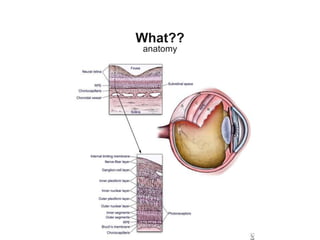
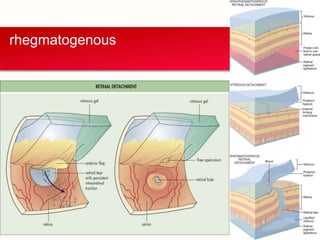
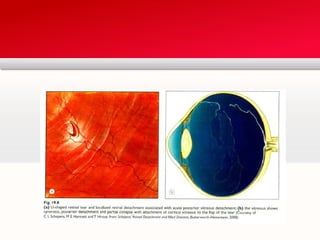
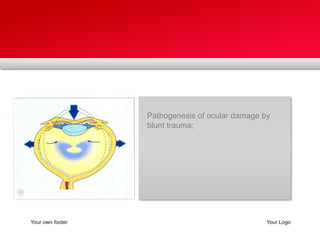
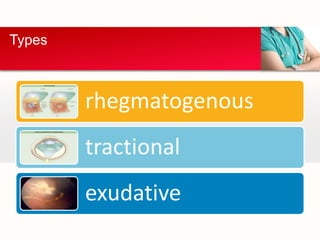
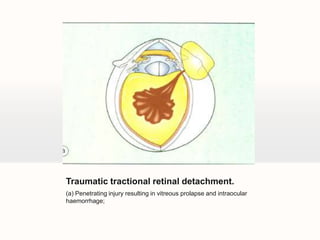
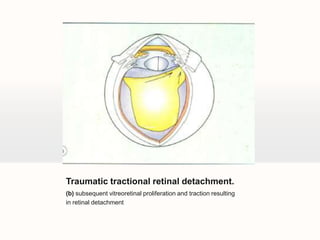
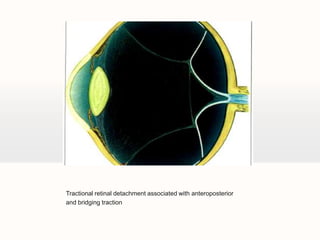
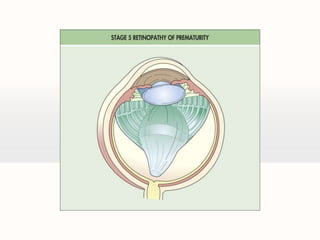
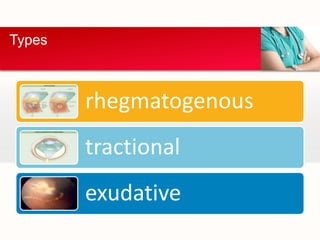
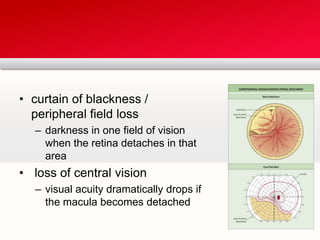
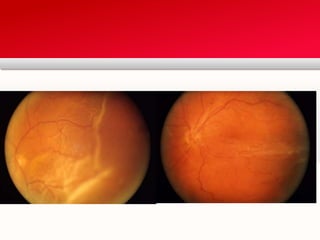
Retinal detachment can occur when there is a separation between the neurosensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium. The most common type is rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, which is caused by a tear or hole in the neurosensory retina that allows fluid to pass into the subretinal space. Tractional retinal detachment is caused by traction from membranes pulling on the retina, which can occur in conditions like diabetic retinopathy. Exudative retinal detachment is caused by fluid accumulation in the subretinal space due to damage to the retinal pigment epithelium. Symptoms of retinal detachment include flashes of light, floaters, curtain-like vision loss, and decreased vision.