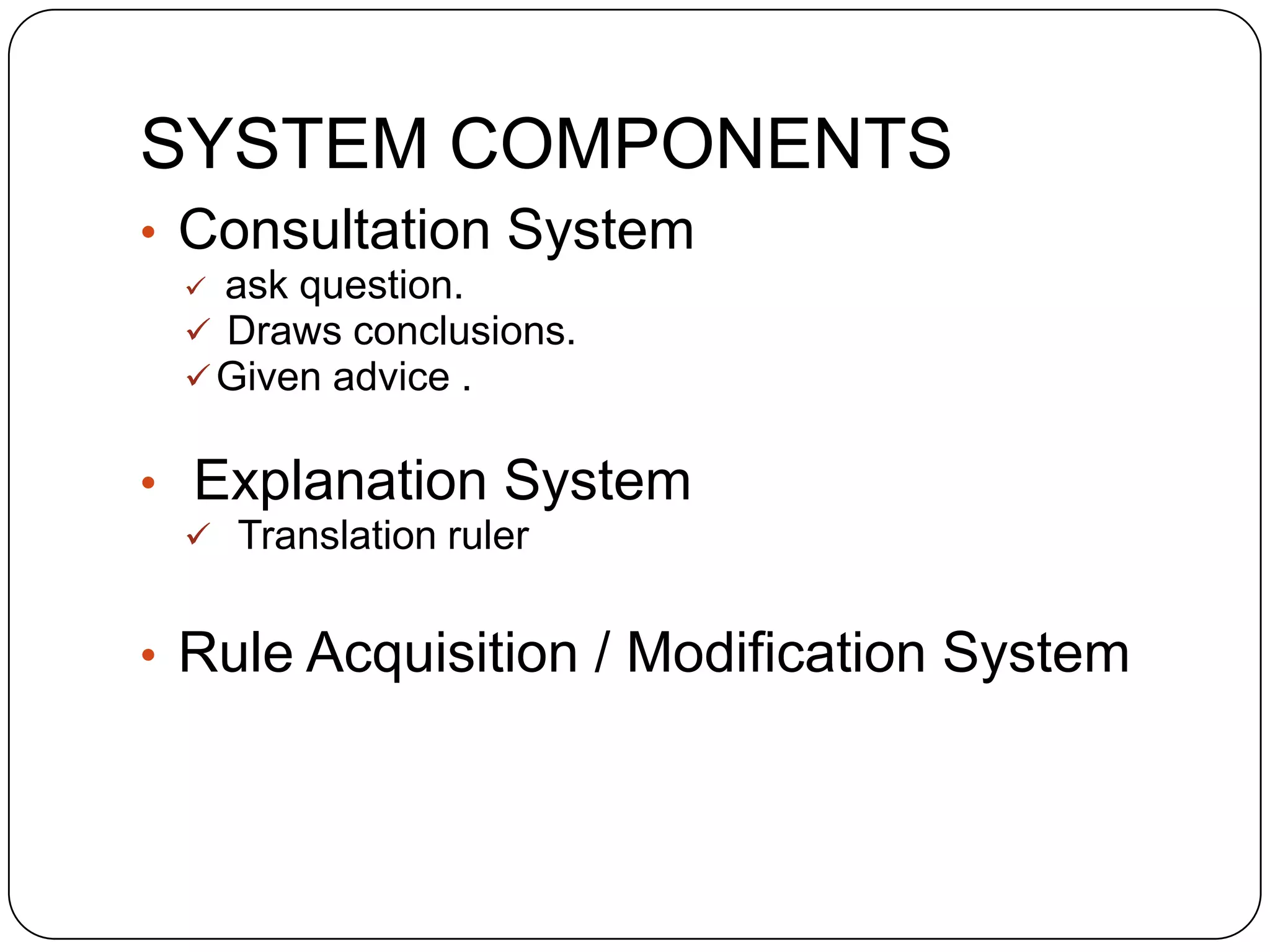
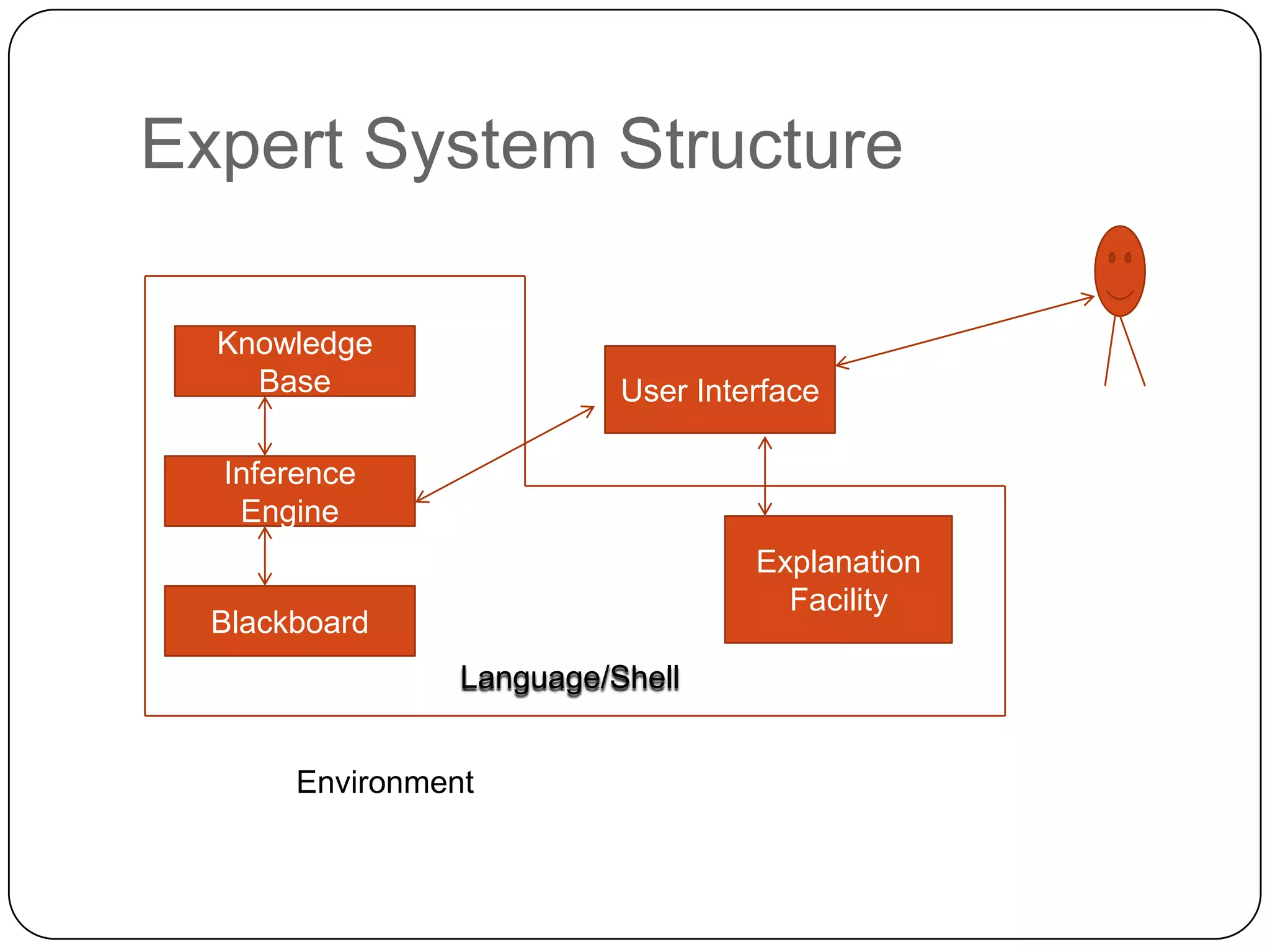
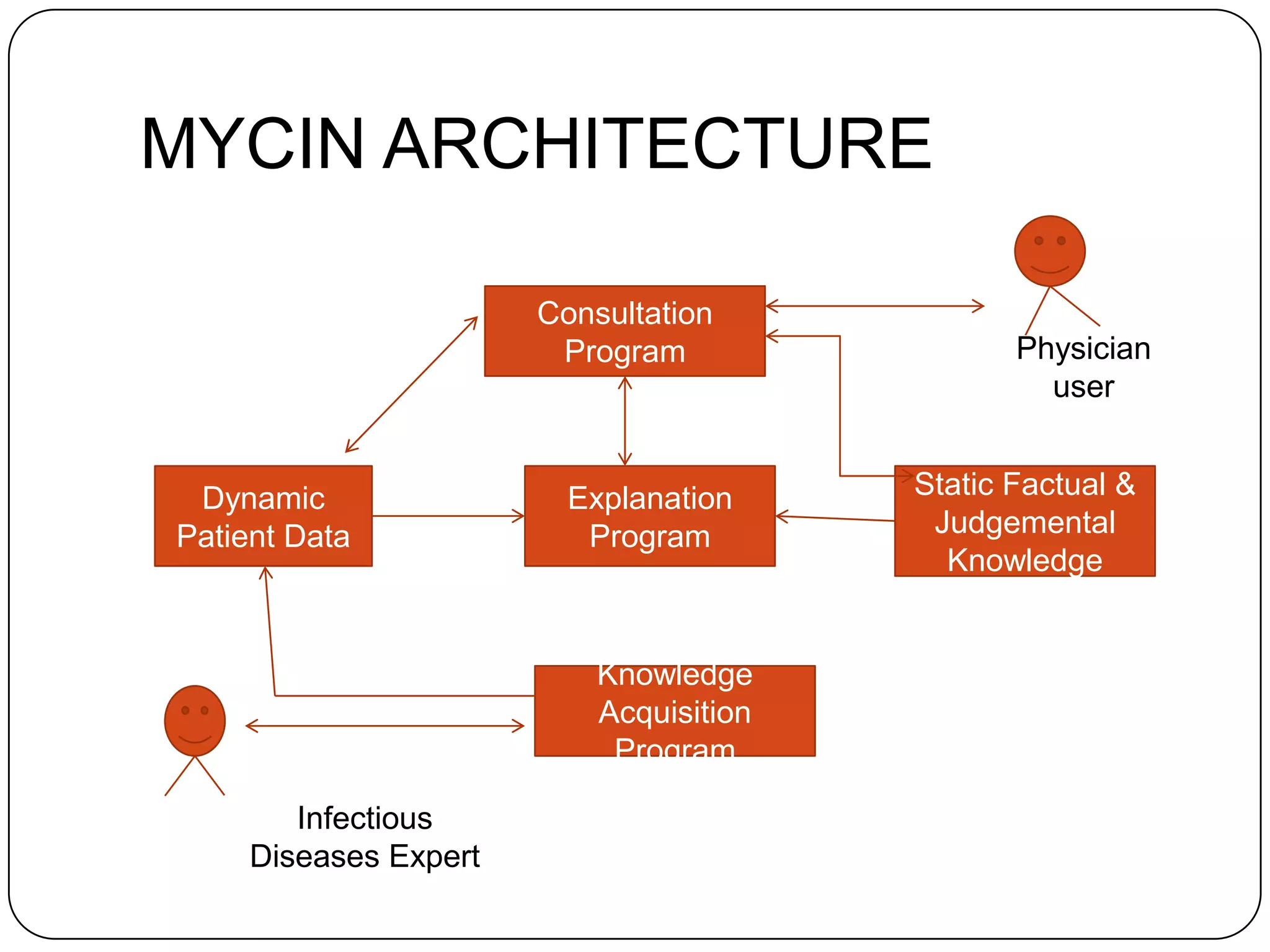
MYCIN was an early expert system developed in the 1970s to diagnose infectious diseases. It used a knowledge base of rules provided by experts and an inference engine to identify bacteria causing infections, determine appropriate antibiotics, and provide treatments. MYCIN could also explain its reasoning. It demonstrated that expert systems could perform competently in domains requiring specialized knowledge.


![MYCIN : The Problem
Roberts & Visconti [1972]:
Only 13% of patients are treated.
66% are being irrational treatment.
21% are being questionable treatment.
• Irrationality means, for example :
Using a contraindicated combination.
Using the wrong agent for a specific
organism.
Not taking the required cultures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mycin016-140115082552-phpapp02/75/Mycin-016-4-2048.jpg)