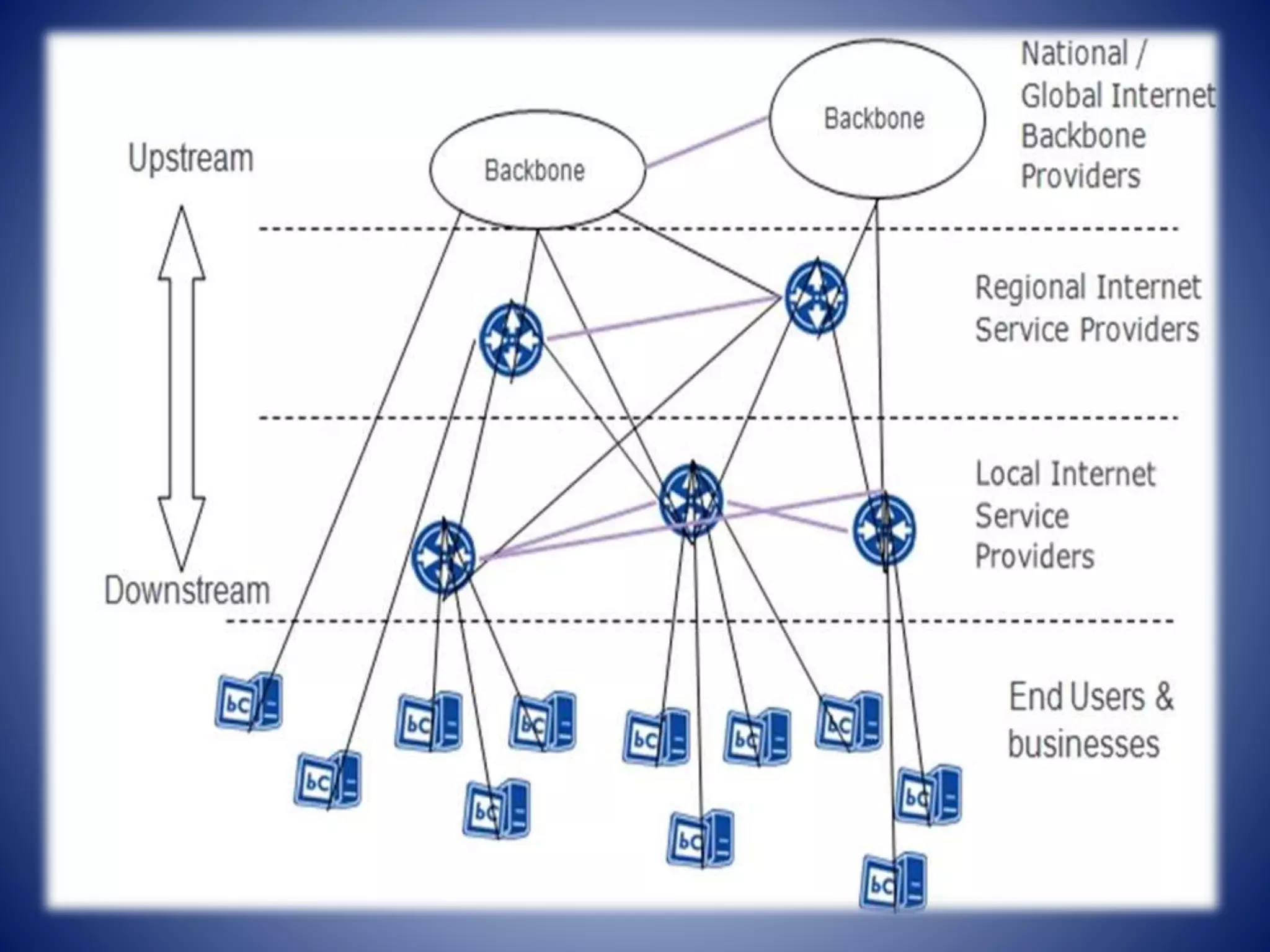
An Internet service provider (ISP) offers customers access to the Internet for a monthly or yearly fee. ISPs are categorized as regional or national based on their geographic coverage area. Regional ISPs service a specific area with a smaller support team, while national ISPs have nationwide coverage and a larger support team. ISPs interconnect with upstream providers to exchange traffic and routes to provide full connectivity to destinations on the Internet for their customers.