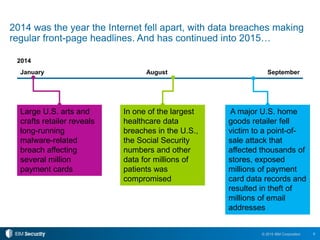
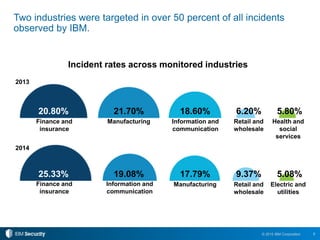
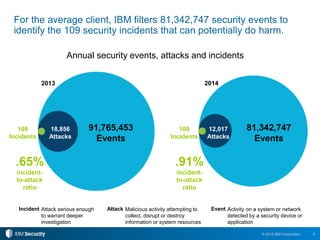
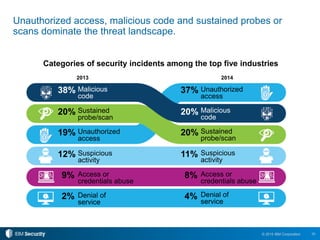
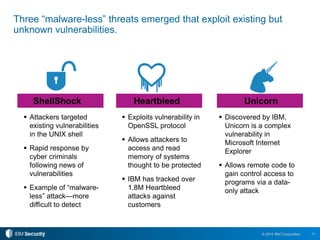
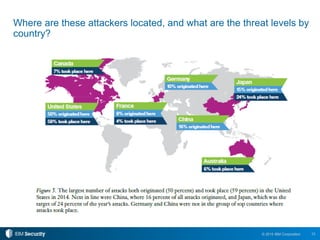
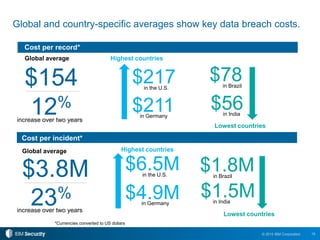
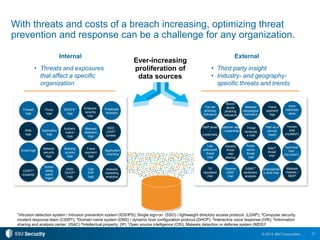
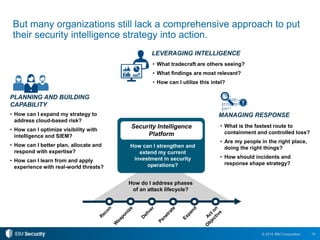
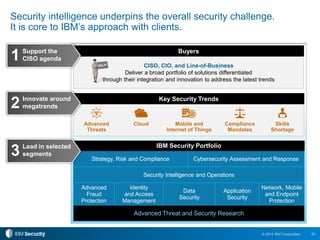
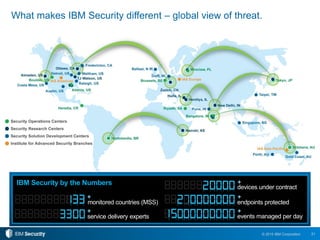
The 2015 IBM Cyber Security Intelligence Index provides insights into the evolving threat landscape, highlighting the prevalence of data theft and cybercrime, and the average cost of data breaches. Key findings indicate that finance and insurance, as well as manufacturing sectors, are among the most targeted by attacks, with significant increases in the cost of breaches over the past two years. The report emphasizes the need for organizations to adapt their security strategies and improve their incident response capabilities in light of these threats.