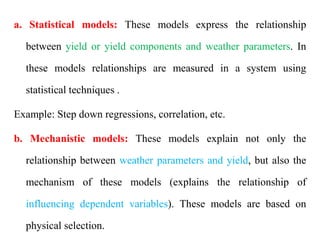
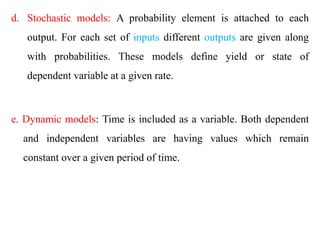
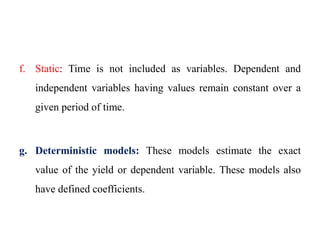
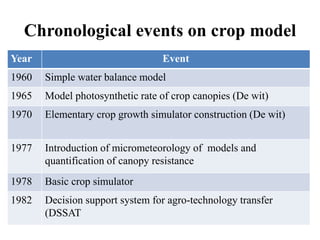
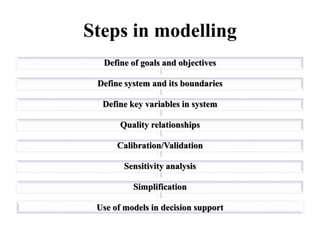
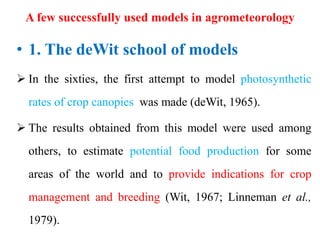
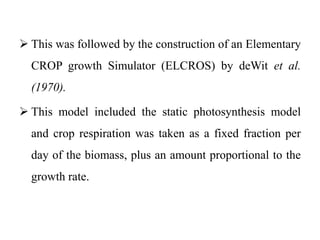
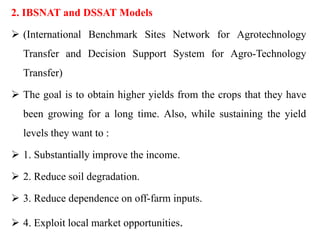
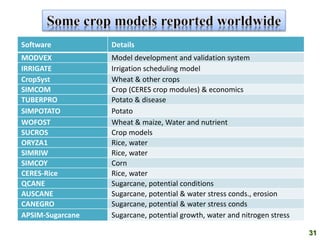
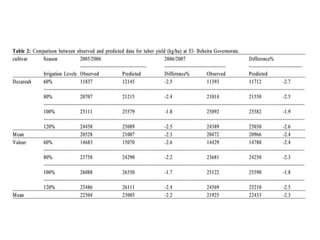
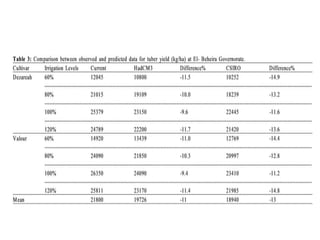
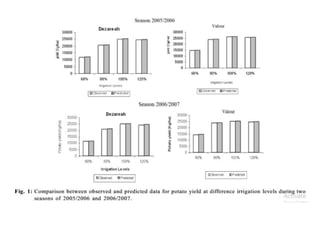
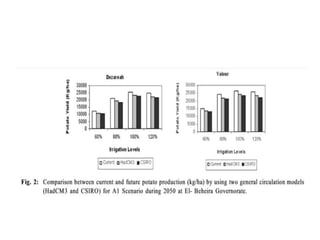
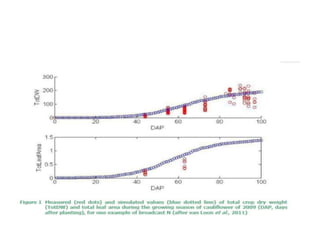
Crop models can be used to estimate crop yield and its variability under different climate scenarios, account for nitrogen use efficiency, and help inform agricultural management decisions. The document discusses different types of crop models and provides examples of some models that have been successfully used in agrometeorology, including for rice, wheat, maize, sugarcane, and potato crops. It also outlines some limitations and advantages of using crop models.