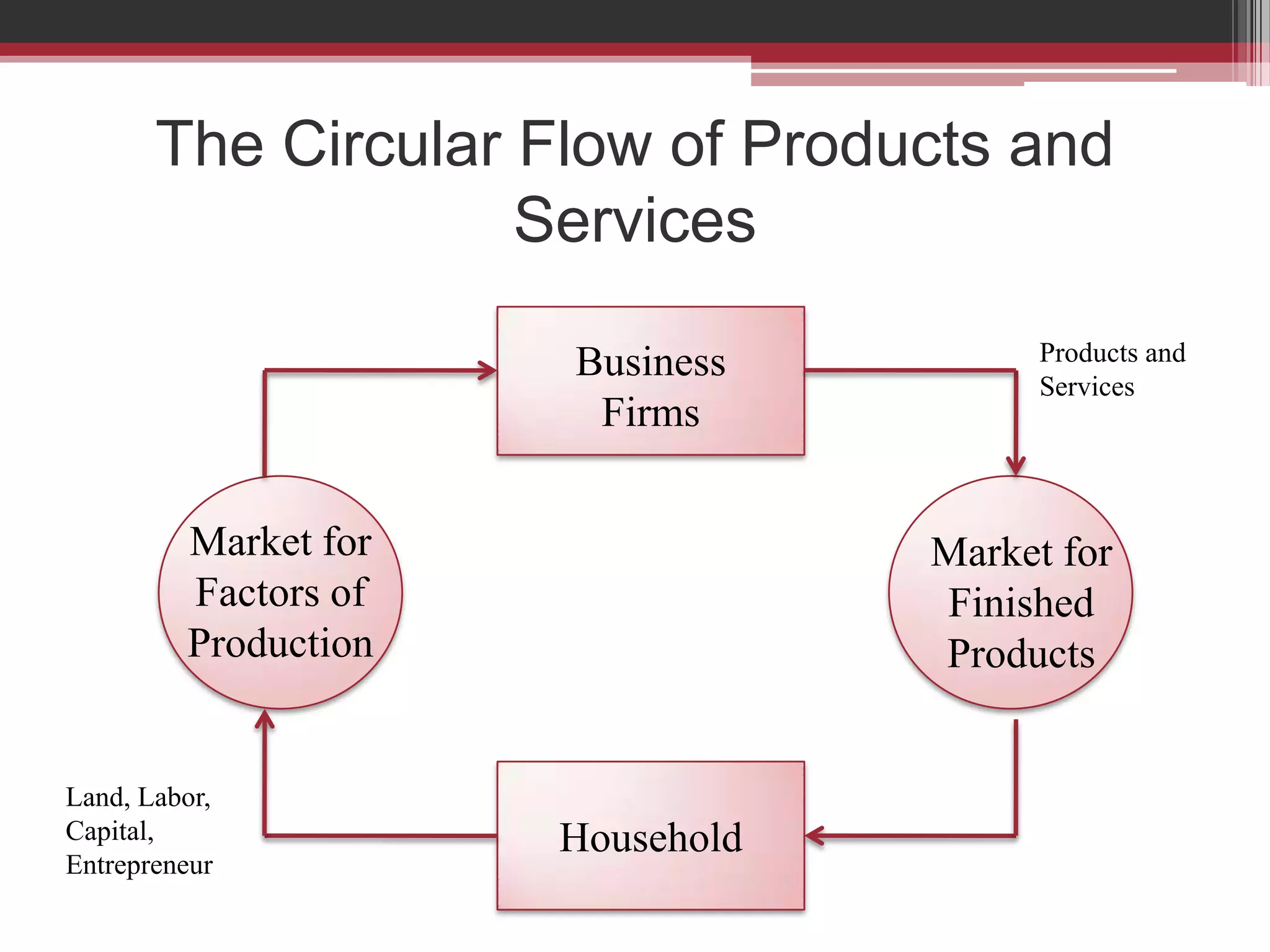
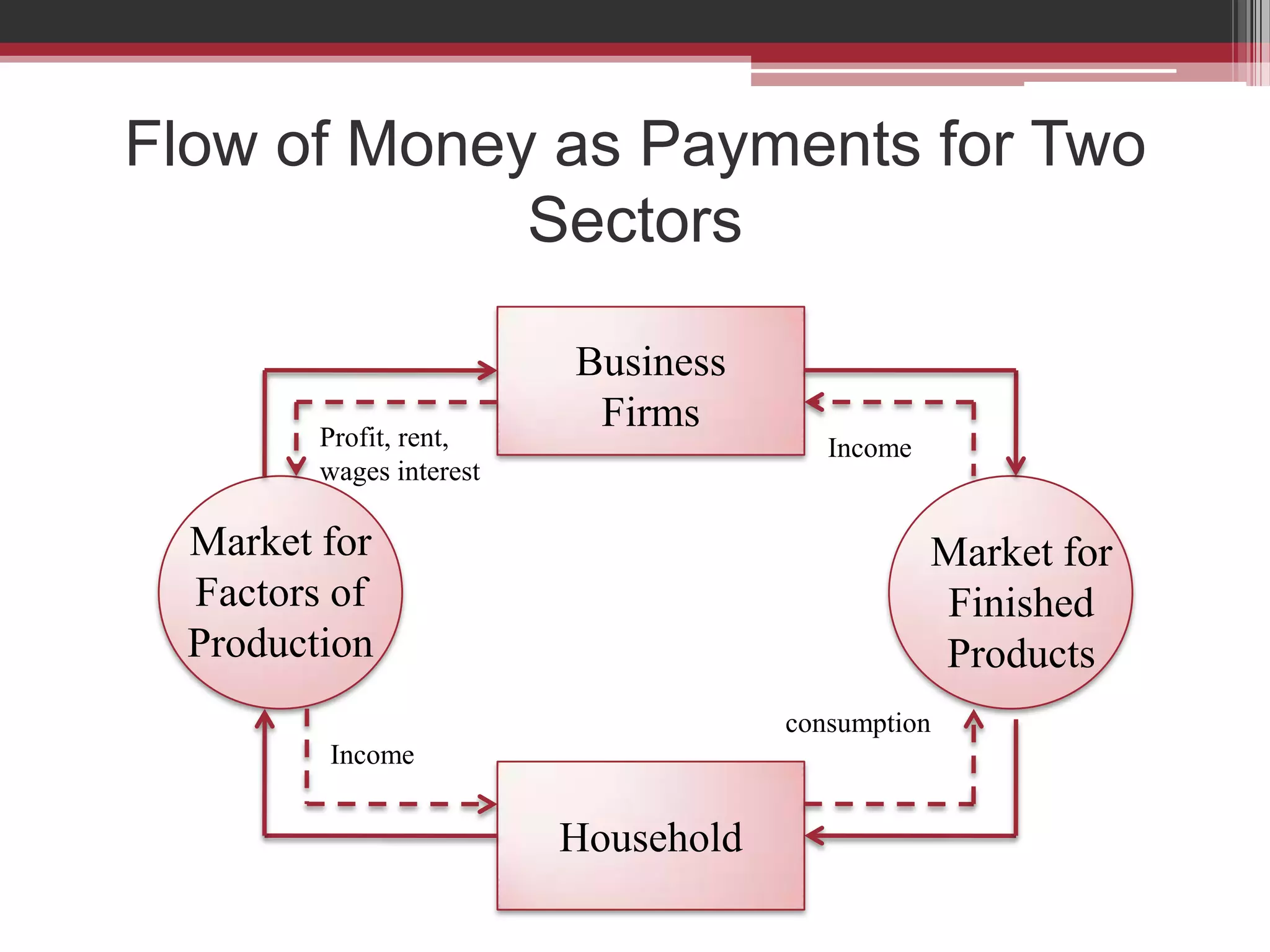
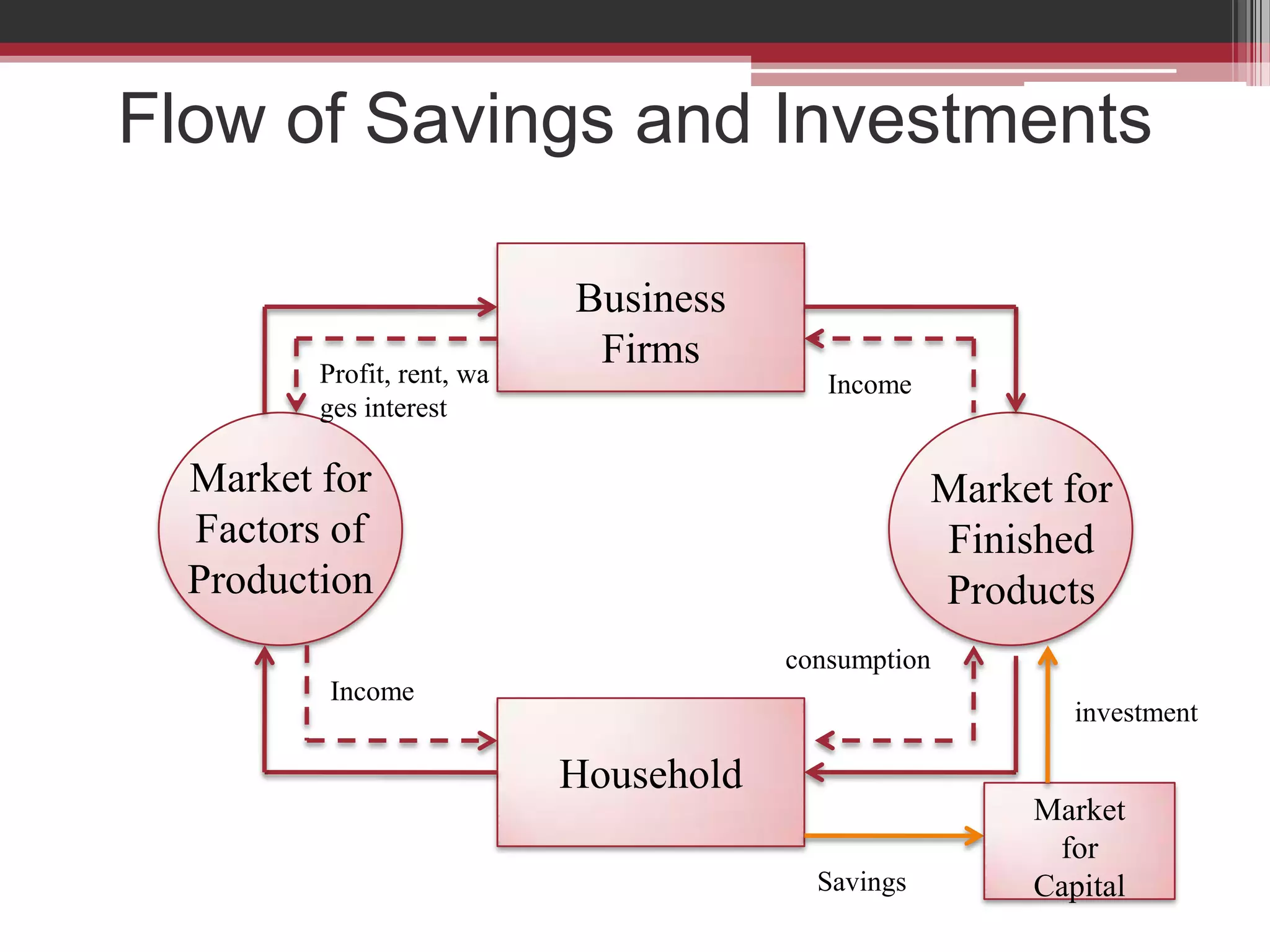
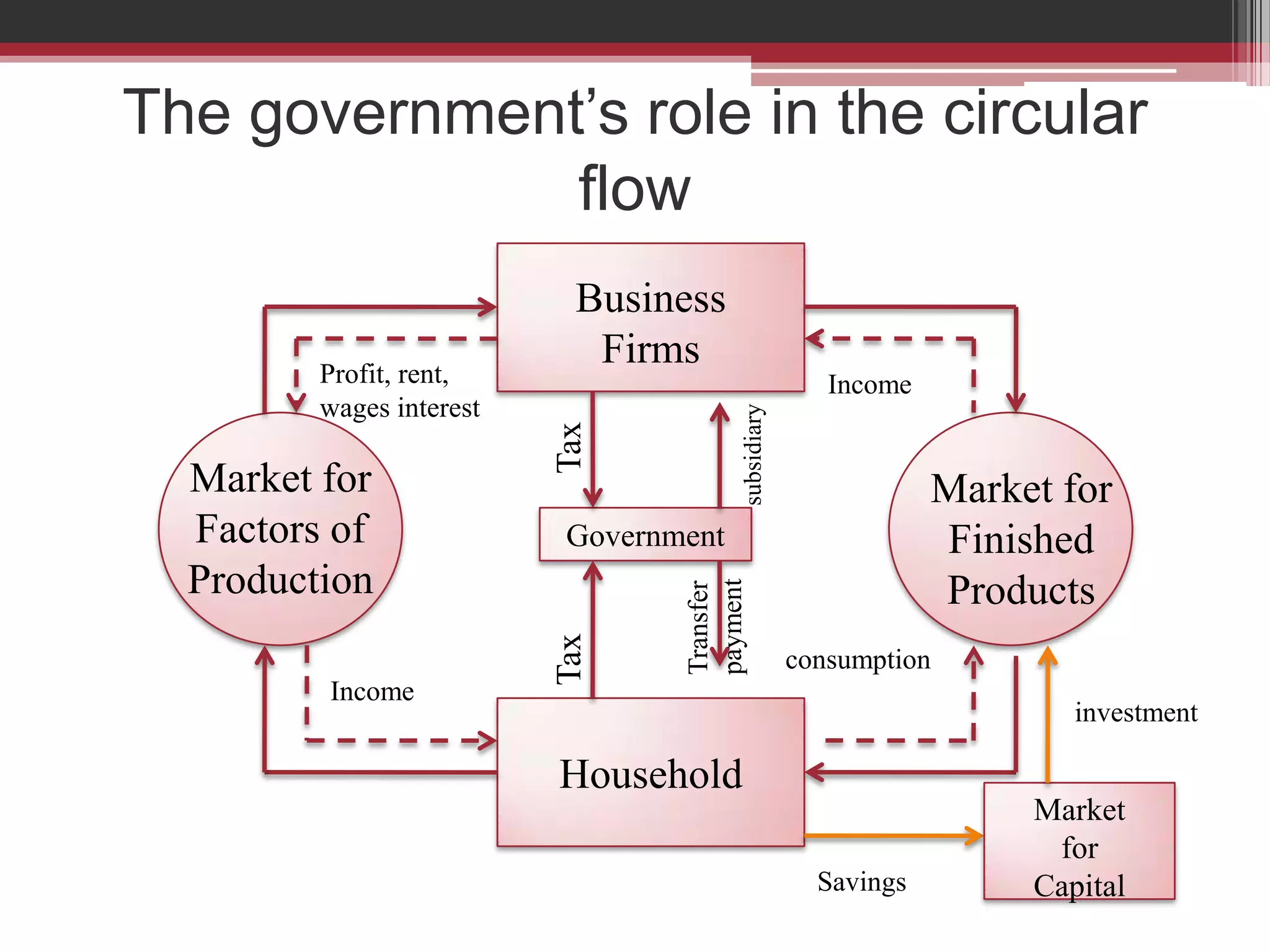
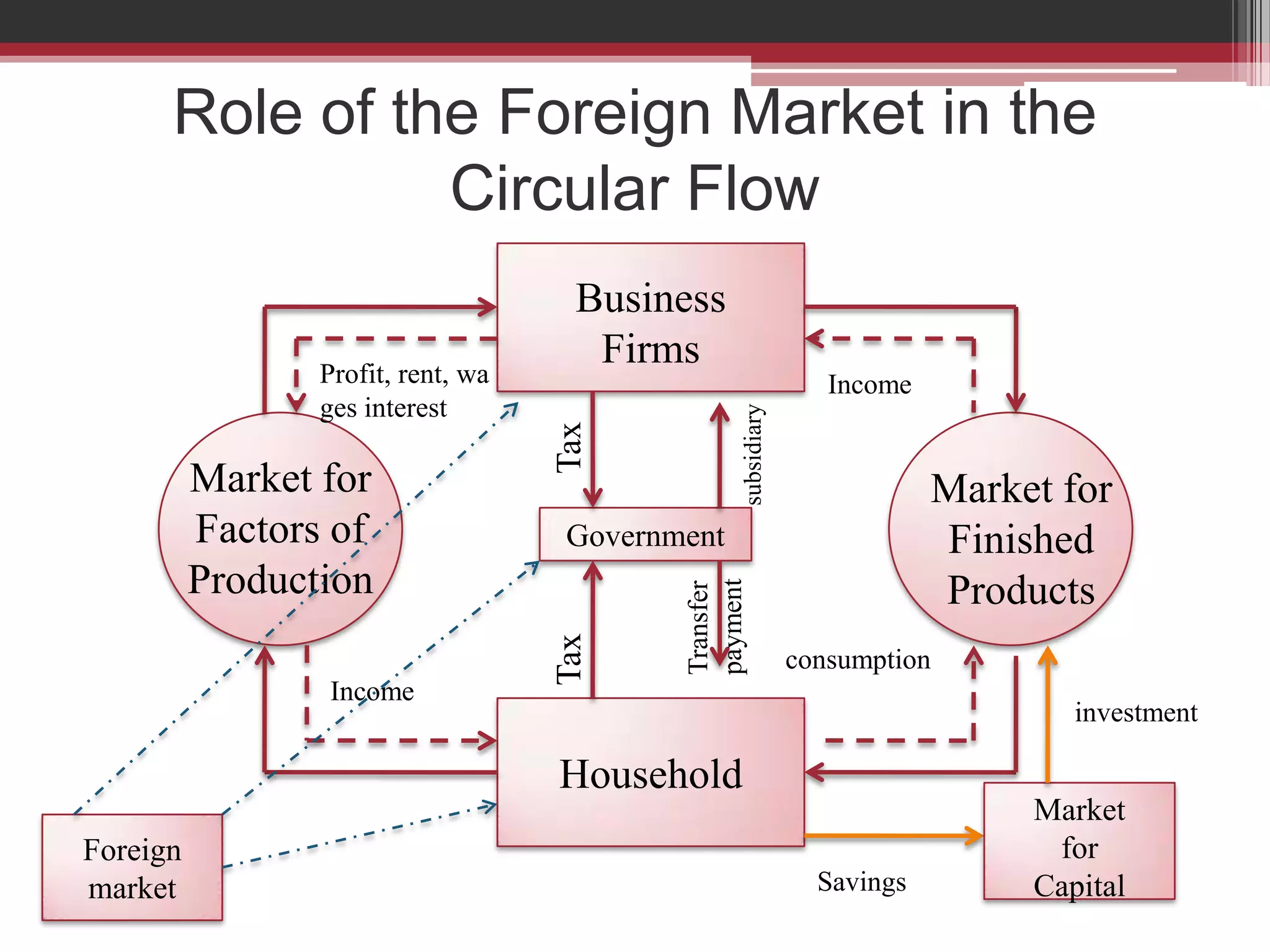
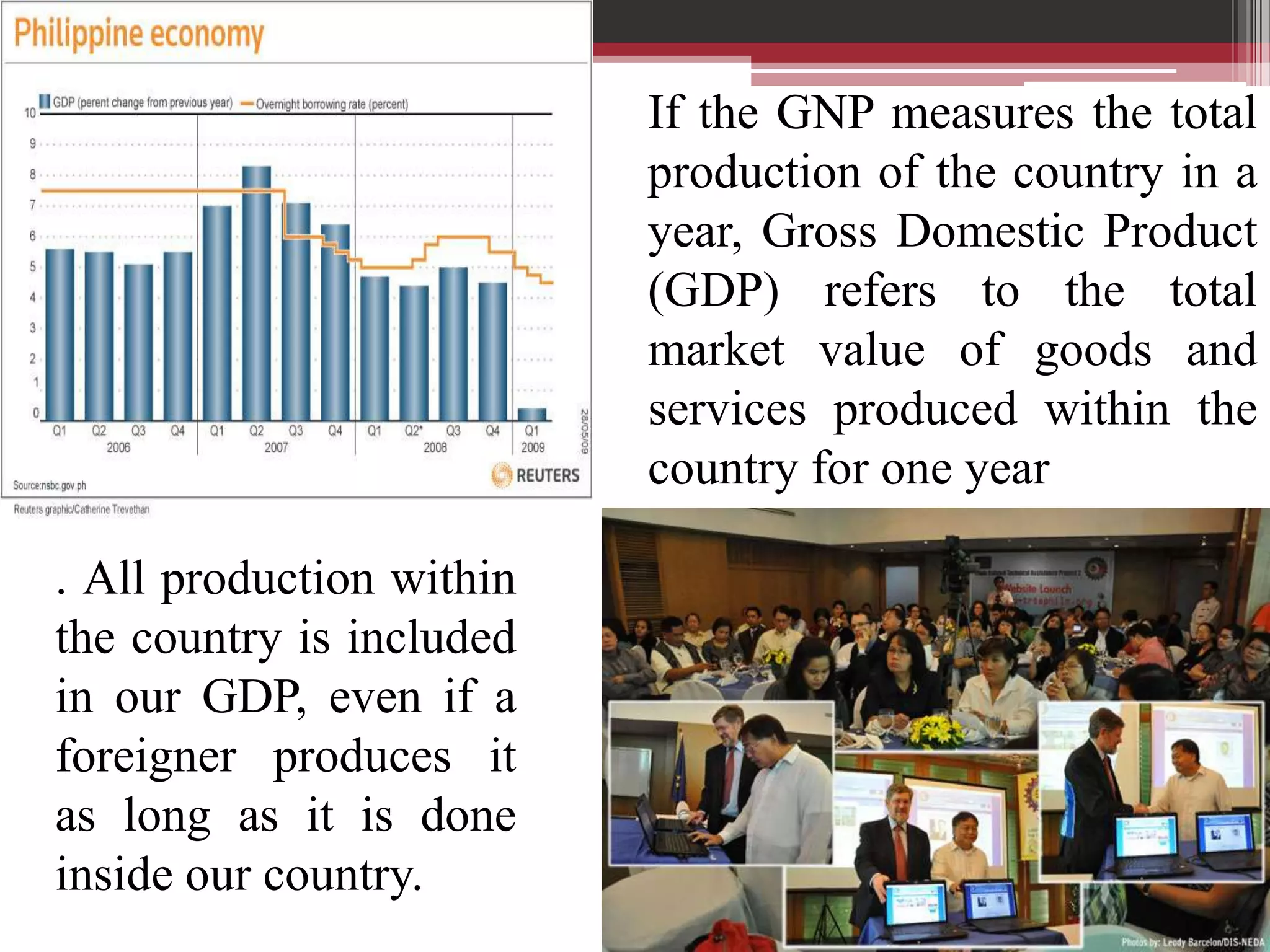
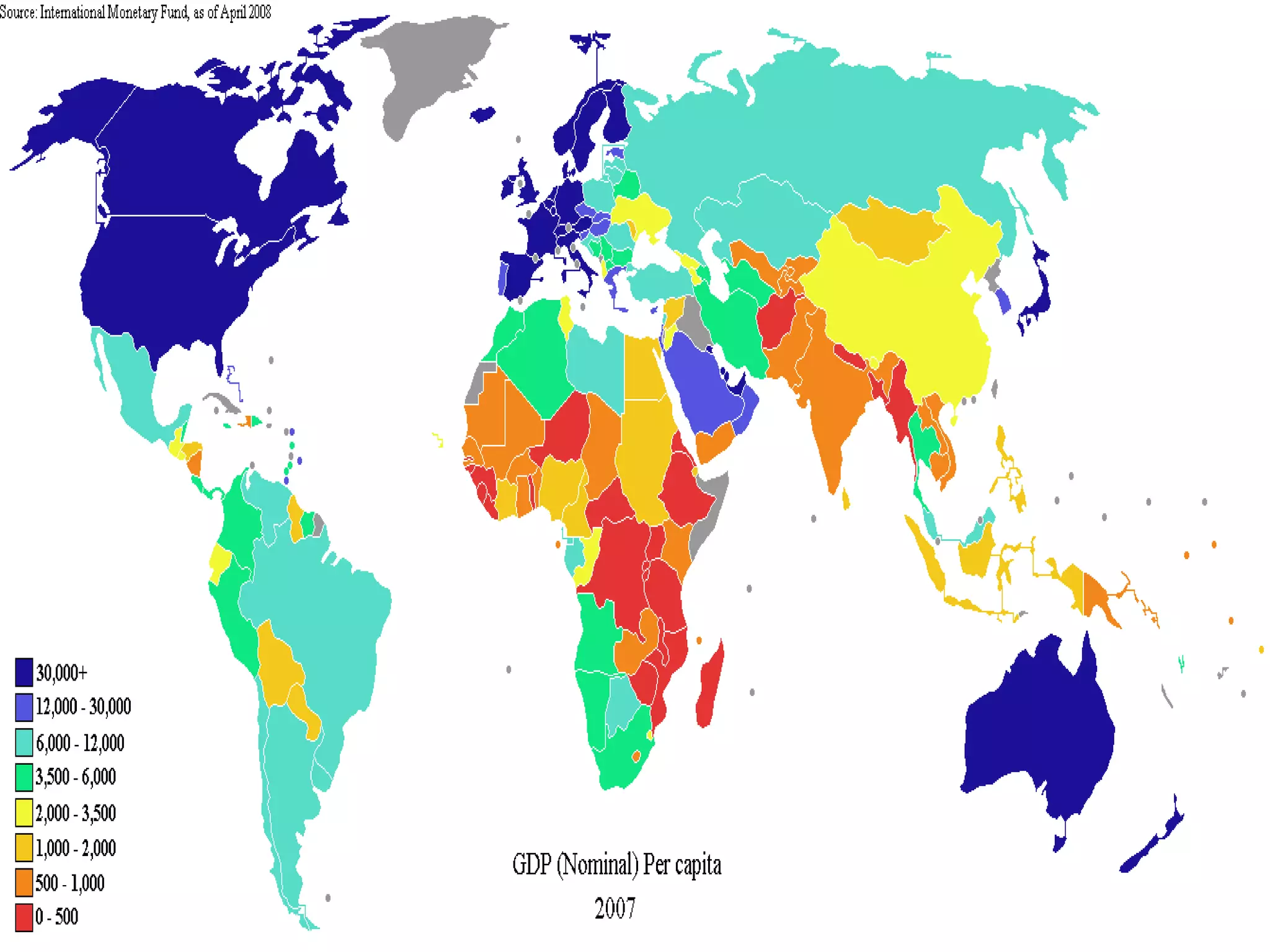
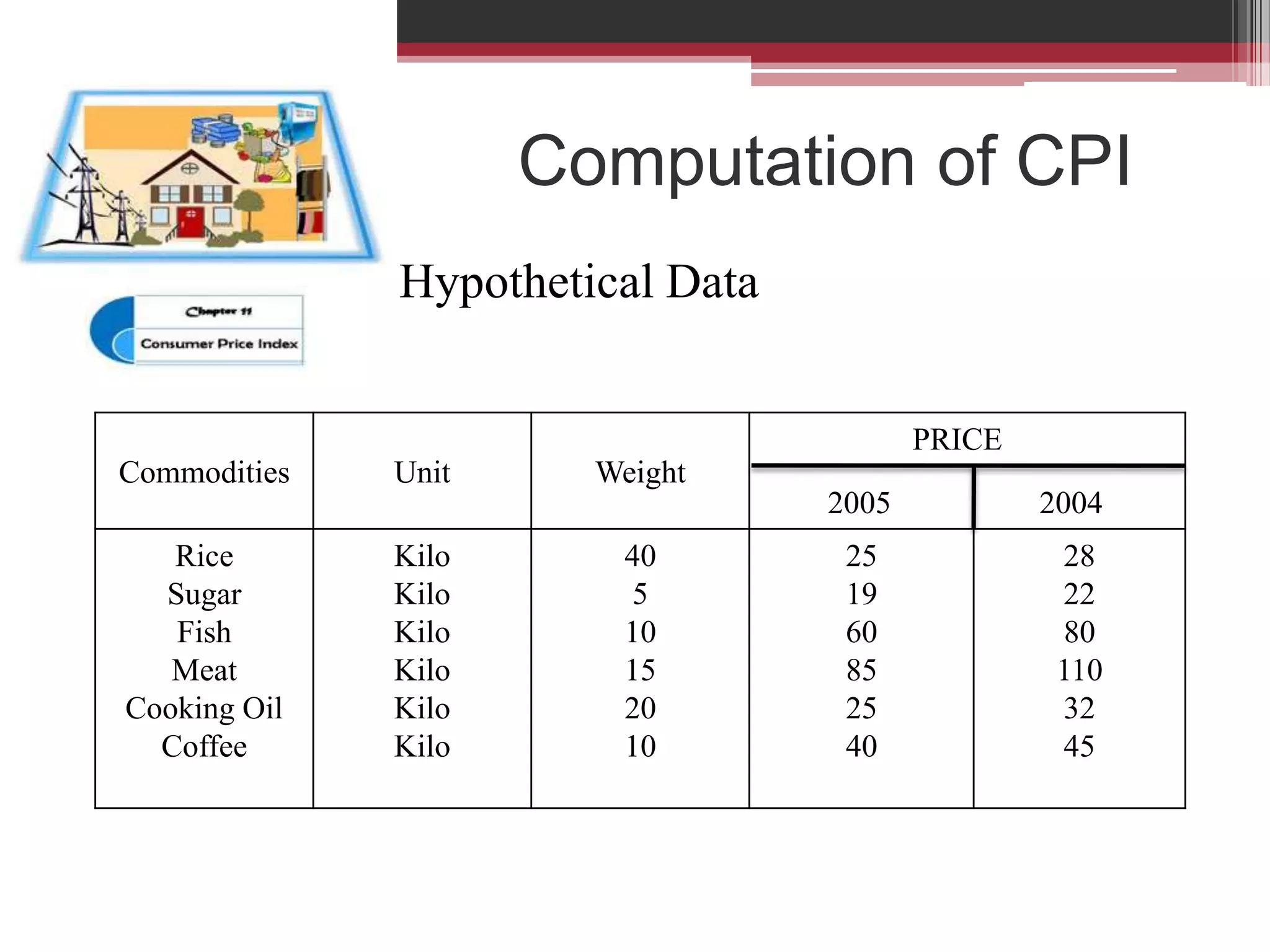
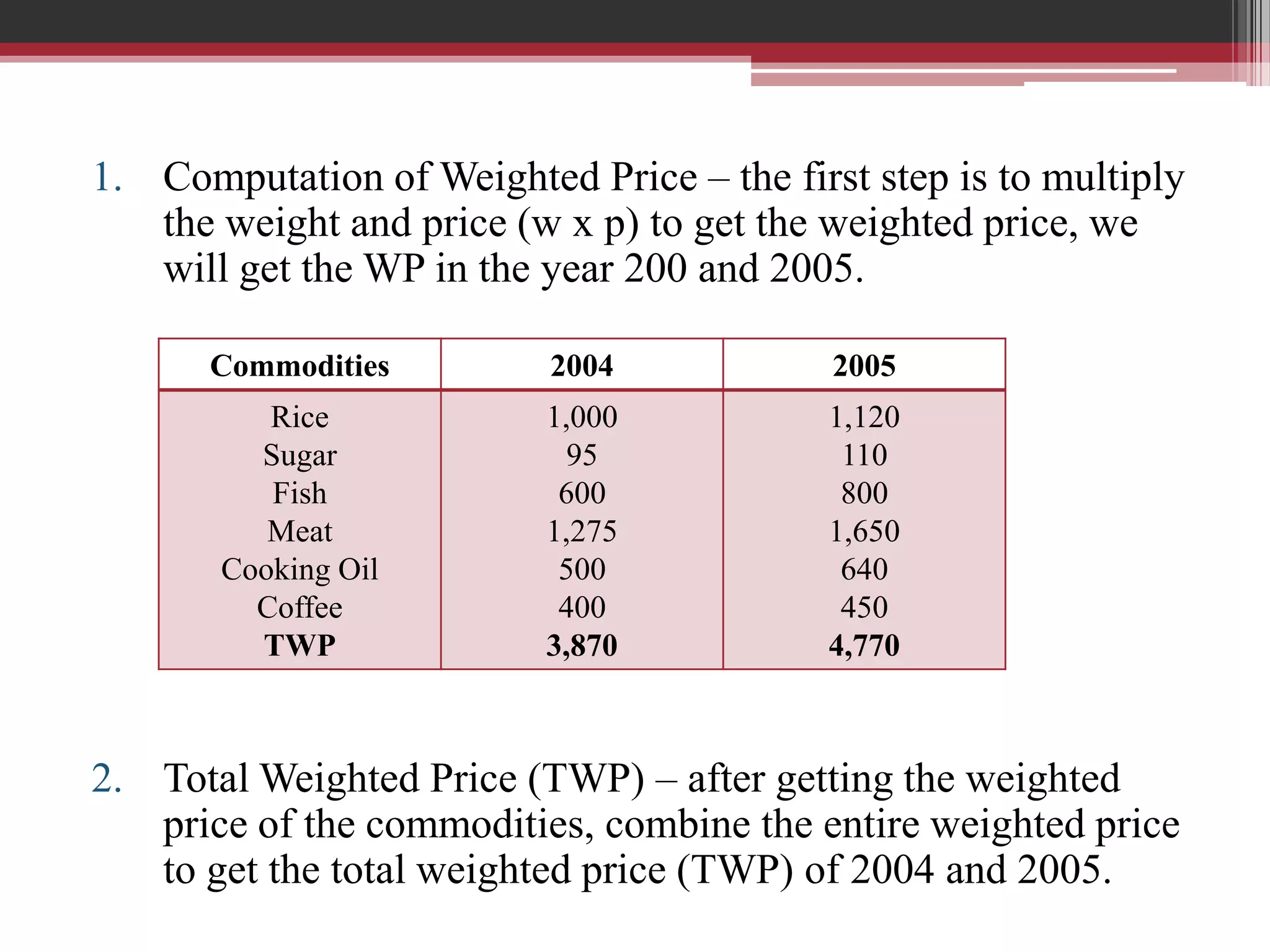
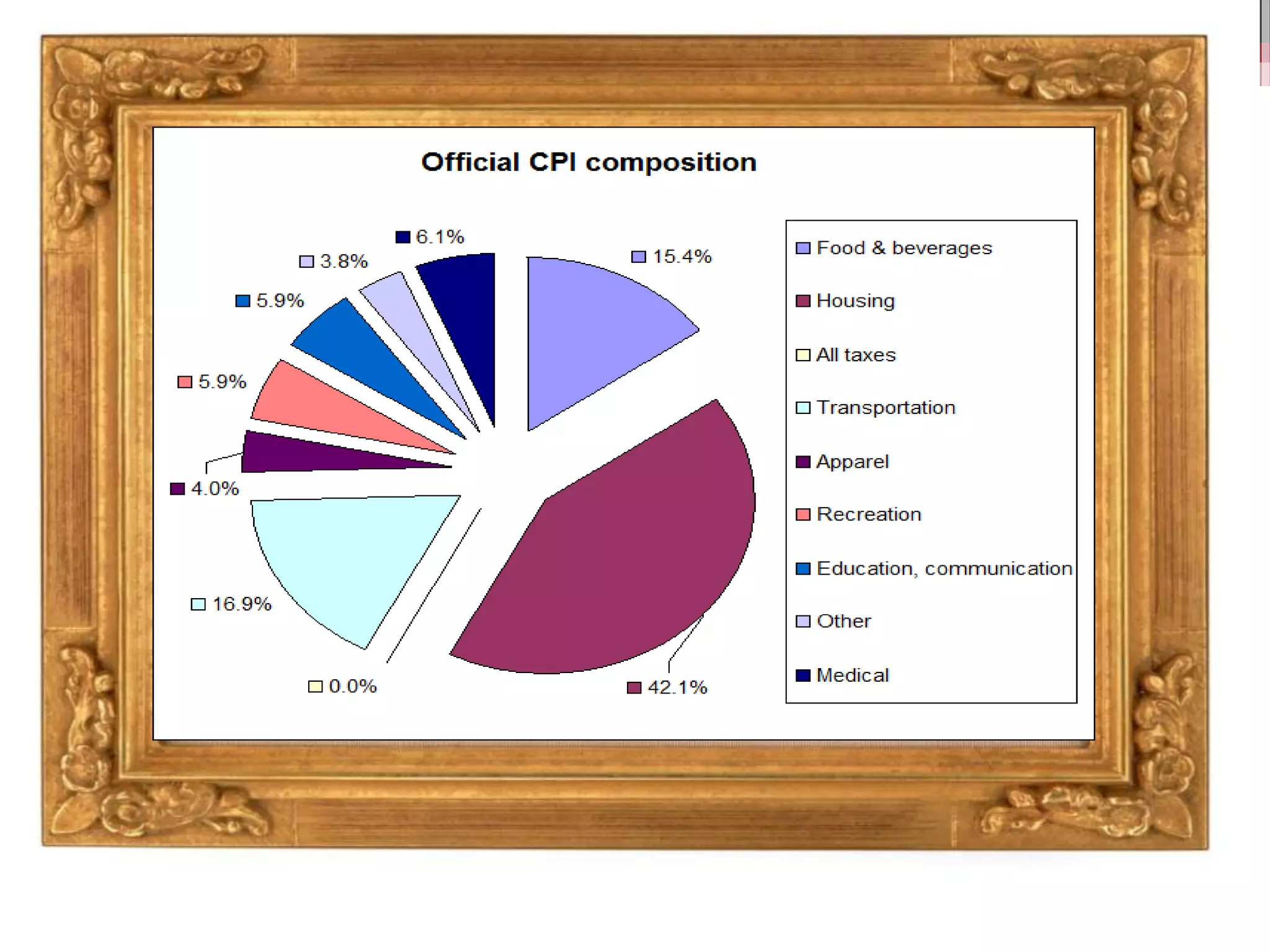
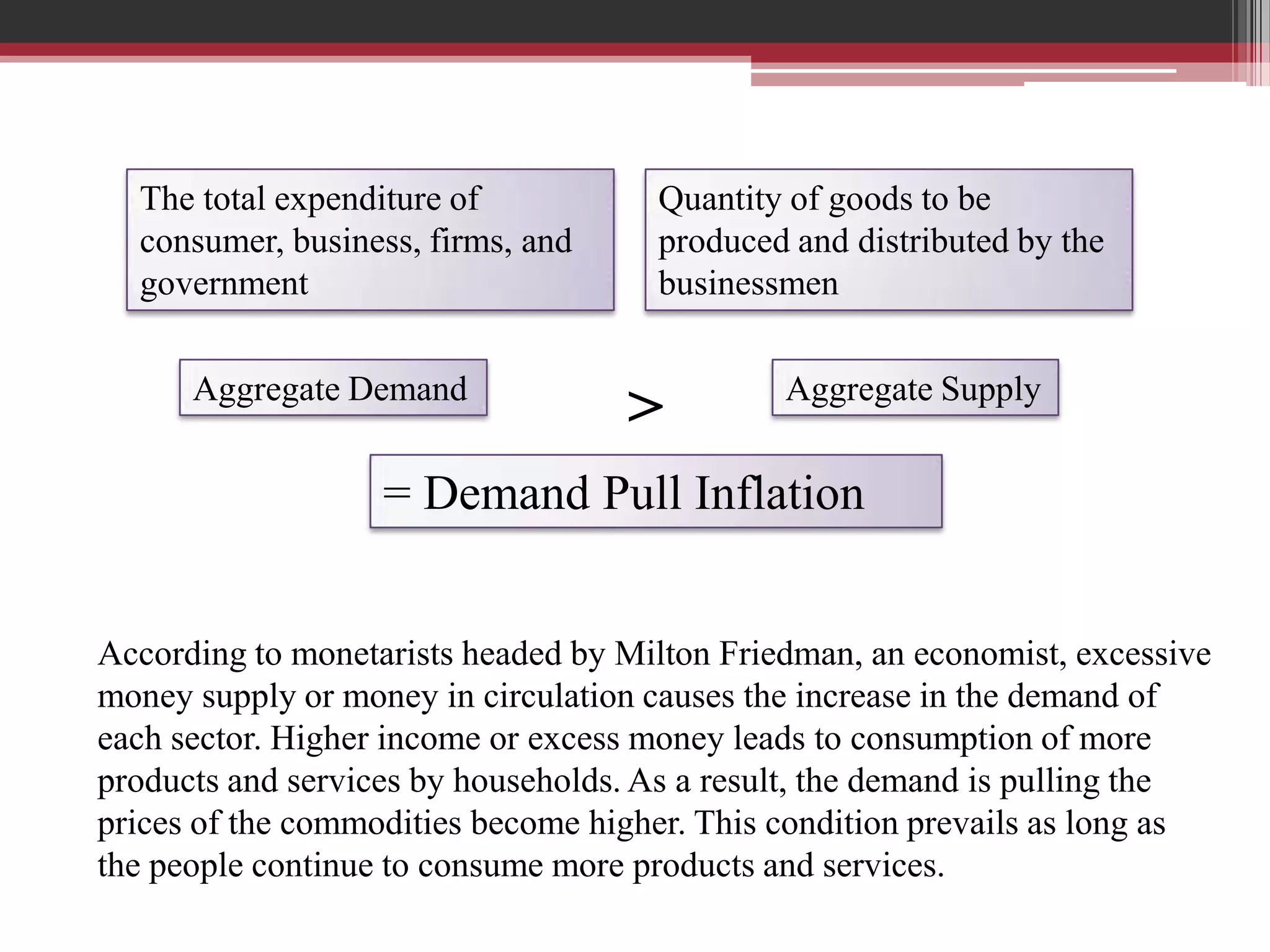
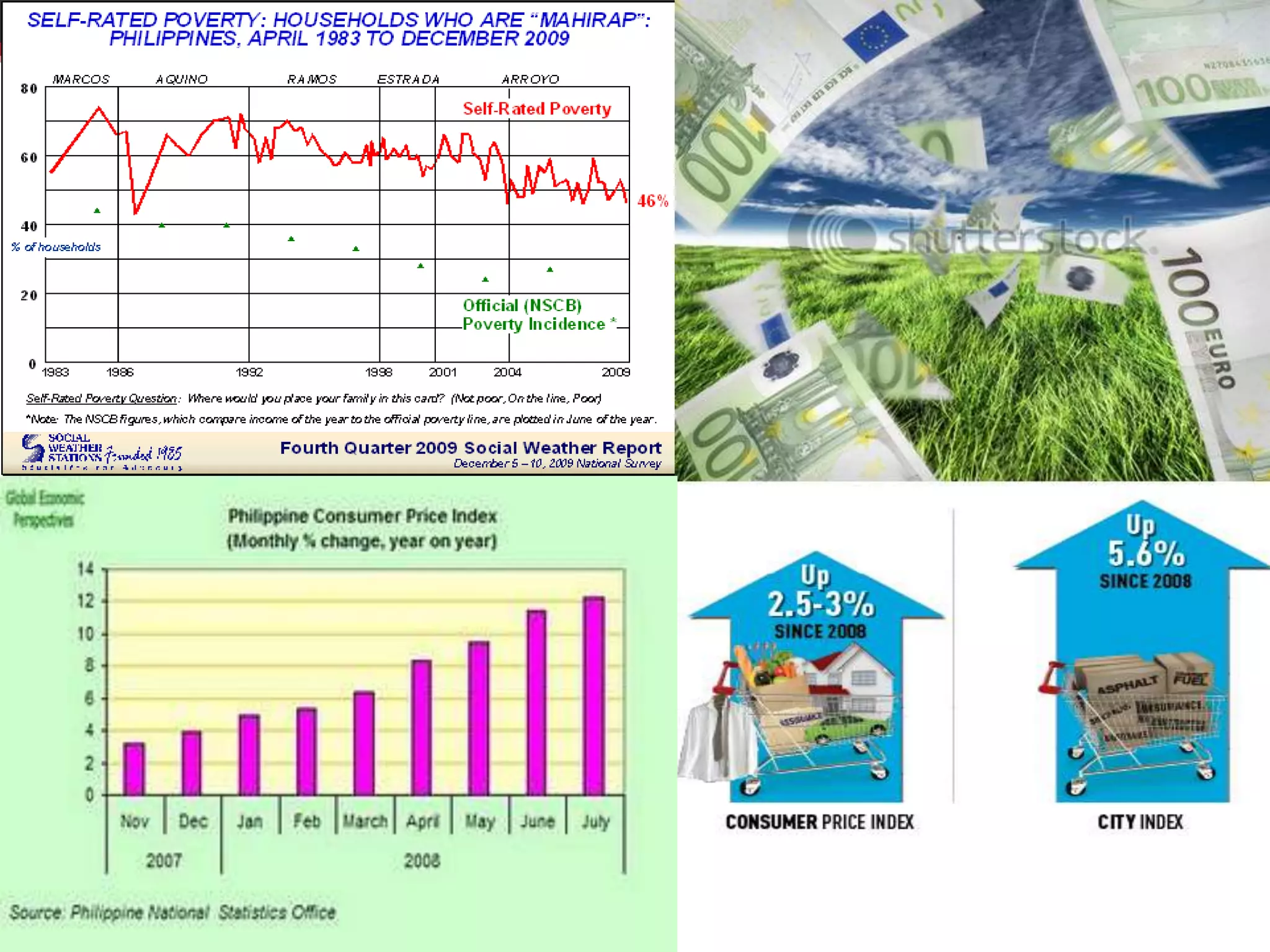
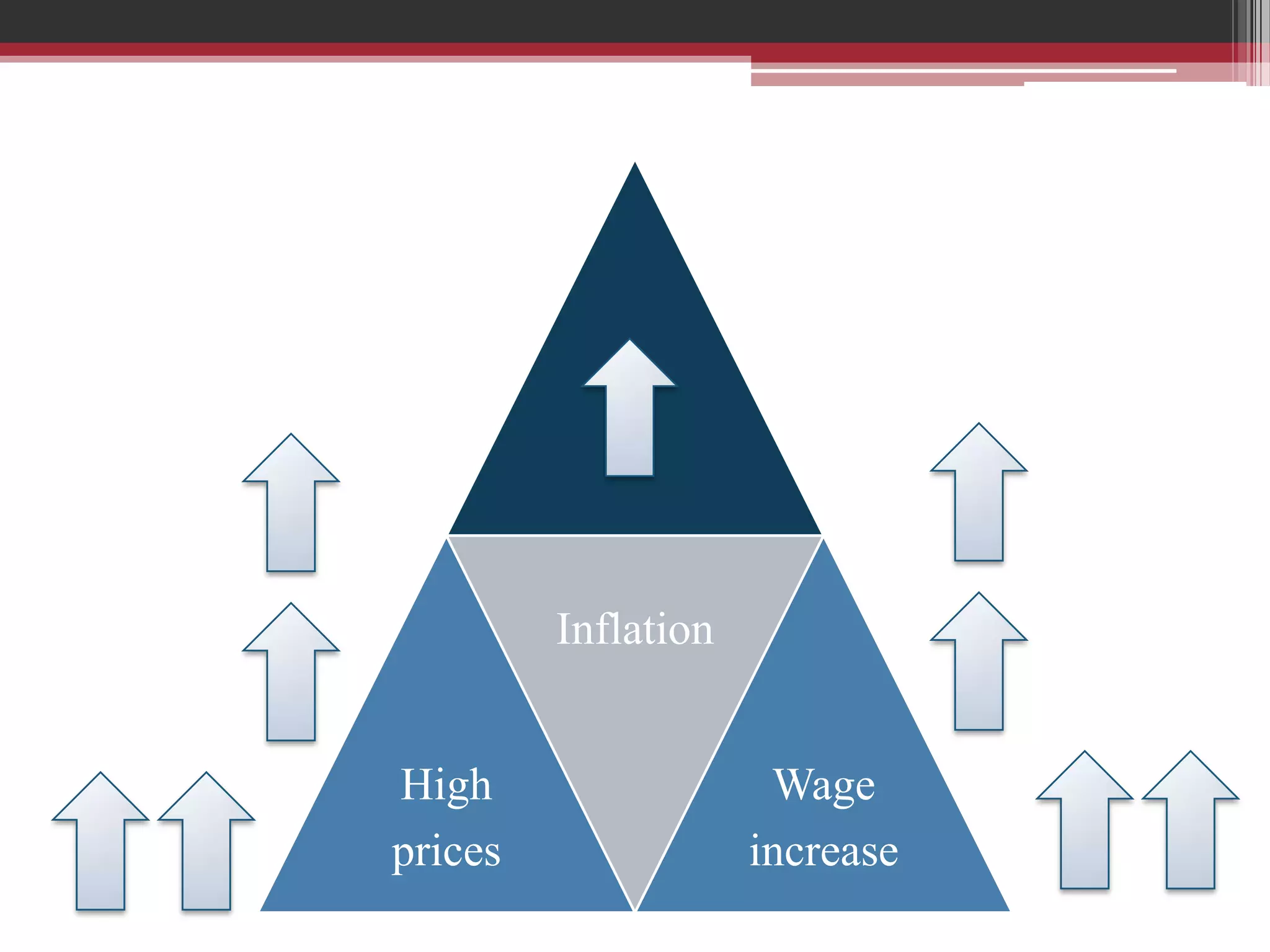
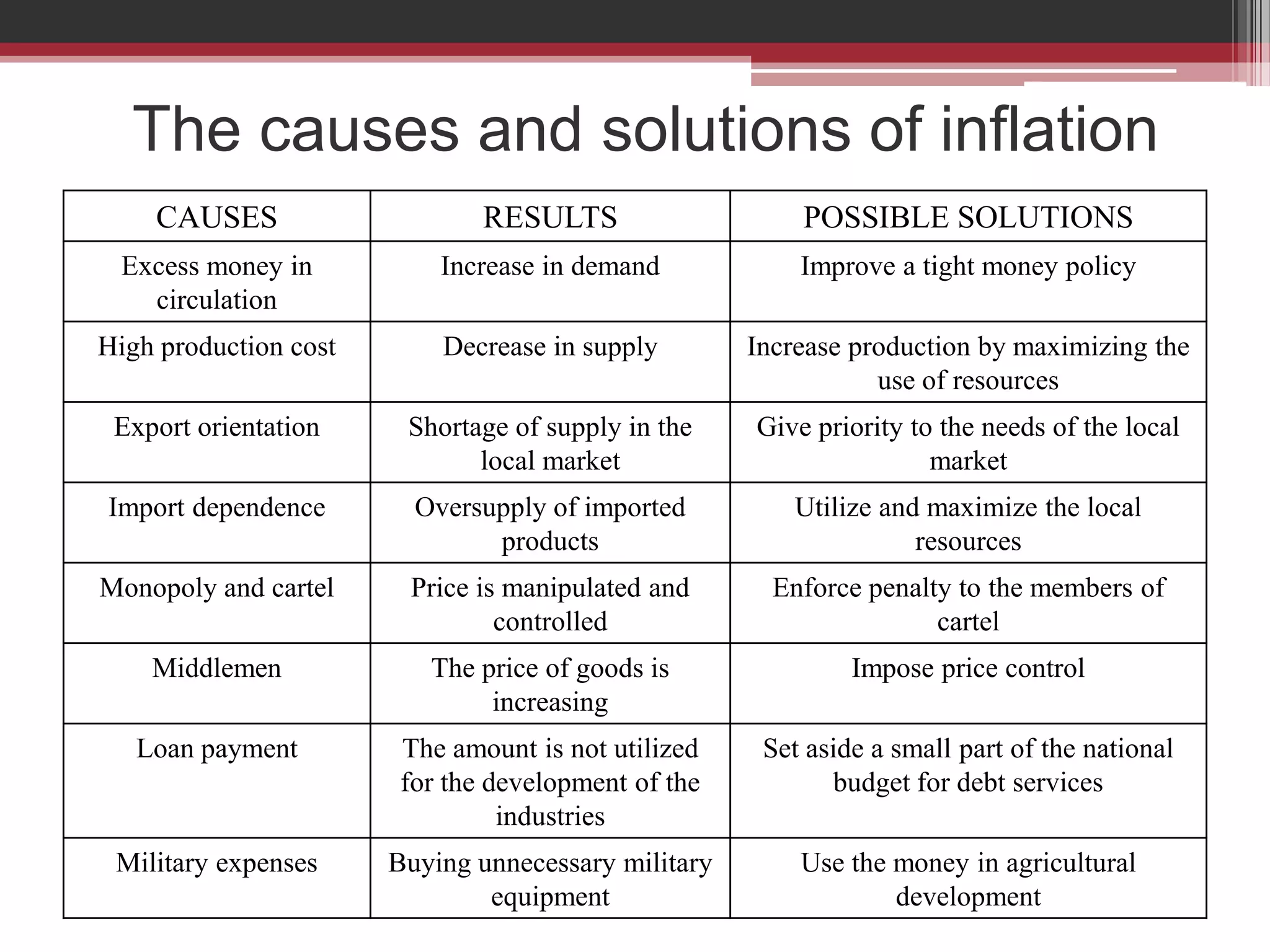
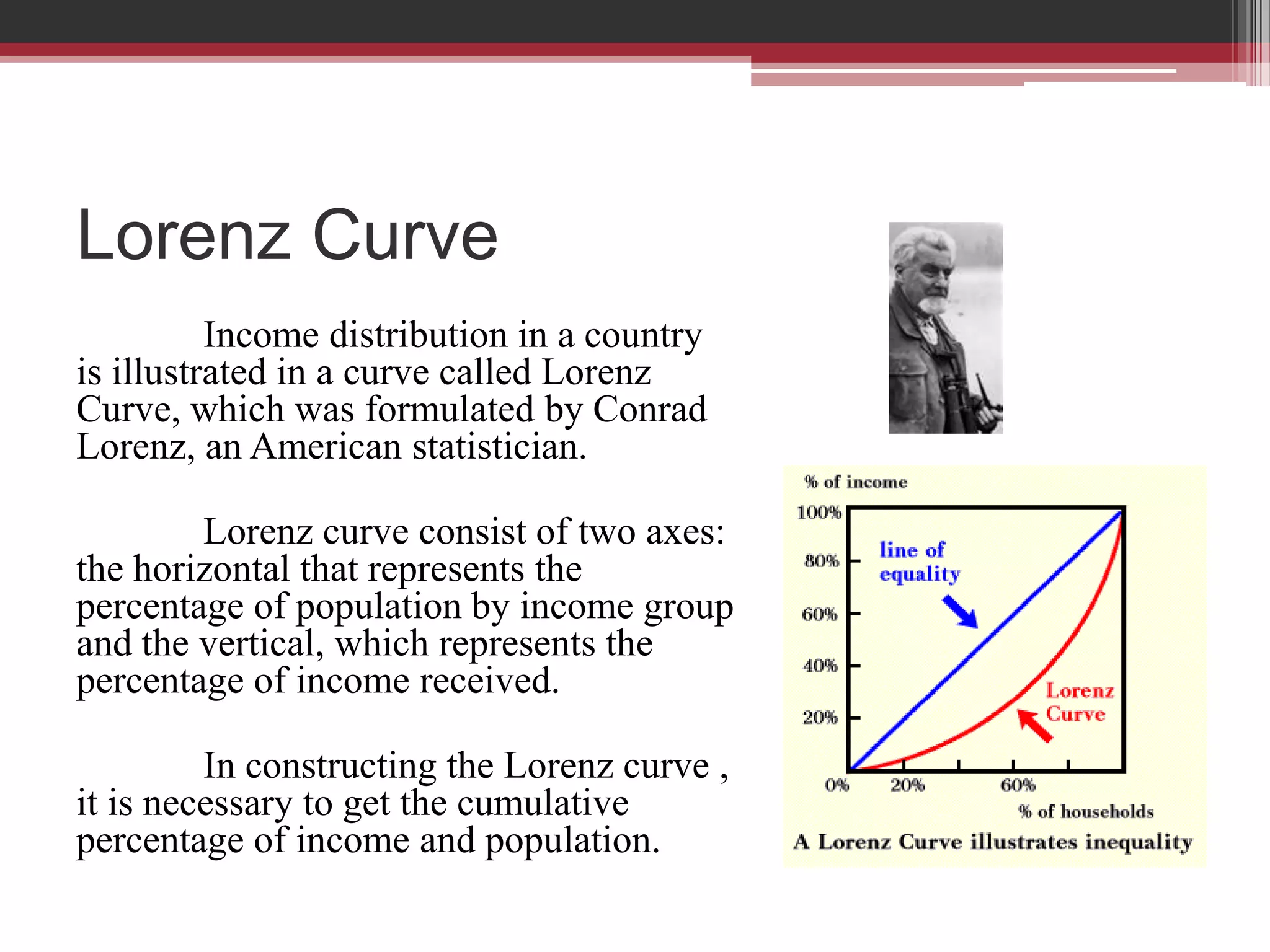
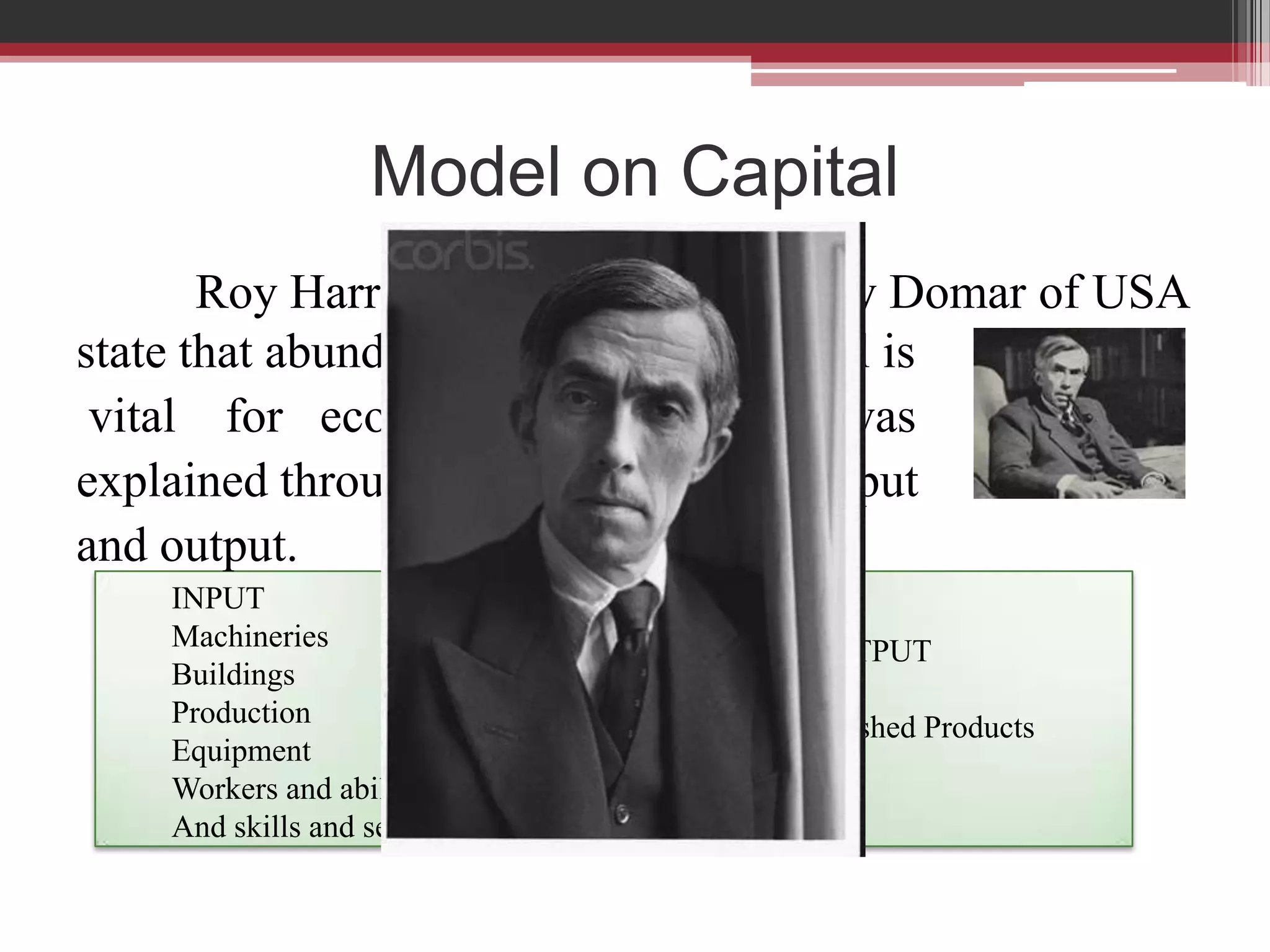
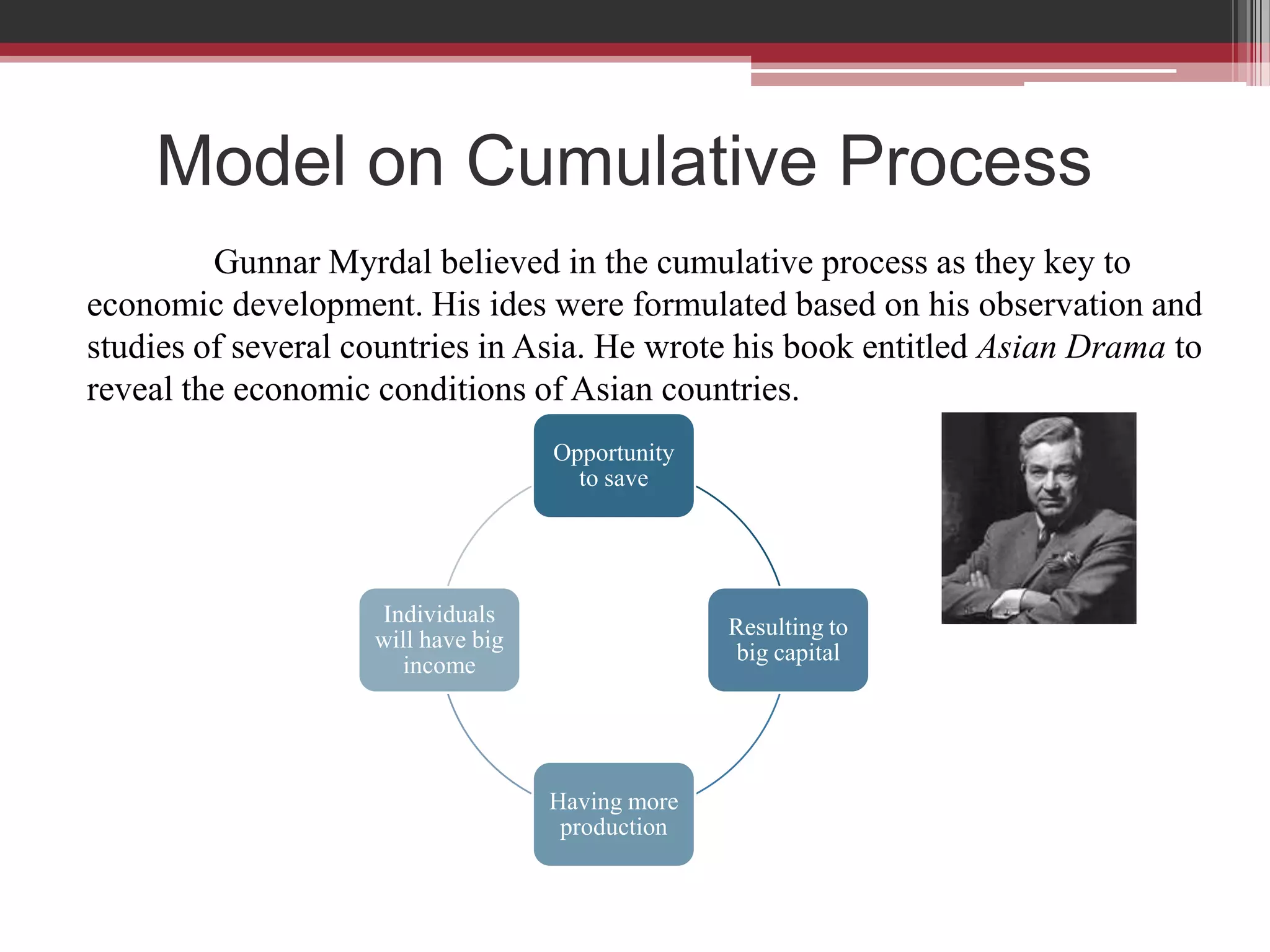
This document discusses approaches to measuring gross national product (GNP). It explains that GNP can be measured using the factor income approach, which involves adding up all income received by the factors of production - compensation of employees, entrepreneurial income, corporate income, and government income. This sums to national income. To calculate GNP, national income is further adjusted by adding indirect business taxes and capital consumption allowance. The factor income approach provides a formula to precisely calculate GNP based on incomes from various economic factors.