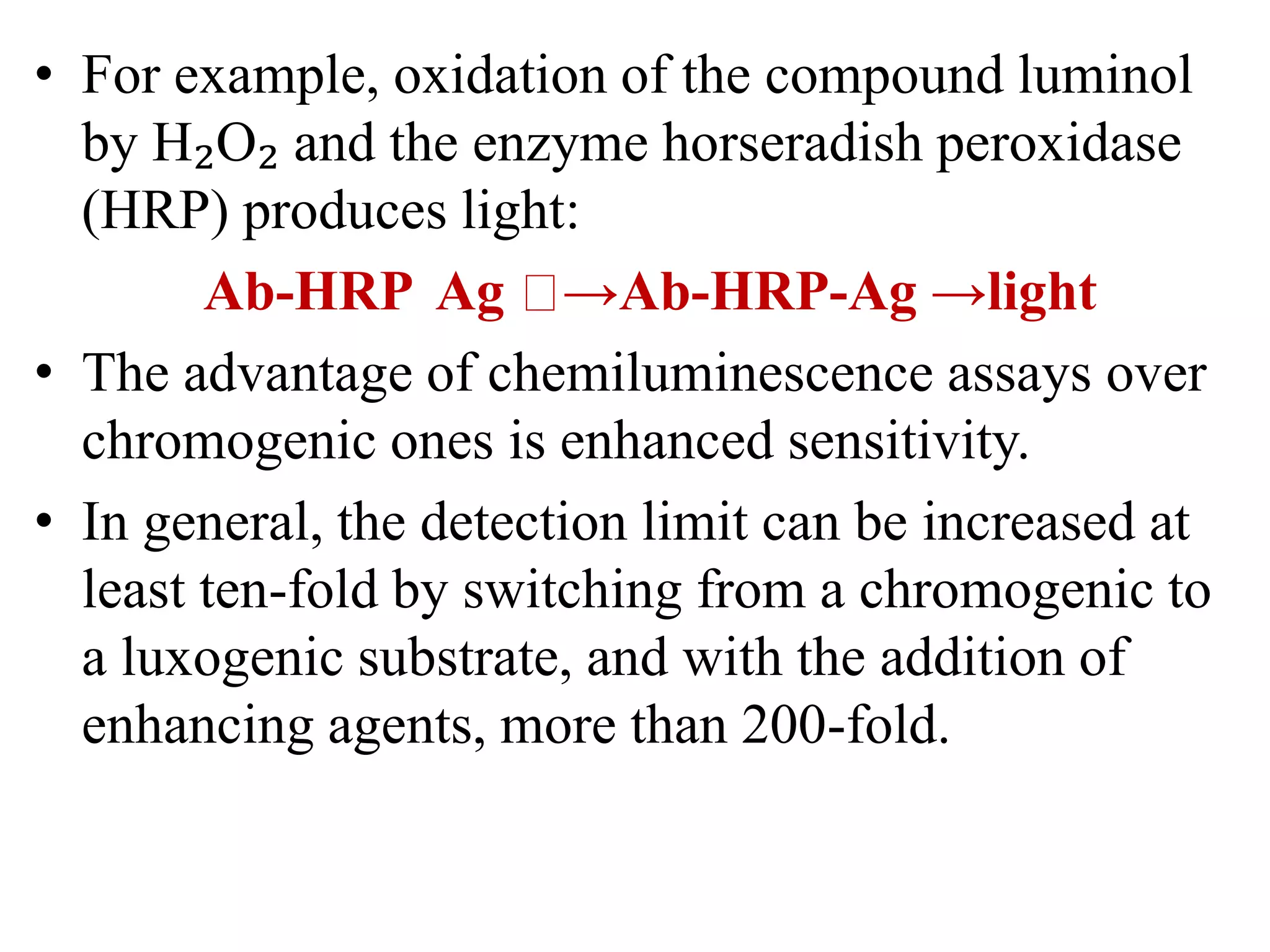
ELISA is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that detects the presence of antigens or antibodies. It uses an enzyme to detect the binding of an antigen to its antibody, which causes a color change in a substrate to indicate a positive result. There are several variants of ELISA including indirect, sandwich, competitive, and ELISPOT assays that can be used to qualitatively detect or quantitatively measure antigens or antibodies. ELISA is a common, sensitive, and cost-effective method used to detect diseases, allergens, and other biomarkers in serum.