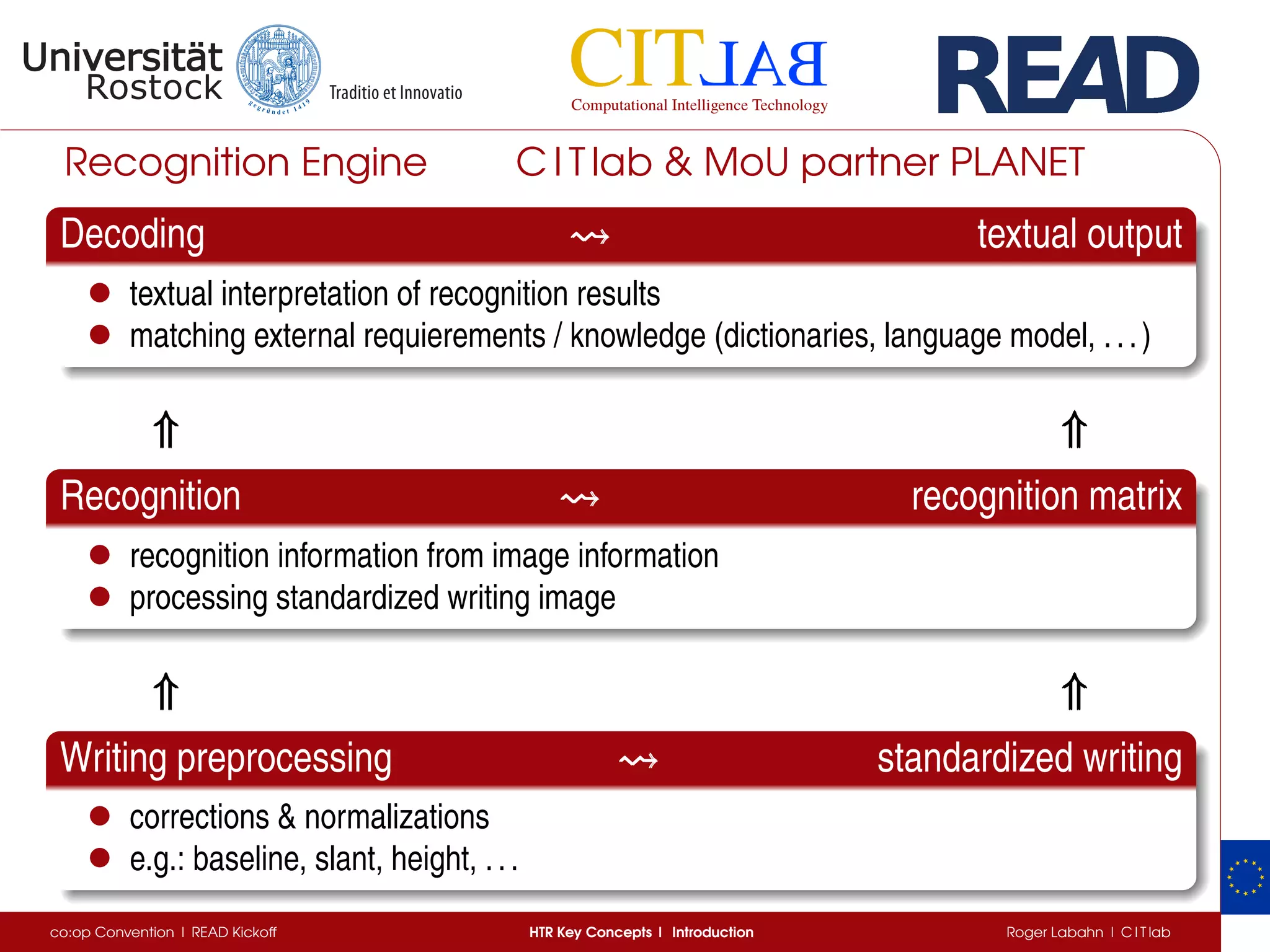
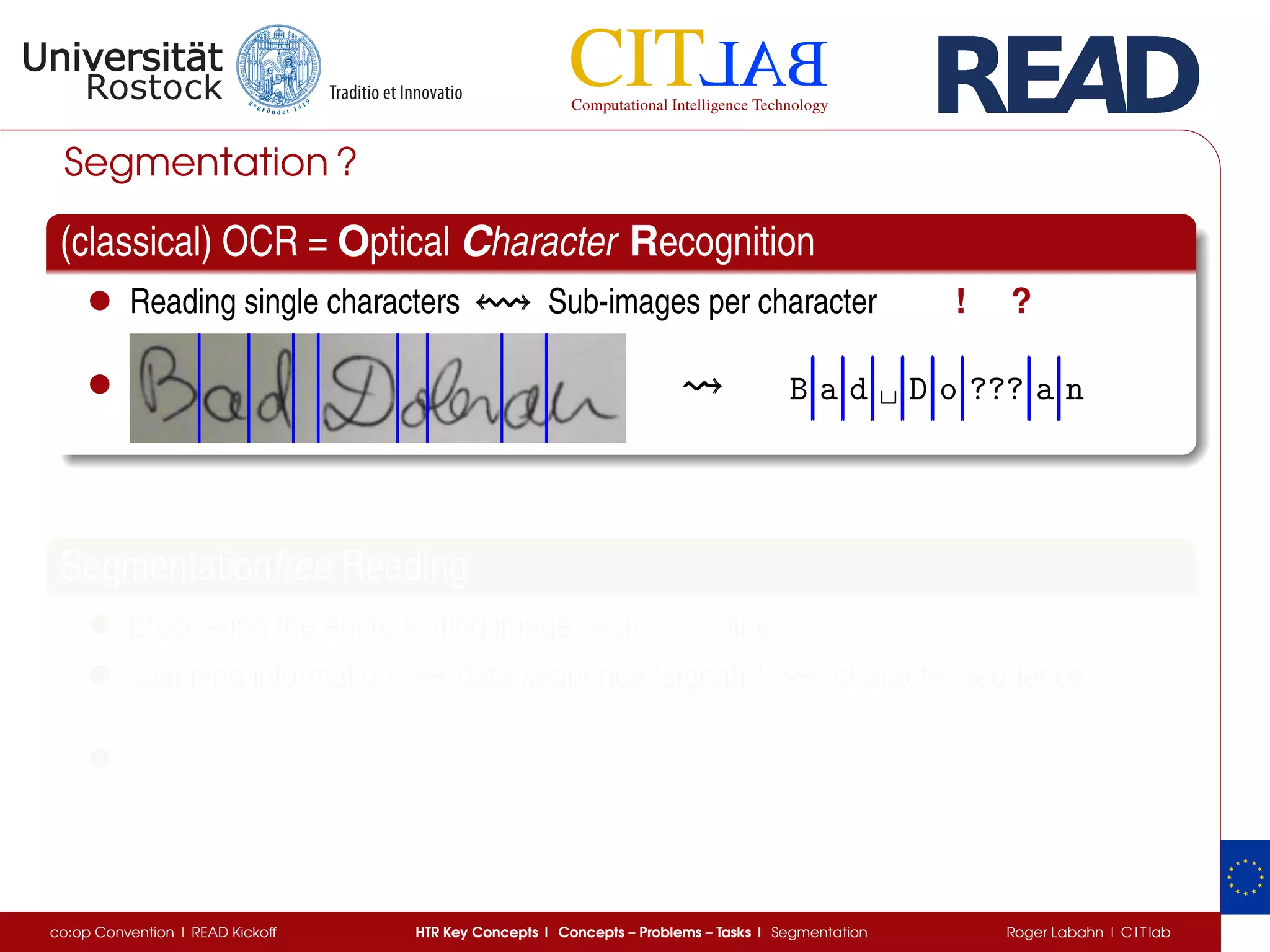
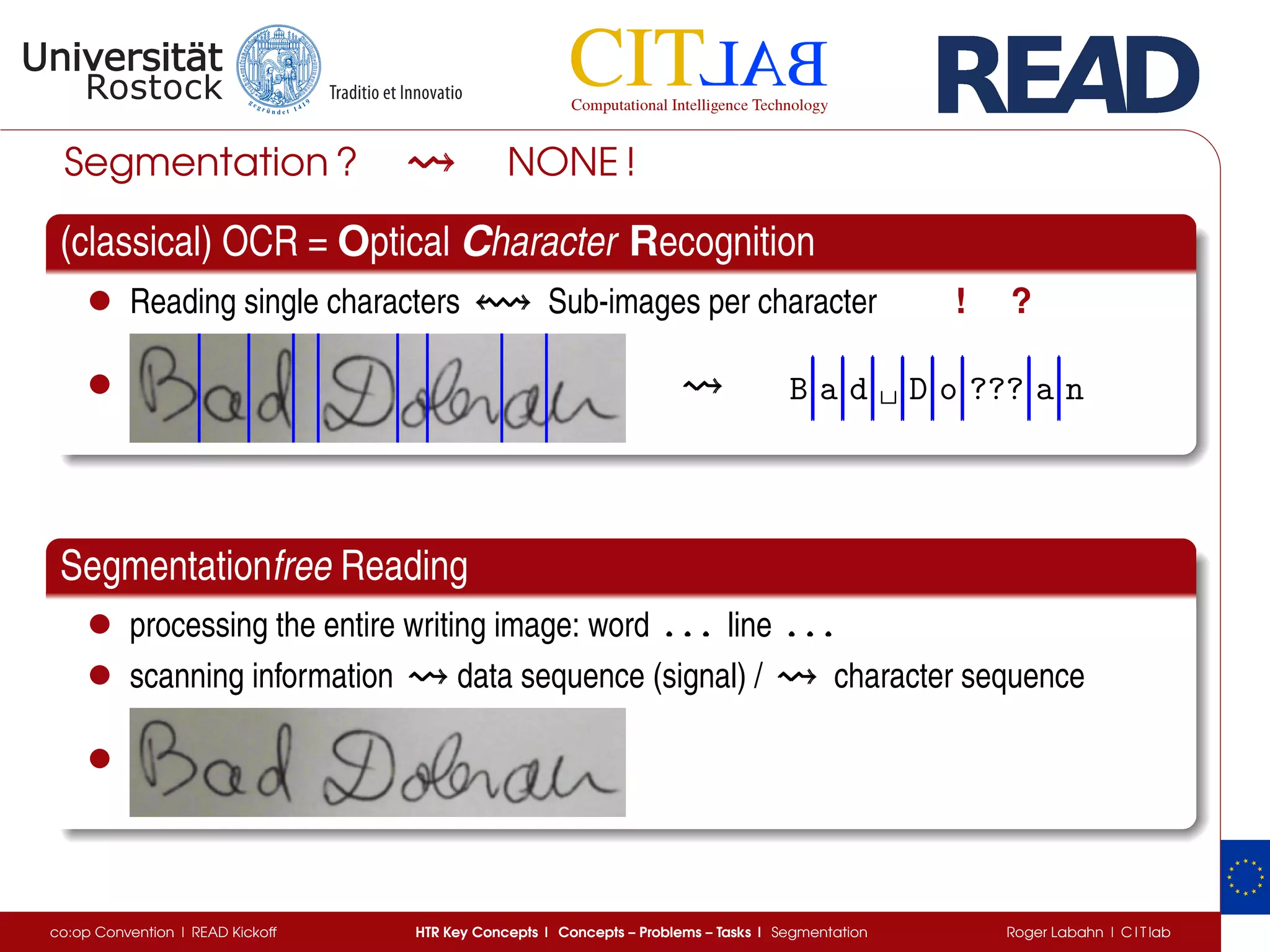
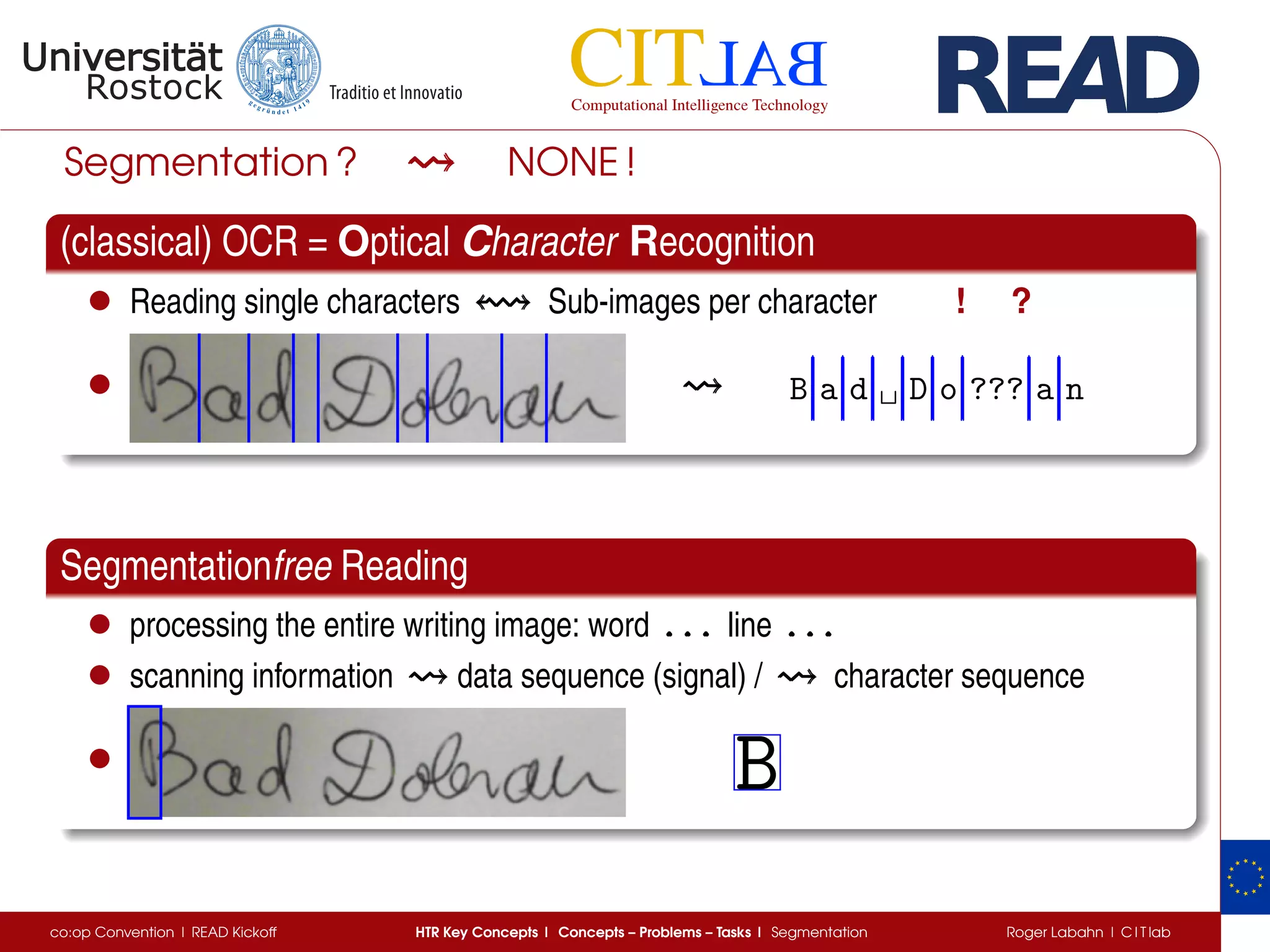
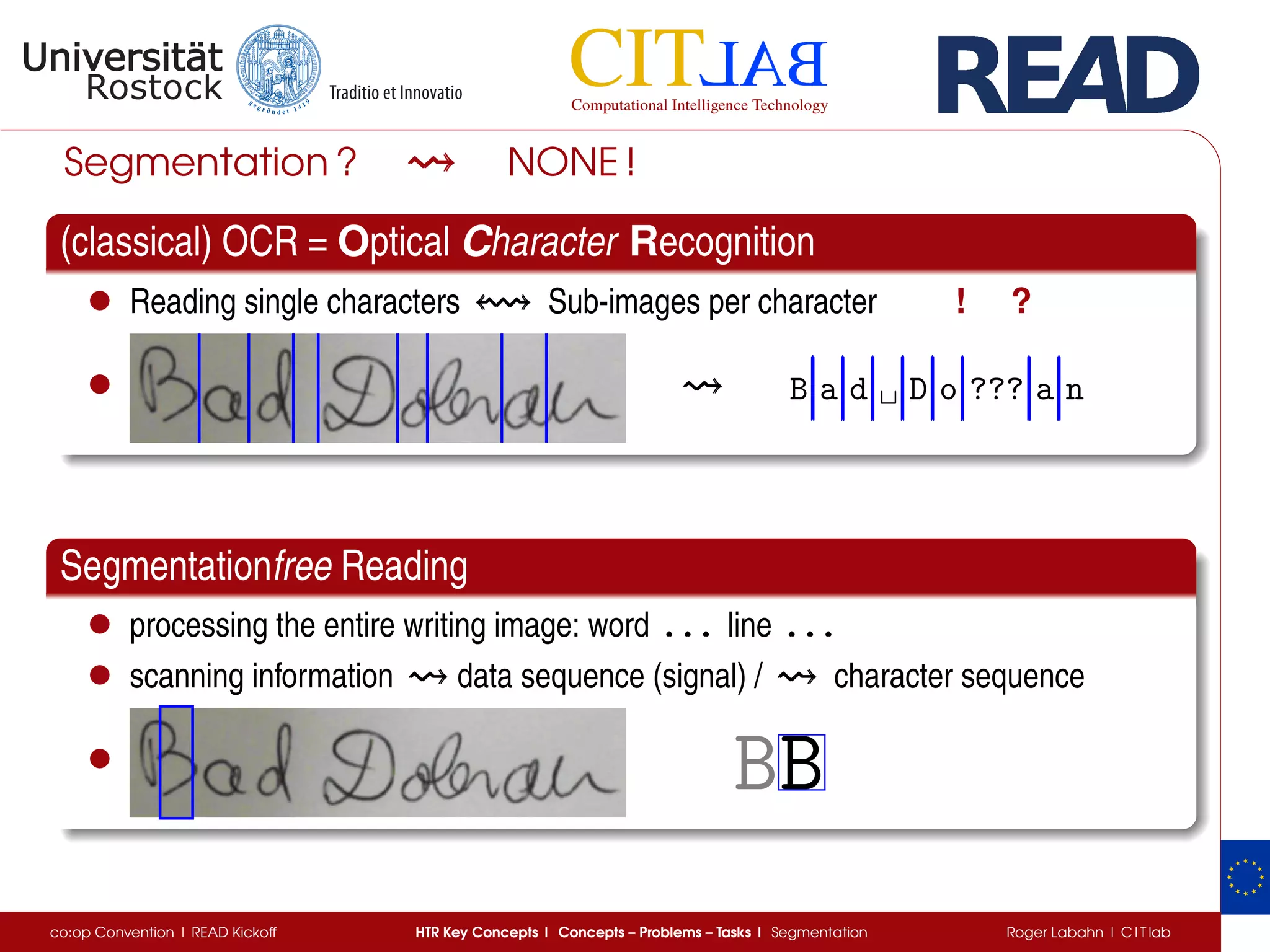
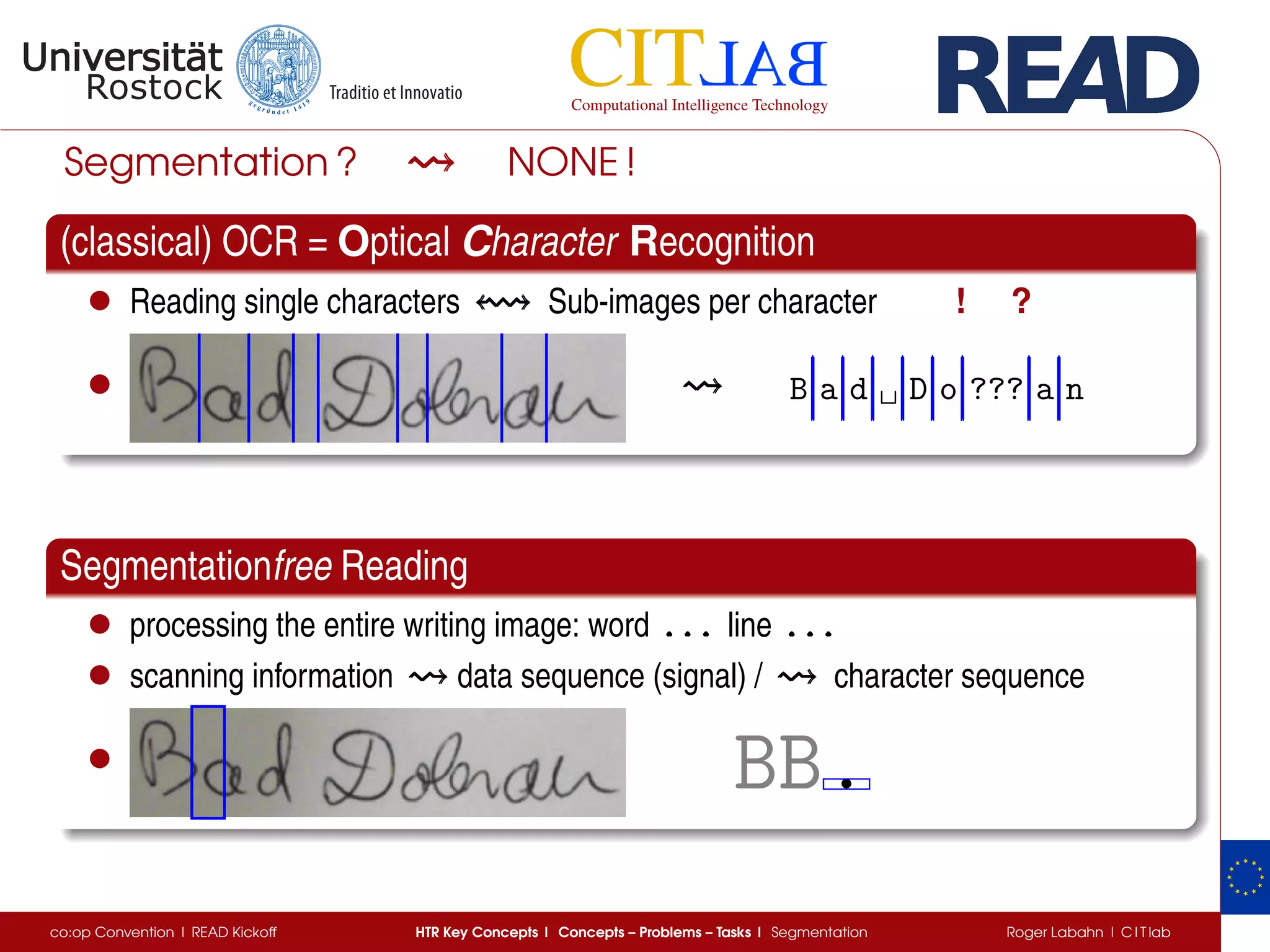
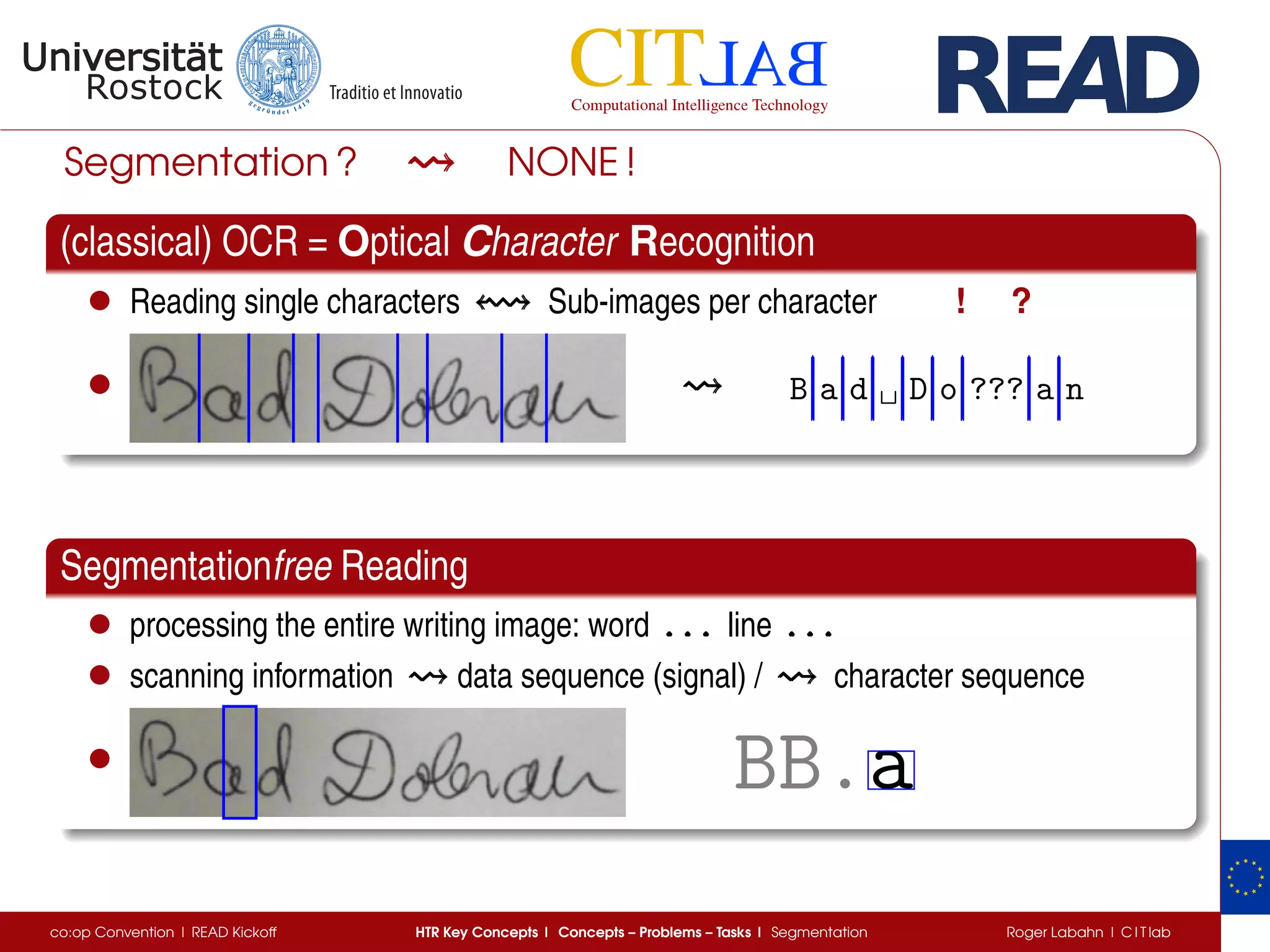
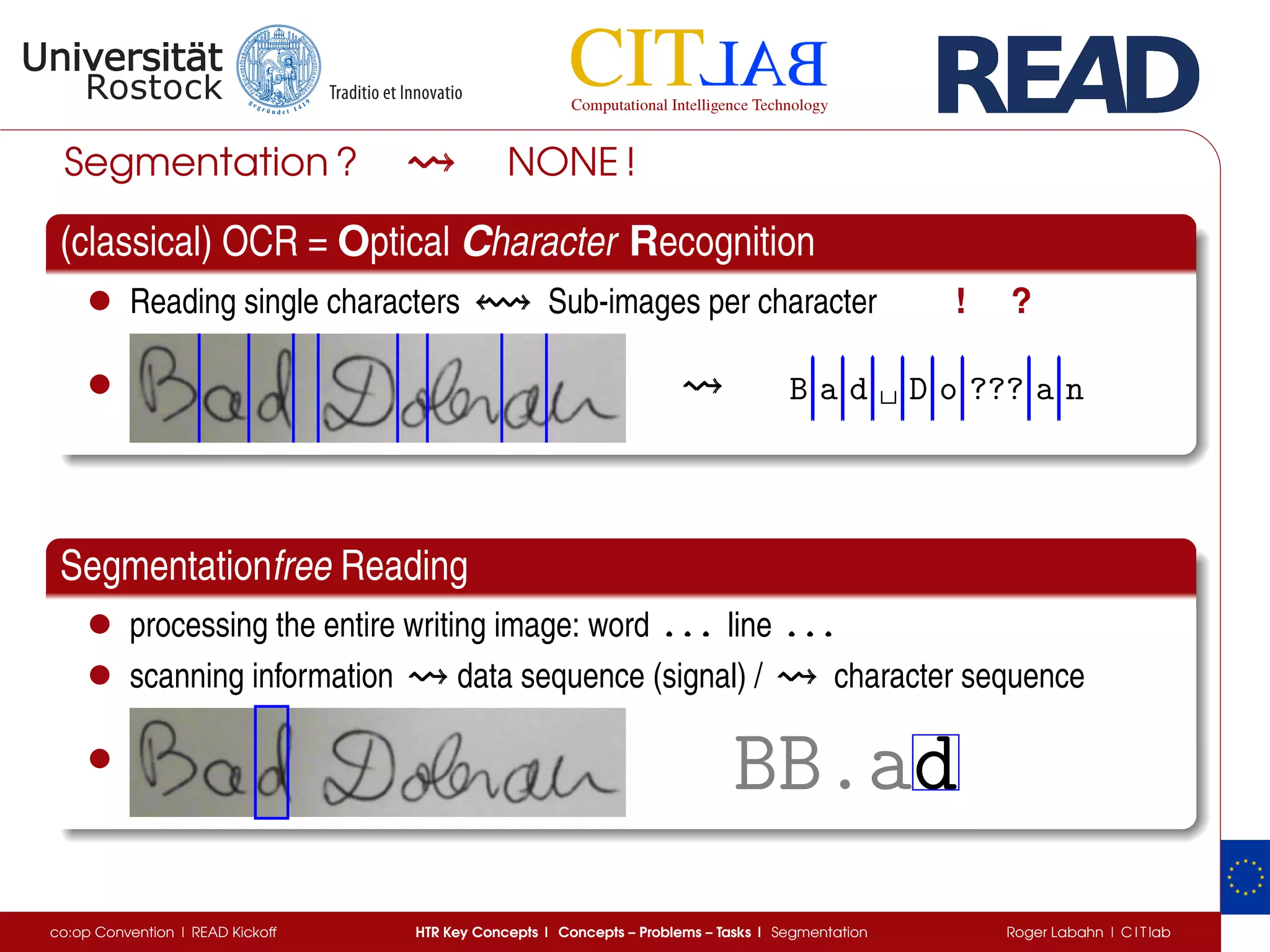
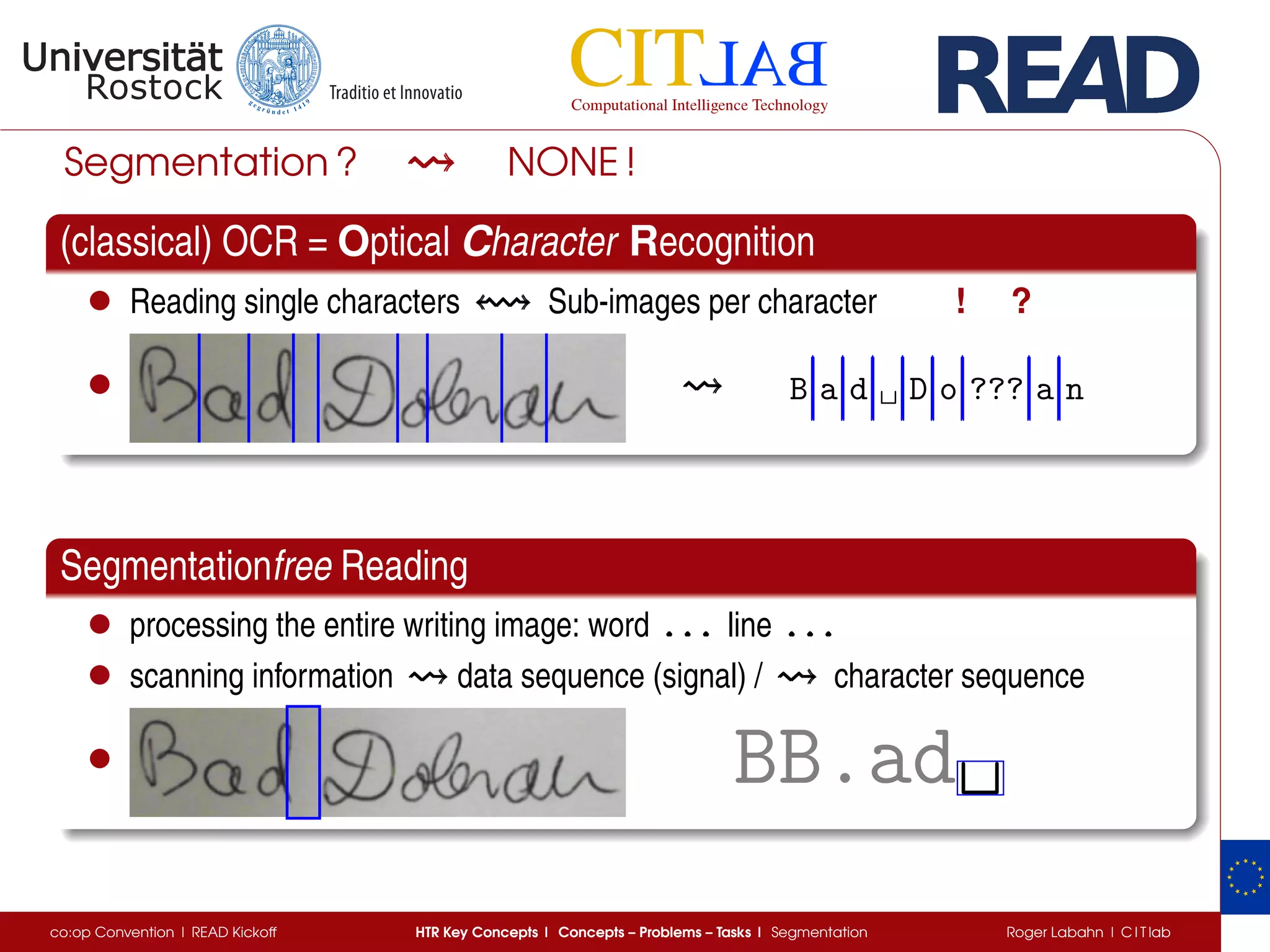
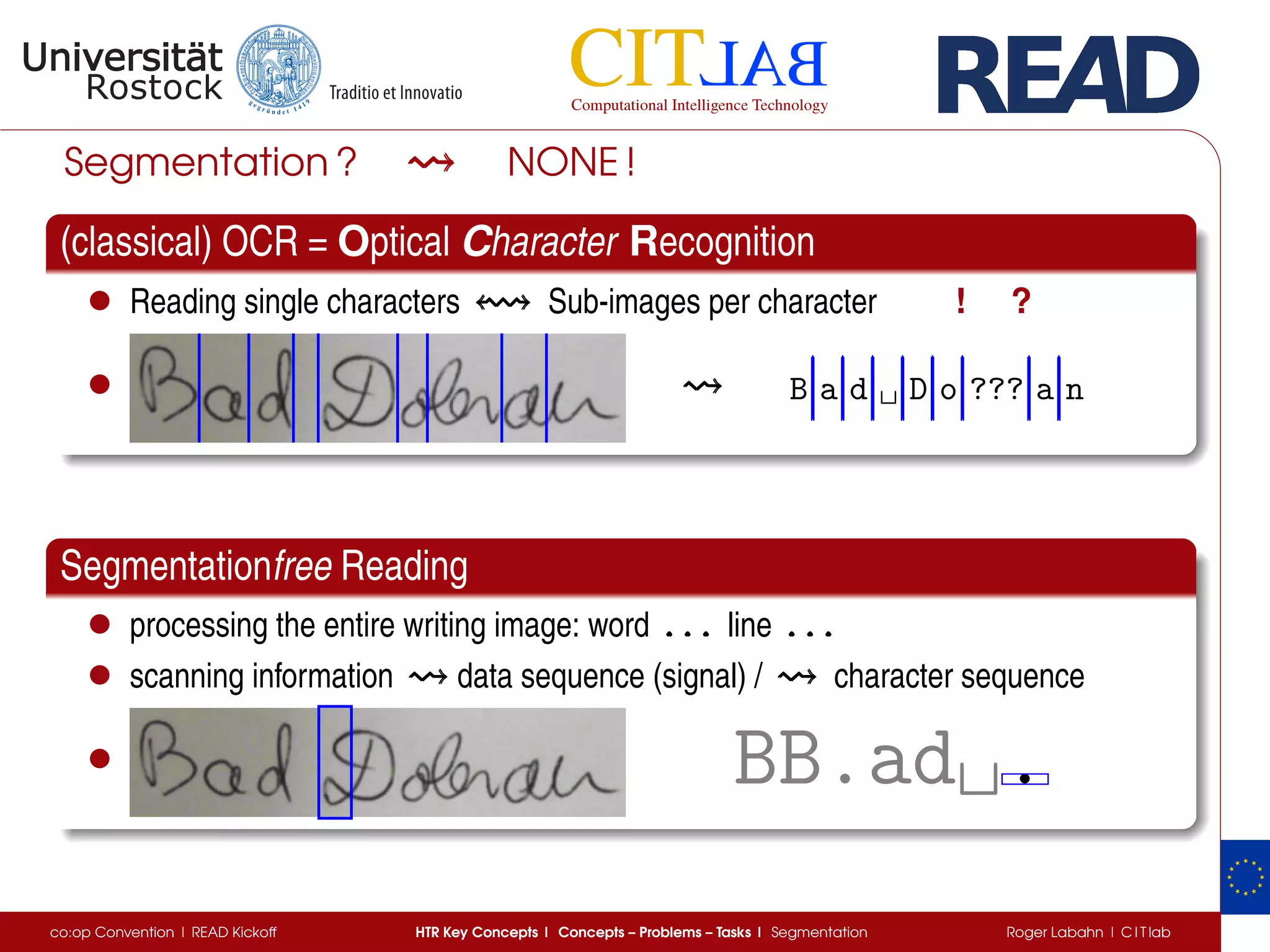
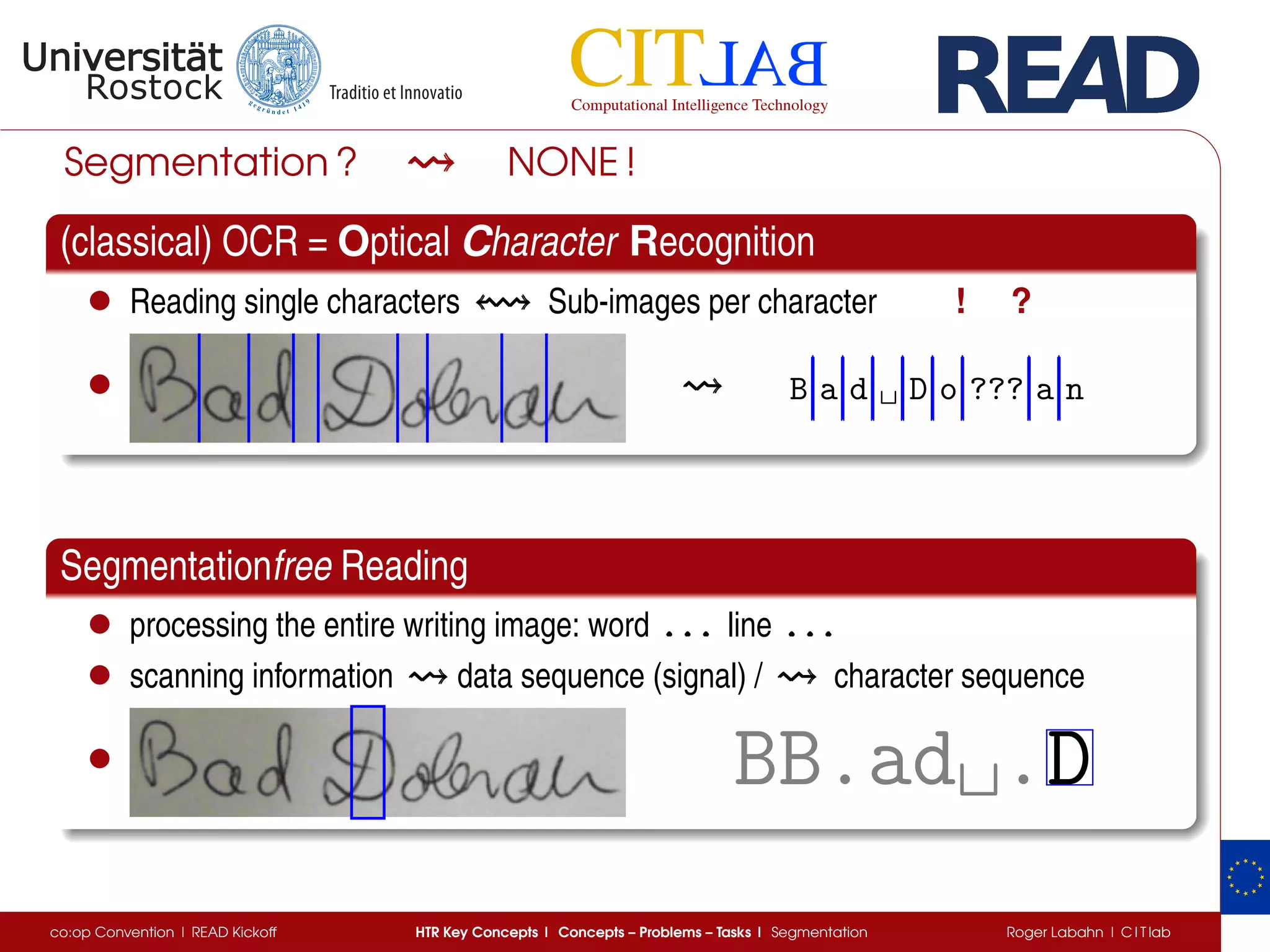
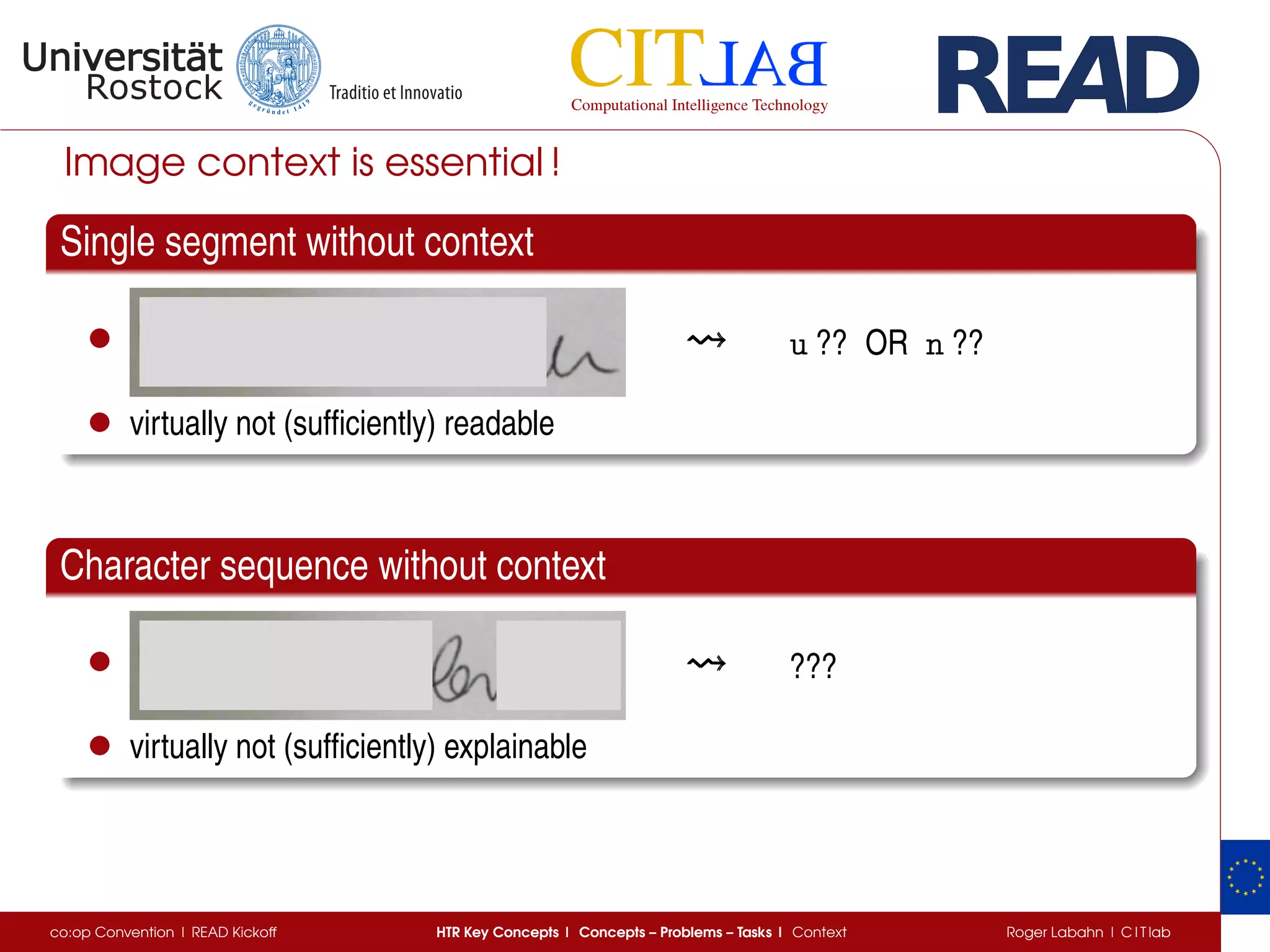
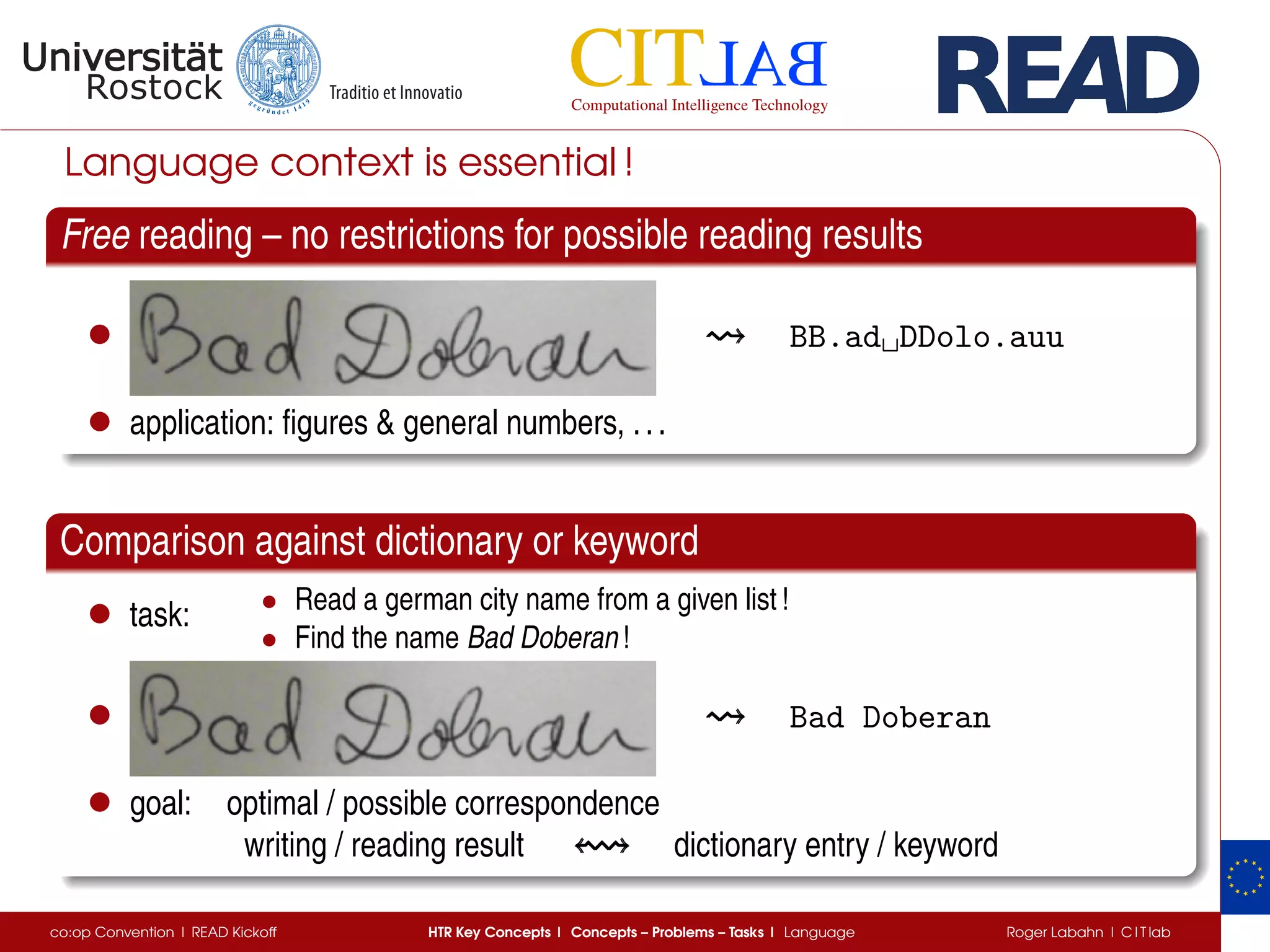
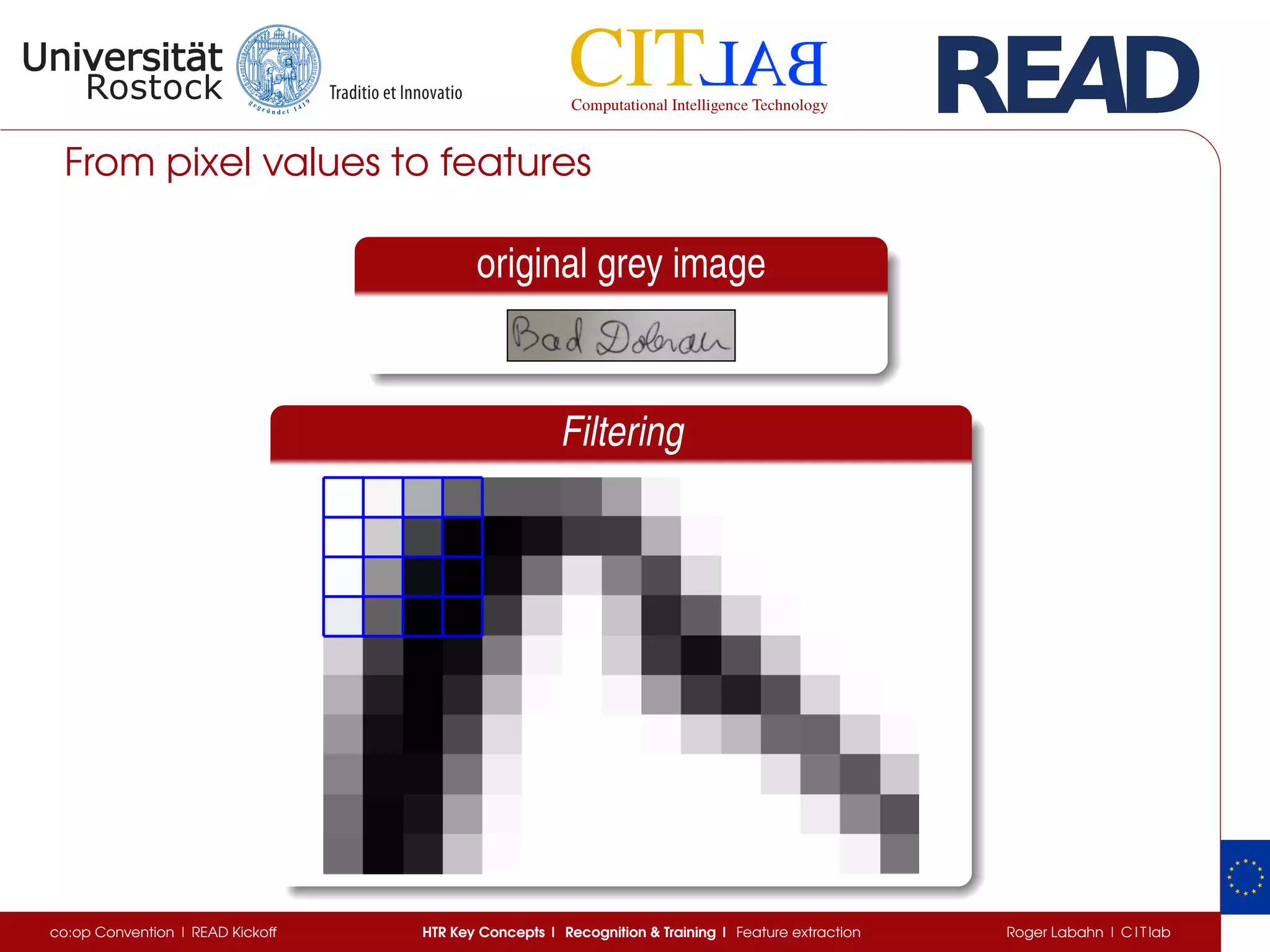
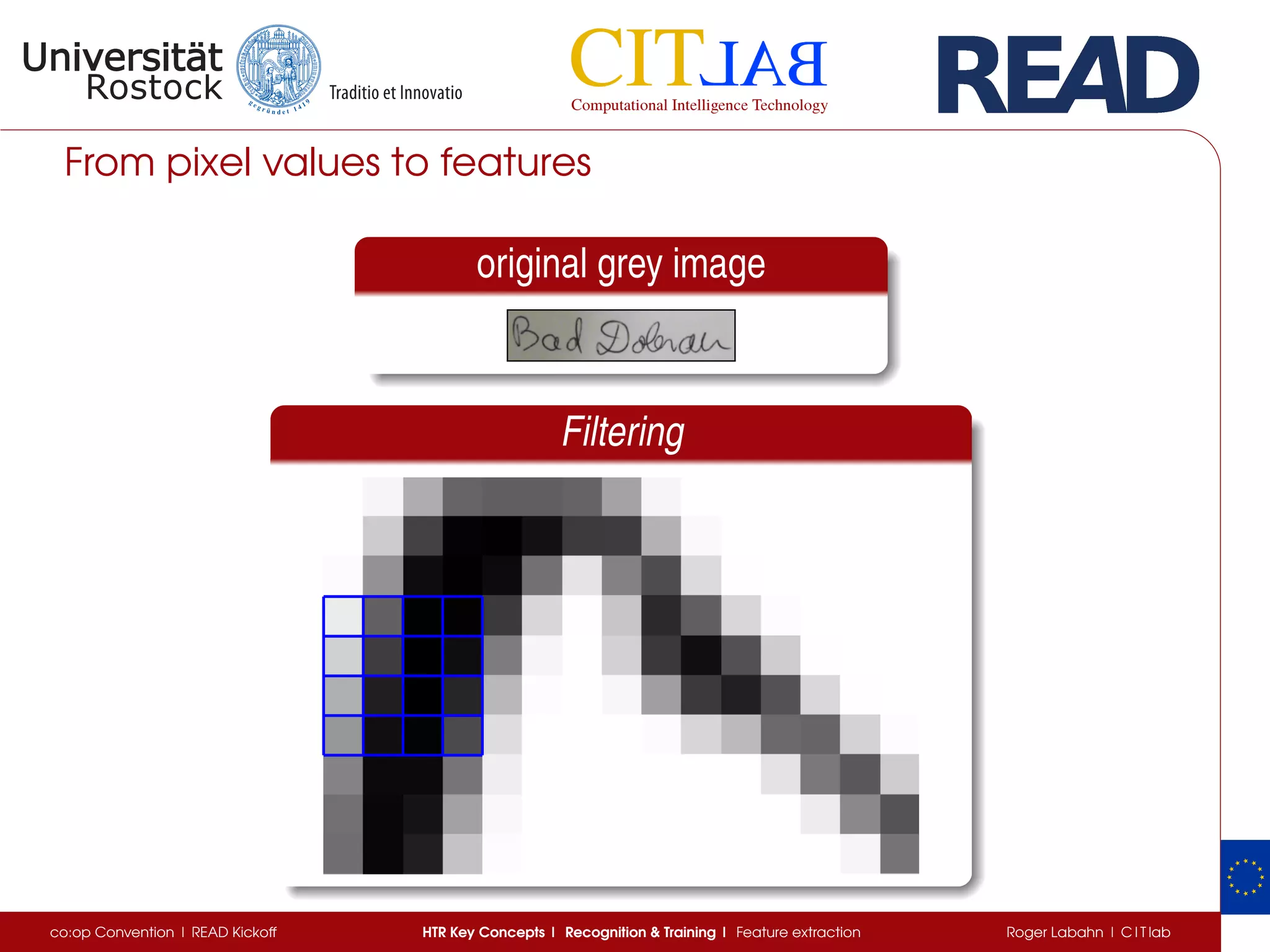
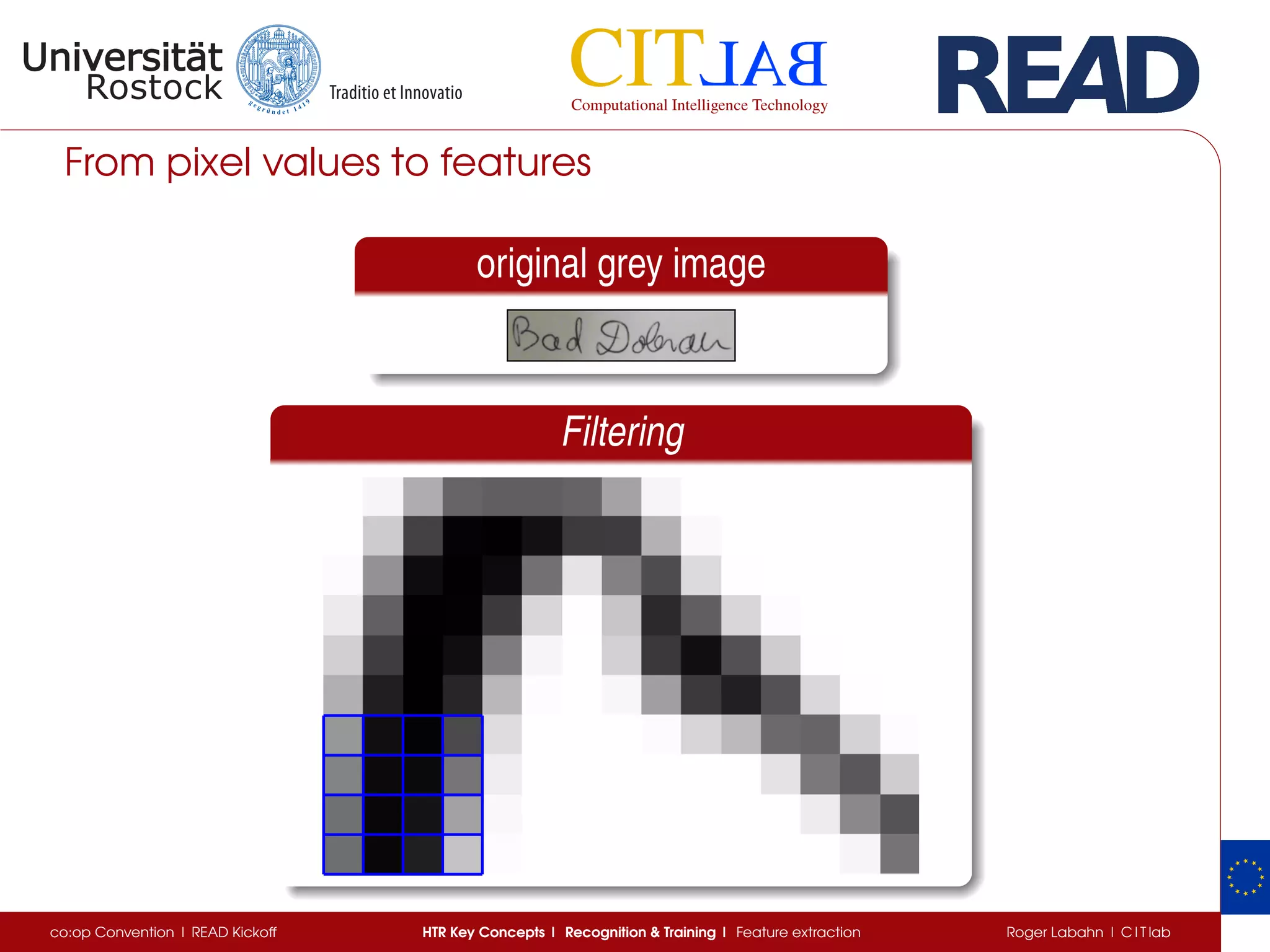
The document discusses key concepts of handwritten text recognition (HTR), focusing on various methodologies including topological, hidden Markov models, and recurrent neural networks for recognition. It addresses important aspects such as segmentation, language context, and parameter training, providing insights into optimizing neural network performance for accurate HTR. Additionally, practical applications and performance metrics are highlighted, showcasing the effectiveness of HTR systems in processing handwritten content.




















![Results
from C I T lab’s contribution to ICDAR’s HTRtS-2015 contest
WER = 0%
CER = 0%
who has with or without right the temporary possession of it : and
who has with or without right the temporary possession of it : and
WER = 17%
CER = 4%
operation of this act is spent upon Titius only ,
operation of this act isspeut upon Titius only ,
WER = 67%
CER = 52%
of the said first issue : the amount of such second consequently gap/ to the
of the and put feet the without of such ; said uitrquunity be the
WER = 80%
CER = 17%
for a simple personal Injury the Offender ’ s punish=
For on simple personal injury the offenders punish .
2. Examples of test line images of increasing difficulty. The reference transcript and the CITlab system hypothesis are displayed (in this order) below
h image. The corresponding WER and CER figures are also shown on the right of each image.
the lines with crossed-out word can be transcribed as the
ine shows. Finally, we can see that sometimes, if the line
a large WER but a low CER, the transcript can be more
ul than if the WER is lower and the CER higher (see third
[4] A. Graves, M. Liwicki, S. Fern´andez, R. Bertolami, H. Bunke, and
J. Schmidhuber, “A Novel Connectionist System for Unconstrained
Handwriting Recognition,” IEEE Tr. PAMI, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 855–
868, 2009.
(Figure from SÁNCHEZ, TOSELLI, ROMERO, VIDAL: ICDAR2015 Competition HTRtS: Handwritten Text Recognition on the tranScriptorium Dataset)
co:op Convention | READ Kickoff HTR Key Concepts | Epilog Roger Labahn | C I T lab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05labahnhandwrittentextrecognitionpresentation-160302101657/75/co-op-READ-Convention-Marburg-Roger-Labahn-53-2048.jpg)

