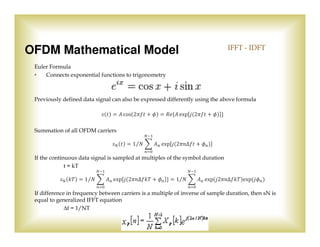
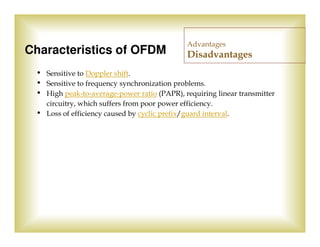
The document is a presentation by John W. Thomas, a PhD candidate from the University of Texas at Dallas, focusing on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). It covers various aspects such as the system model, mathematical representation, advantages, disadvantages, and applications in both wired and wireless communications. The speaker's biography highlights significant educational and professional experiences in electrical engineering and communications research.