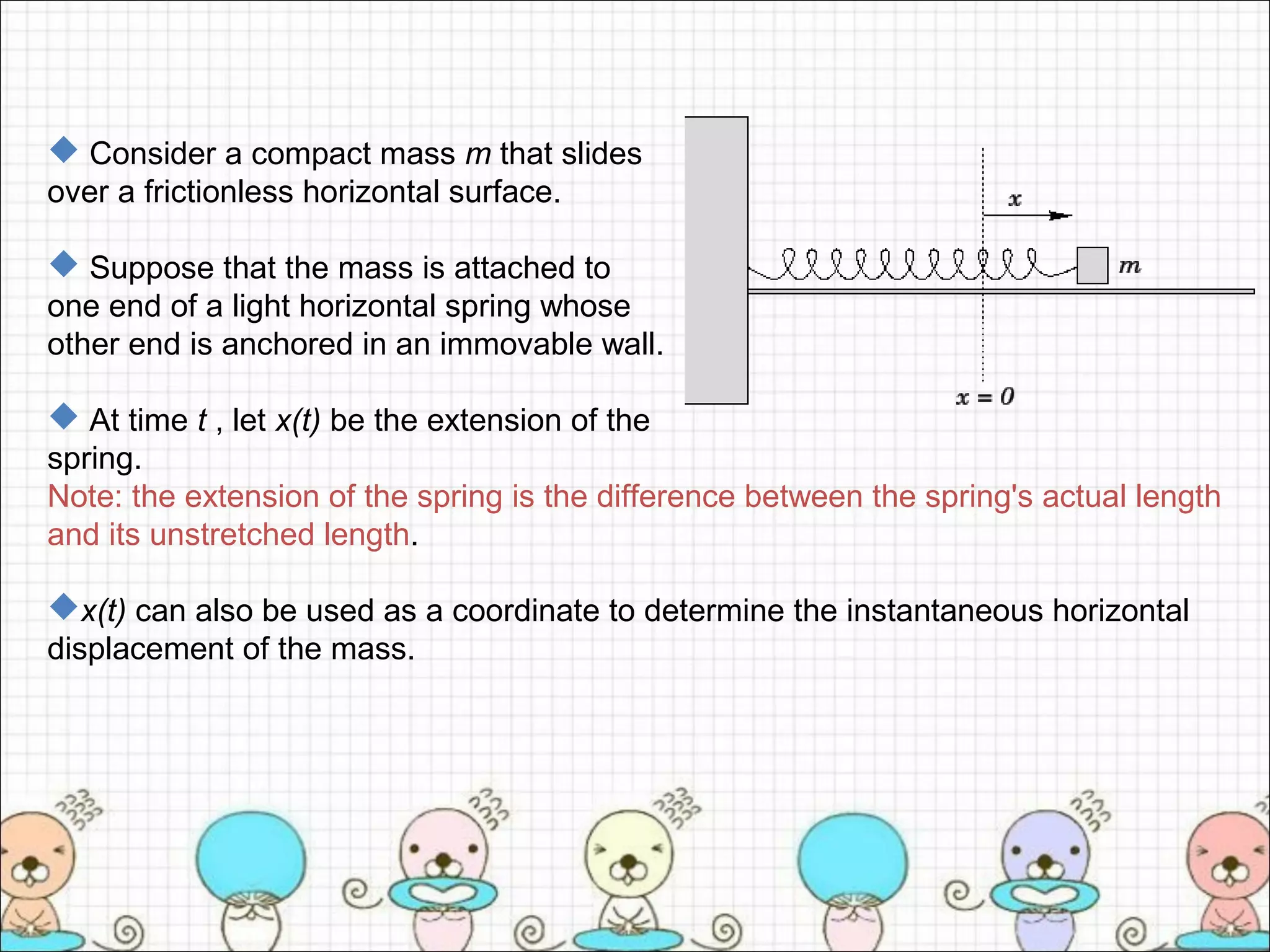
- A mass m is attached to one end of a horizontal spring, while the other end is anchored to a wall. The extension x(t) of the spring from its unstretched length determines the horizontal displacement of the mass.
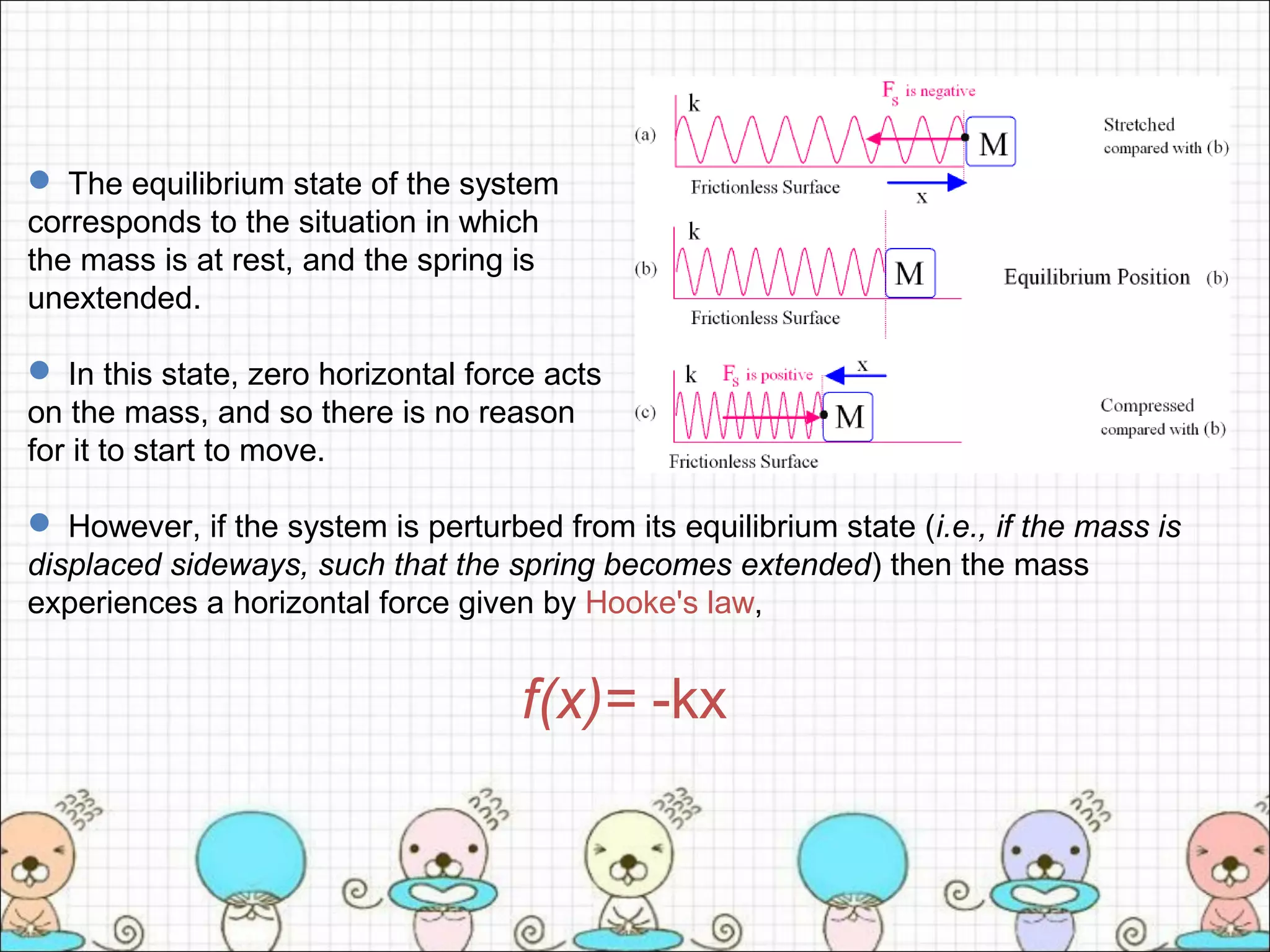
- When undisturbed, the mass is at rest and the spring is unextended. But if displaced from this equilibrium, the spring exerts a restoring force f(x) = -kx on the mass according to Hooke's law, where k is the spring constant.
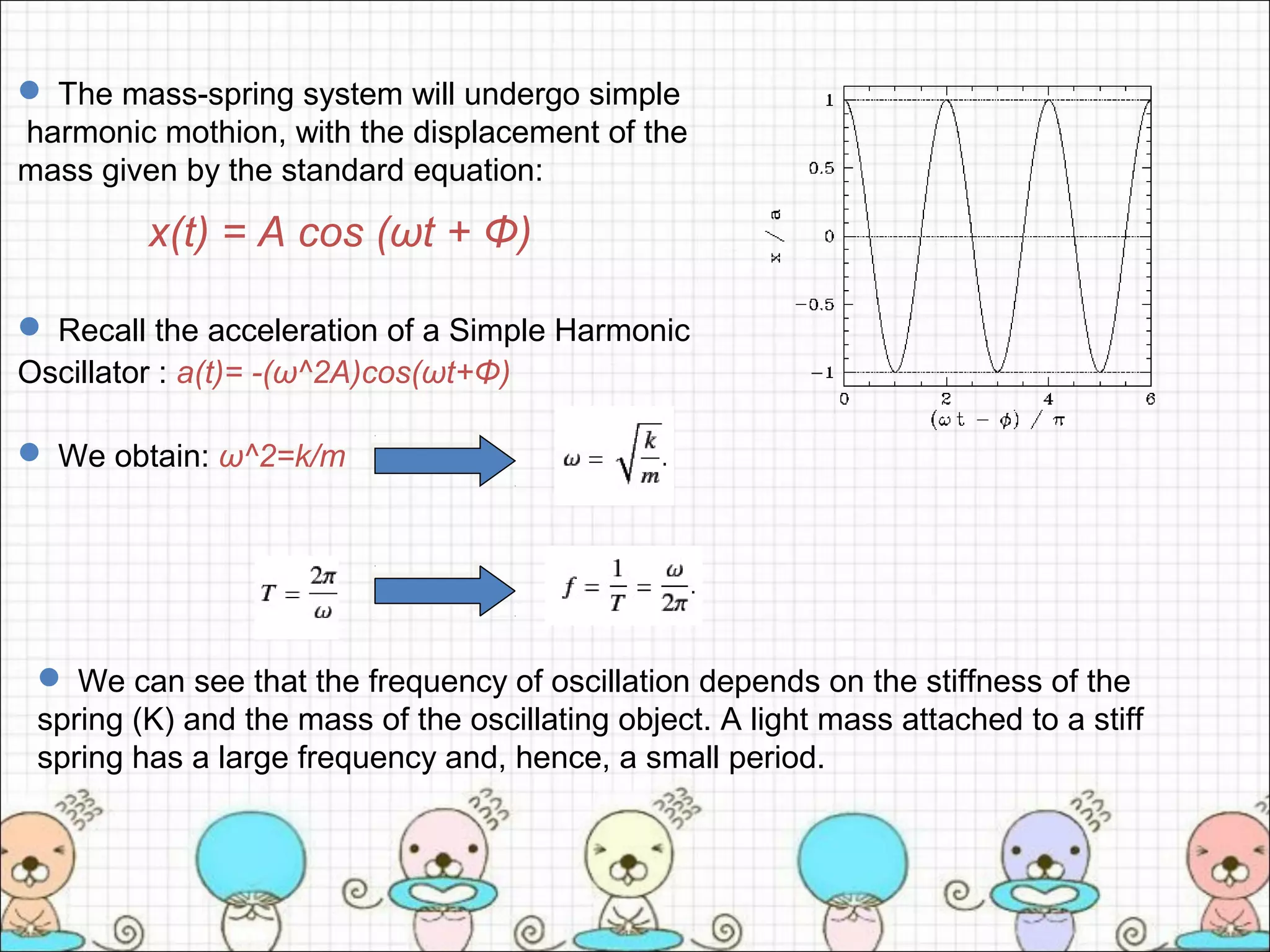
- Using Newton's second law, F=ma, this results in the mass undergoing simple harmonic motion described by the equation x(t) = A cos(ωt + Φ), where the frequency