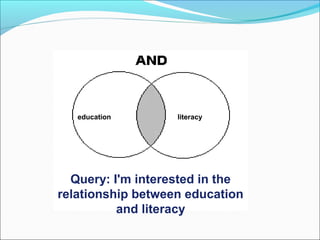
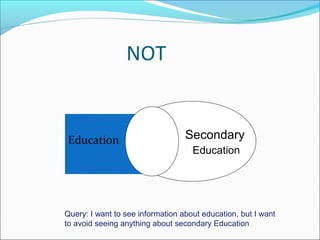
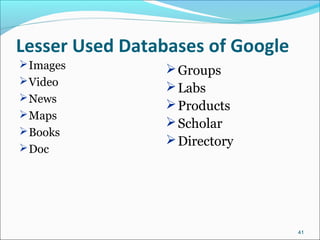
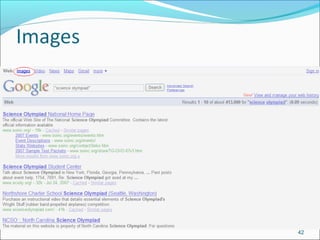
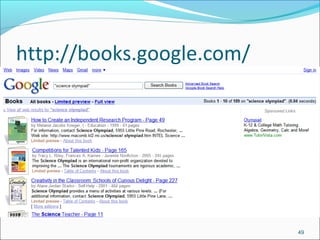
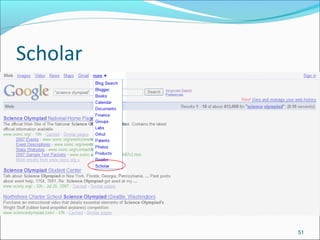
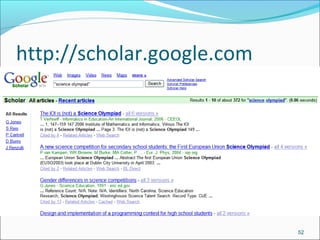
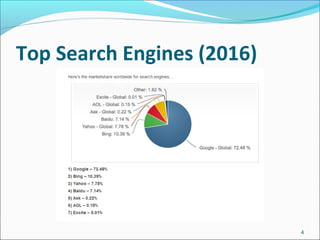
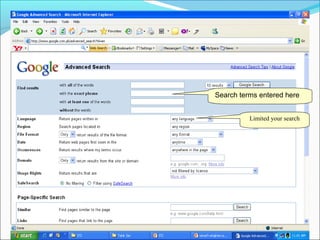
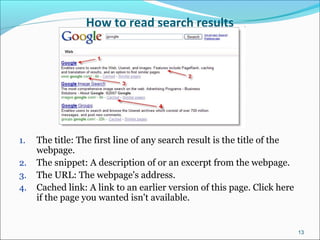
Google is a search engine that indexes webpages and content on the internet. It allows users to search for keywords and returns relevant results from its index in less than a second. The document discusses various search engine concepts like how they work, different search features available on Google like boolean operators, phrase searching and file type limiting. It also introduces some other Google products and databases like Images, News, Books, Scholar etc. and how they can be used to find images, videos, books and scholarly articles on the topics searched.






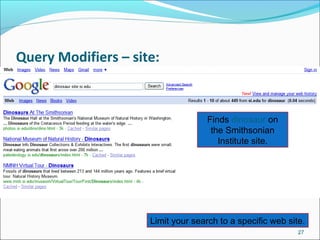
![Google: Advance Search Features
Phrase Search [ “ ” ]: always use quotations to search a
phrase
Example: “Digital Library”
Hyphen [ -]: always hyphenate a word that is sometimes
hyphenated
Example: front-line searches front-line, frontline, and
front line
Synonyms Search [~ ]: let google “think” of synonyms
Example: ~youth finds youth, juvenile, adolescent
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancesearchingtechniques-181128051849/85/Advance-searching-techniques-14-320.jpg)
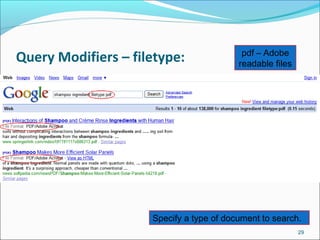
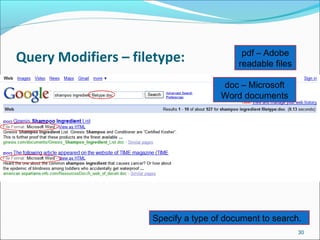
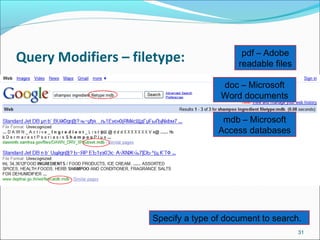
![More search features…
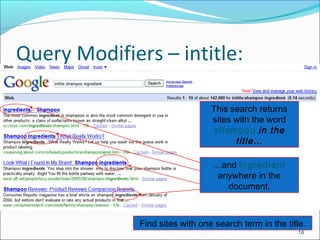
Intitle: Requires terms to appear in the title of the document
Example: intitle: “global warming”
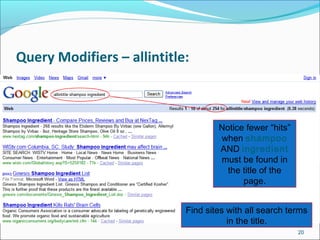
Allintitle: Requires all terms to appear in the title of the document
Example: Allintitle: traditional knowledge intellectual property
pacific
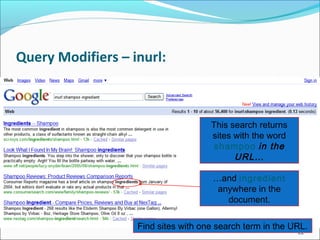
Inurl: requires terms to be in the url
Example: Inurl: ICP “Central Library” will find all references to Central Library
on websites with ICP in the url.
Allinurl: Requires All terms to appear in the URL of the document.
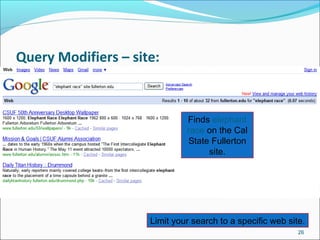
Domain Search [Site:] used to search within a particular Site
Example: Site:icp.edu.pk “Central Library”
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancesearchingtechniques-181128051849/85/Advance-searching-techniques-15-320.jpg)