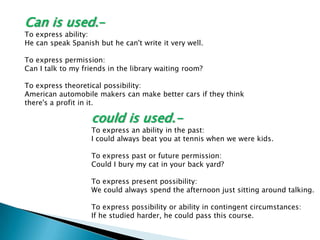
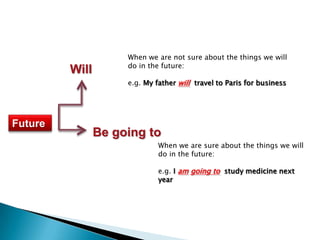
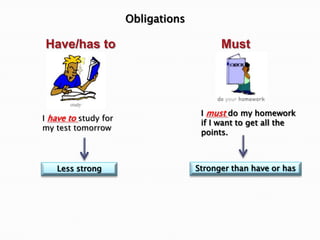
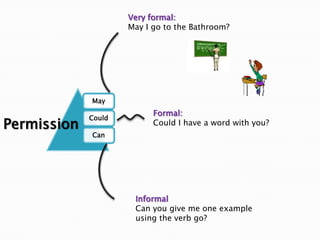
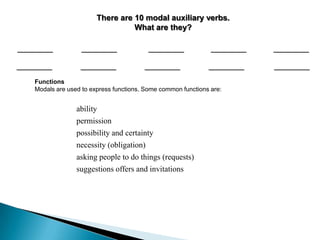
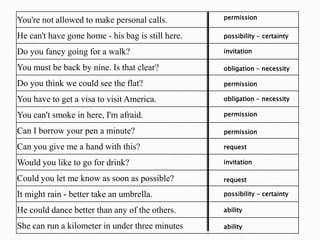
This document discusses English modal auxiliary verbs and their functions. It provides examples of 10 modal verbs - can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, have to/has to. It explains their uses such as expressing: ability, advice, intention, obligation, permission, possibility, prohibition, suggestion. For each modal, it gives examples of how they are used for different tenses and contexts. It also includes exercises matching modal verbs to their functions and examples.