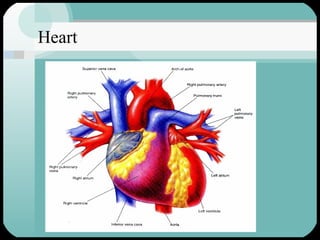
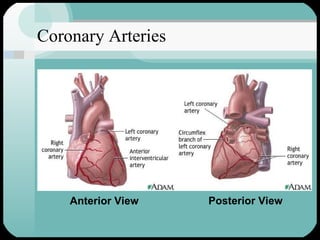
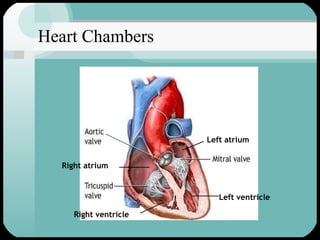
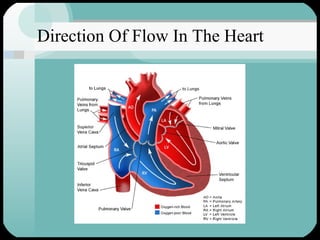
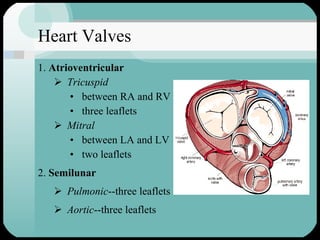
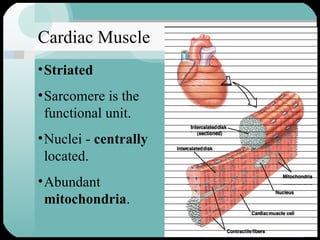
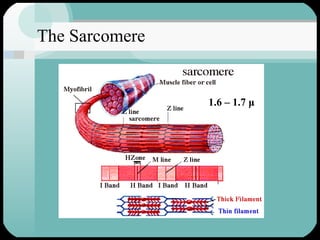
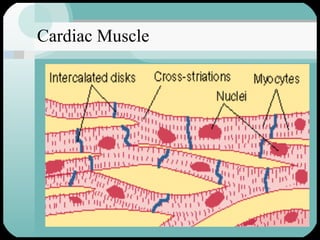
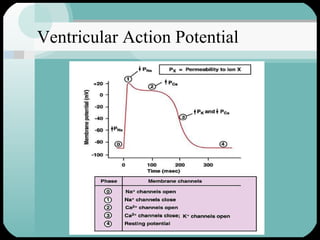
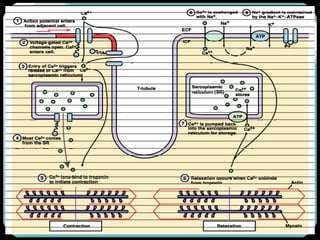
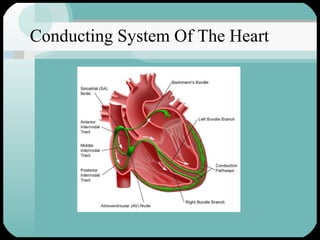
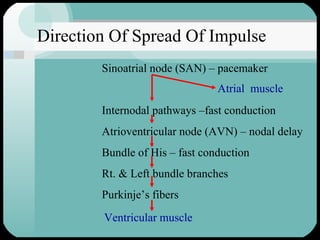
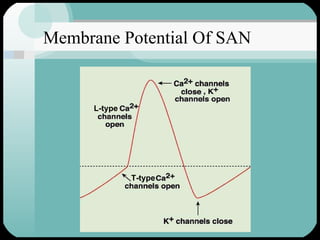
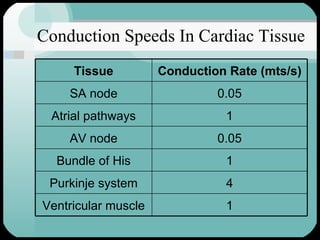
The document discusses the structure and function of the cardiac muscle and heart. It describes the heart chambers, valves, and blood flow through the heart. It explains that the heart pumps blood through contraction and relaxation in a cardiac cycle. It details the conducting system of the heart which generates and spreads the electrical impulse for heart contraction. This includes the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. It notes that cardiac muscle cells are striated like skeletal muscle but have specialized ion channels and gap junctions allowing rapid impulse transmission.