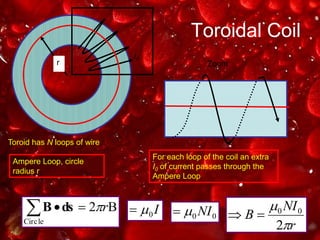
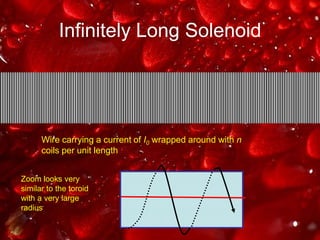
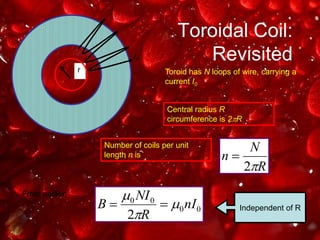
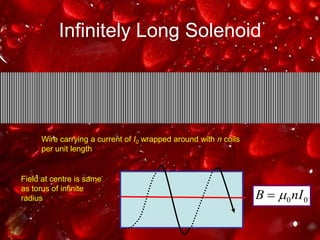
Ampere's law relates the magnetic field around a closed loop to the electric current passing through the loop. It states that the line integral of the magnetic field around the loop equals the net current passing through the loop times the permeability of free space. The document provides examples of using Ampere's law to calculate magnetic fields for various current carrying wire configurations, including inside and outside a long straight wire, inside a solenoid, and inside and outside a toroidal coil.