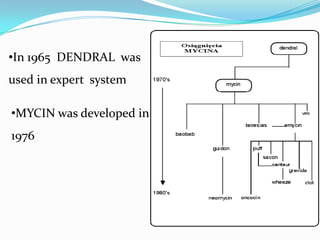
This document discusses the development and testing of the MYCIN expert system. MYCIN was developed in 1976 at Stanford University to diagnose and recommend treatment for bacterial infections. It was tested against physicians and found to be as or more accurate in its diagnoses and treatment recommendations. However, MYCIN was never fully implemented in clinical practice due to legal liability concerns if it provided incorrect diagnoses.