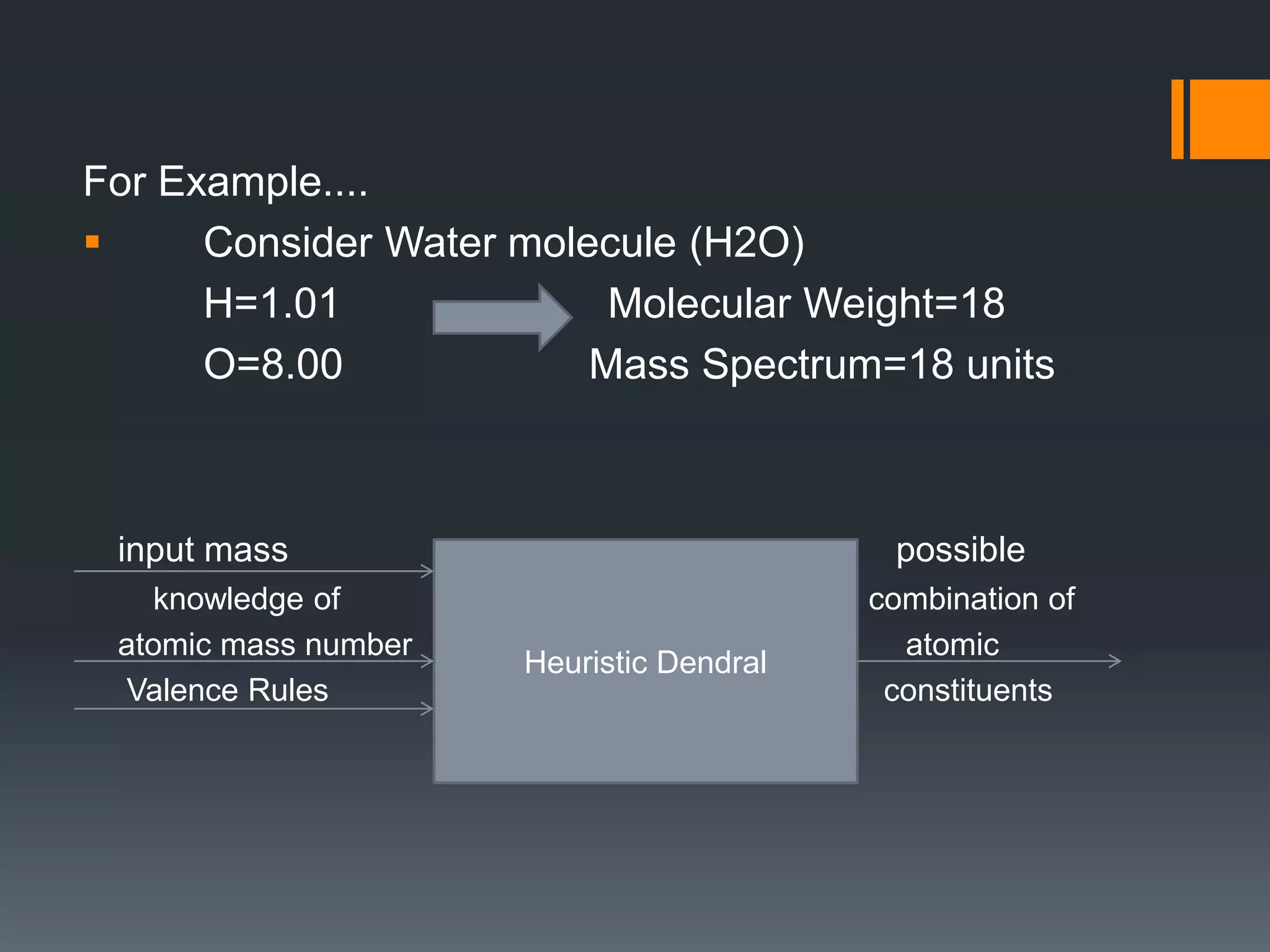
Dendral was an early expert system developed in the 1960s at Stanford University to help organic chemists identify unknown organic molecules. It used mass spectrometry data and knowledge of chemistry to generate possible chemical structures. Dendral included both Heuristic Dendral, which produced candidate structures, and Meta Dendral, a machine learning system that proposed mass spectrometry rules relating structure to spectra. The project pioneered the use of heuristics programming and helped establish artificial intelligence approaches like the plan-generate-test problem solving paradigm. Many subsequent expert systems were influenced by Dendral.