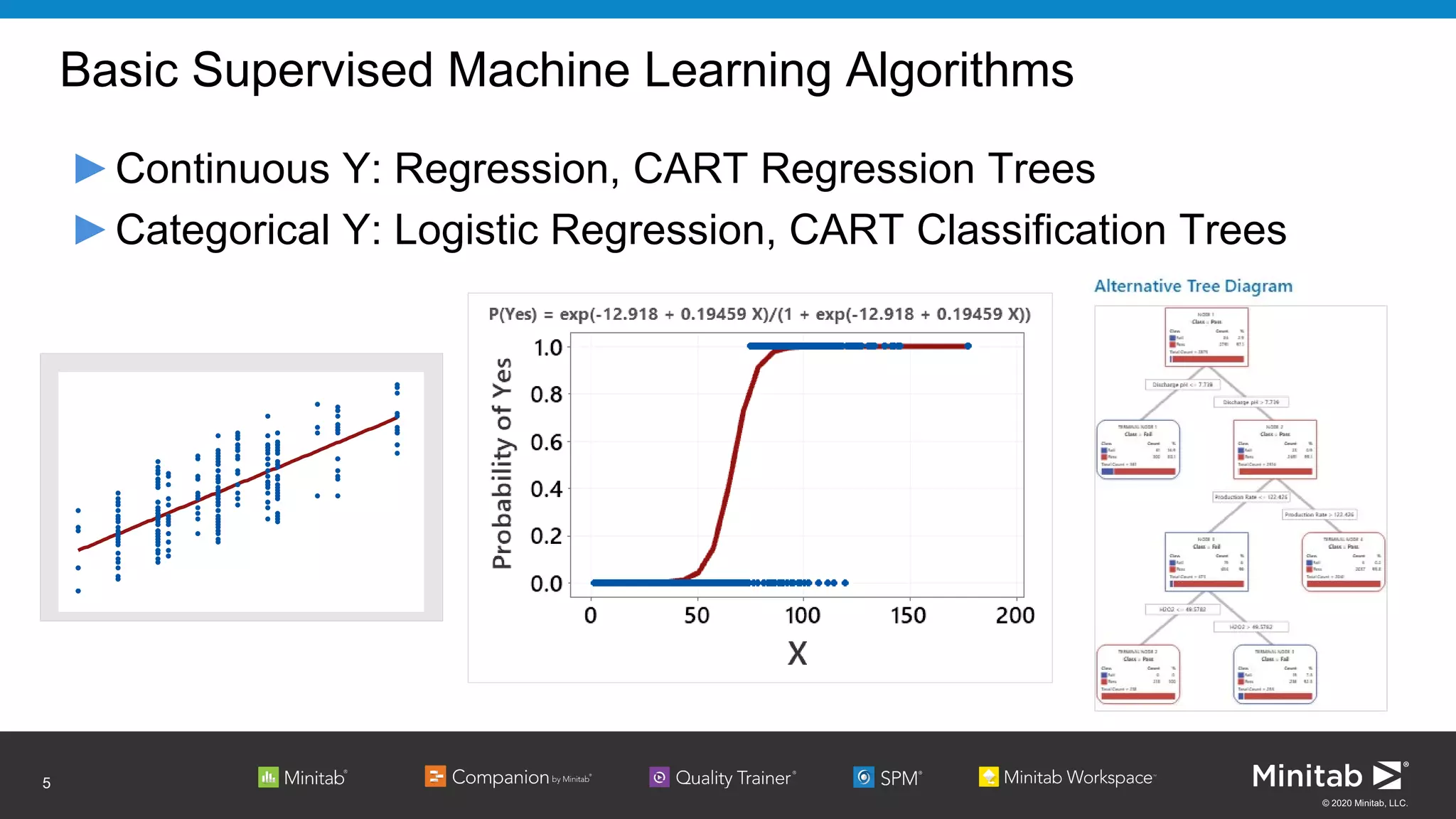
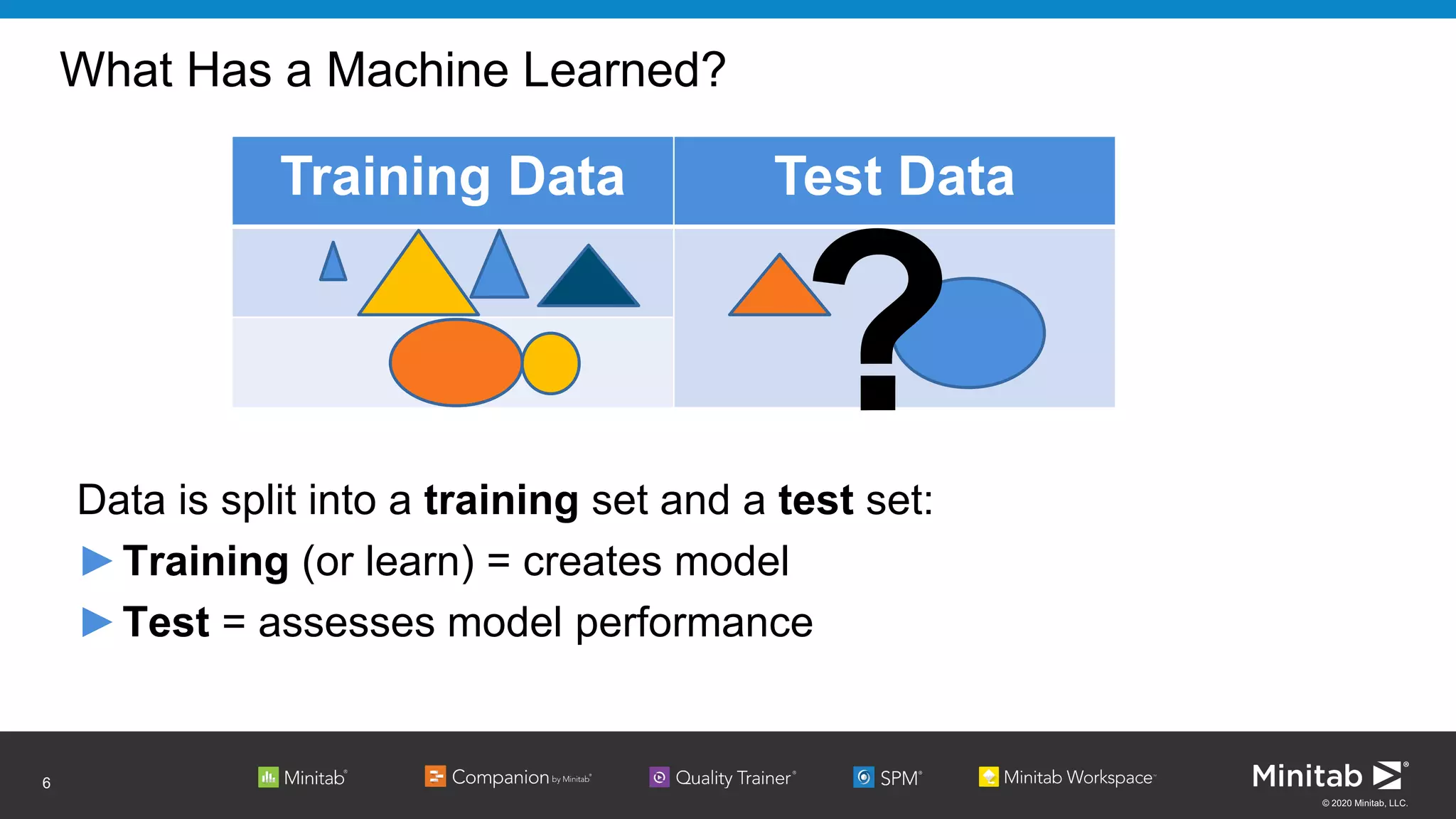
Relationship can be expressed as an equation:
Loge[p/(1-p)] = β0 + β1x1 + … + βkxk
Probability (Event) = exp(β0 + β1x1 + … + βkxk)
(1 + exp(β0 + β1x1 + … + βkxk))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningwithbinarylogisticregression-apac-200628220638/75/Machine-Learning-with-Binary-Logistic-Regression-APAC-11-2048.jpg)