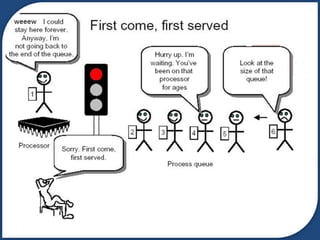
This document discusses the First Come First Served (FCFS) CPU scheduling algorithm. FCFS is a non-preemptive algorithm that allocates the CPU to the process that requests it first. It is simple to implement using a first-in first-out queue, but it is not optimal and can result in longer waiting times for shorter processes. While easy to understand, FCFS is not suitable for time-sharing systems due to its non-preemptive nature.