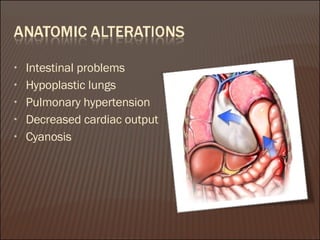
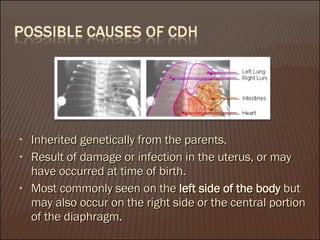
The document discusses congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH), including the risk factors, clinical presentation, radiologic findings, complications, and management. It notes that CDH is a birth defect involving an abnormal opening in the diaphragm, with the most common type being a Bochdalek hernia on the left side. Signs include breathing difficulties and abdominal abnormalities. Advances have allowed fetal treatments to be performed while still in the uterus.