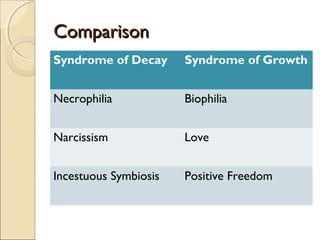
Erich Fromm was a German-American psychologist who developed humanistic psychoanalysis, which emphasizes sociobiological influences on personality. Fromm believed humanity's separation from nature causes basic anxiety and dichotomies like life/death that people try to resolve. He identified existential needs like relatedness, transcendence, and identity. Productive orientations like working and loving help fulfill needs, while unproductive ones like authoritarianism and destructiveness rely on escape mechanisms. Fromm's theory organizes knowledge but lacks consistency, parsimony, and falsifiability for research.