Moléculas org prot-429
- 1. Cell Biology
- 2. Leeuwenhoek's microscope Later, in the 17th century, Anton van Leeuwenhoek enlightened the world to what he dubbed “animacules” such as protozoa found in standing water. He was the first to identify sperm and red blood cells Zacharias Janssen invented the first compound microscope in 1595
- 3. Microscopes
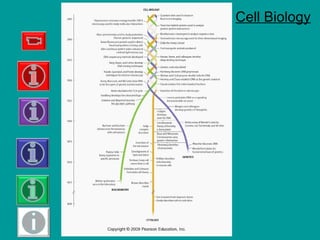
- 8. Fig. 4-1, p. 75 1 μm Atom Amino acids Protein Ribosomes Virus Mitochondrion 0.1 nm Smallest bacteria 1 nm 10 nm 100 nm 10 μm Chloroplast Nucleus 10 m1 m100 mm Electron microscope Light microscope 10 mm Typical bacteria Red blood cells Epithelial cell Human egg Frog egg Chicken egg Some nerve cells Adult human 1 mm100 μm Measurements 1 meter = 1000 millimeters (mm) 1 millimeter = 1000 micrometers (μm) 1 micrometer = 1000 nanometers (nm) Human eye
- 9. Carbon Atoms • form four covalent bonds – single, double, or triple – straight or branched chains – rings • bond with many different elements
- 10. Fig. 3-1, p. 46
- 12. Table 3-1a, p. 49
- 13. Table 3-1b, p. 49
- 22. Figure 2.8
- 25. Fig. 3-13, p. 58 Fatty acidsCholine Phosphate group Glycerol Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Water
- 26. Ionización del Agua *Escala de pH
- 27. Figure 2.9 [ H+ ] =1 X 10-7 M [ OH- ] = 1 X 10-7 M H2O H+ + OH -
- 28. pH = 2 [H+ ] = 0.01 pH = 5 [H+ ] = 0.00001 pH = 8 [H+ ] = 0.000000001 pH = 10 [H+ ] = 0.0000000001
- 29. Moléculas orgánicas en los organismos vivos Monómeros, Polímeros o macromoléculas
- 31. Polymers and Macromolecules • Polymers – long chains of monomers – linked through condensation reactions • Macromolecules – large polymers – polysaccharides, proteins, and DNA – broken down by hydrolysis reactions
- 37. Estructura y función de las proteínas
- 44. 1953 James Watson, Francis Crick y Rosalind Franklin
- 48. Nucleotides • ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – essential in energy metabolism • NAD+ – electron acceptor in biological oxidation and reduction reactions
- 49. Monosaccharides
- 50. Fig. 3-6, p. 51
- 51. Disaccharides
- 52. Polysaccharides • Long chains – repeating units of simple sugar • Storage polysaccharides – starch in plants – glycogen in animals • Structural polysaccharide – cellulose, cell walls of plants – chitin in arthropods
- 53. • Starch • Glycogen
- 54. Cellulose
- 57. • Triglycerides = three fatty acids attached to one molecule of glycerol Figure 2.15 Lipids
- 58. Triacylglycerol
- 61. Fig. 3-13, p. 58 Fatty acidsCholine Phosphate group Glycerol Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Water
- 62. Steroids • Carbon atoms arranged in 4 rings – cholesterol, bile salts, some hormones
- 63. Figure 2.16 Steroids Figure 2.16
Editor's Notes
- Figure 4.1: Biological size and cell diversity. We can compare relative size from the chemical level to the organismic level by using a logarithmic scale (multiples of 10). The prokaryotic cells of bacteria typically range in size from 1 to 10 μm long. Most eukaryotic cells are between 10 and 30 μm in diameter. The nuclei of animal and plant cells range from about 3 to 10 μm in diameter. Mitochondria are about the size of small bacteria, whereas chloroplasts are usually larger, about 5 μm long. Ova (egg cells) are among the largest cells. Although microscopic, some nerve cells are very long. The cells shown here are not drawn to scale.
- Figure 3.1: Organic molecules. Note that each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds, producing a wide variety of shapes.
- Figure 2.3 Hydrogen bonding between two water molecules. A partially positive (+) hydrogen atom of one water molecule attracts the partially negative (2 –) oxygen atom of a second water molecule, forming a hydrogen bond. The distances between atoms of two water molecules in ice are shown. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines highlighted in yellow as shown here and throughout the book.
- Figure 2.5 Structure of ice. Water molecules in ice form an open, hexagonal lattice in which every water molecule is hydrogen-bonded to four others. The geometrical regularity of these hydrogen bonds contributes to the strength of the ice crystal. The hydrogen-bonding pattern of liquid water is more irregular than that of ice. The absolute structure of liquid water has not been determined.
- Figure 2.6 Dissolution of sodium chloride (NaCl) in water. (a) The ions of crystalline sodium chloride are held together by electrostatic forces. (a) Water weakens the interactions between the positive and negative ions, and the crystal dissolves. Each dissolved Na+ and Cl– is surrounded by a solvation sphere. Only one layer of solvent molecules is shown. Interactions between ions and water molecules are indicated by dashed lines.
- Figure 2.11 Hydrogen bonding between the complementary bases guanine and cytosine in DNA.
- Figure 2.7 Structure of glucose. Glucose contains five hydroxyl groups and a ring oxygen, each of which can form hydrogen bonds with water.
- Figure 2.8 Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a synthetic detergent.
- Figure 2.9 Cross-sectional views of structures formed by detergents in water. Detergents can form monolayers at the air–water interface. They can also form micelles, aggregates of detergent molecules in which the hydrocarbon tails (yellow) associate in the water-free interior and the polar head groups (blue) are hydrated.
- Figure 3.13: A phospholipid and a phospholipid bilayer.
- Figure 2.14 Hydrolysis of a peptide. In the presence of water the peptide bonds in proteins and peptides are hydrolyzed. Condensation, the reverse of hydrolysis, is not thermodynamically favored.
- Figure 3.6: Monosaccharides. Shown are 2-D chain structures of (a) three-carbon trioses, (b) five-carbon pentoses, and (c) six-carbon hexoses. Although it is convenient to show monosaccharides in this form, the pentoses and hexoses are more accurately depicted as ring structures, as in Figure 3-7. The carbonyl group (gray screen) is terminal in aldehyde sugars and located in an internal position in ketones. Deoxyribose differs from ribose because deoxyribose has one less oxygen; a hydrogen (white screen) instead of a hydroxyl group (blue screen) is attached to carbon 2. Glucose and galactose are enantiomers that differ in the arrangement of the hydroxyl group and hydrogen attached to carbon 4 (red box).
- FIGURE 3-9 Cellulose structure and function Cellulose can be incredibly tough. (a) Wood in this 3000-year-old bristlecone pine is primarily cellulose. (b) Cellulose forms the cell wall that surrounds each plant cell. (c) Plant cell walls often consist of cellulose fibers in layers that run at angles to each other and resist tearing in both directions. (d) Cellulose is composed of glucose subunits. Compare this structure with Fig. 3-8c and notice that every other glucose molecule in cellulose is "upside down."
- FIGURE 3-10 Chitin: A unique polysaccharide Chitin has the same bonding configuration of glucose molecules as cellulose does. In chitin, however, the glucose subunits have a nitrogen-containing functional group (yellow) instead of a hydroxyl group. Tough, flexible chitin supports the otherwise soft bodies of arthropods (insects, spiders, and their relatives) and certain fungi, such as this mushroom.
- Figure 3.13: A phospholipid and a phospholipid bilayer.