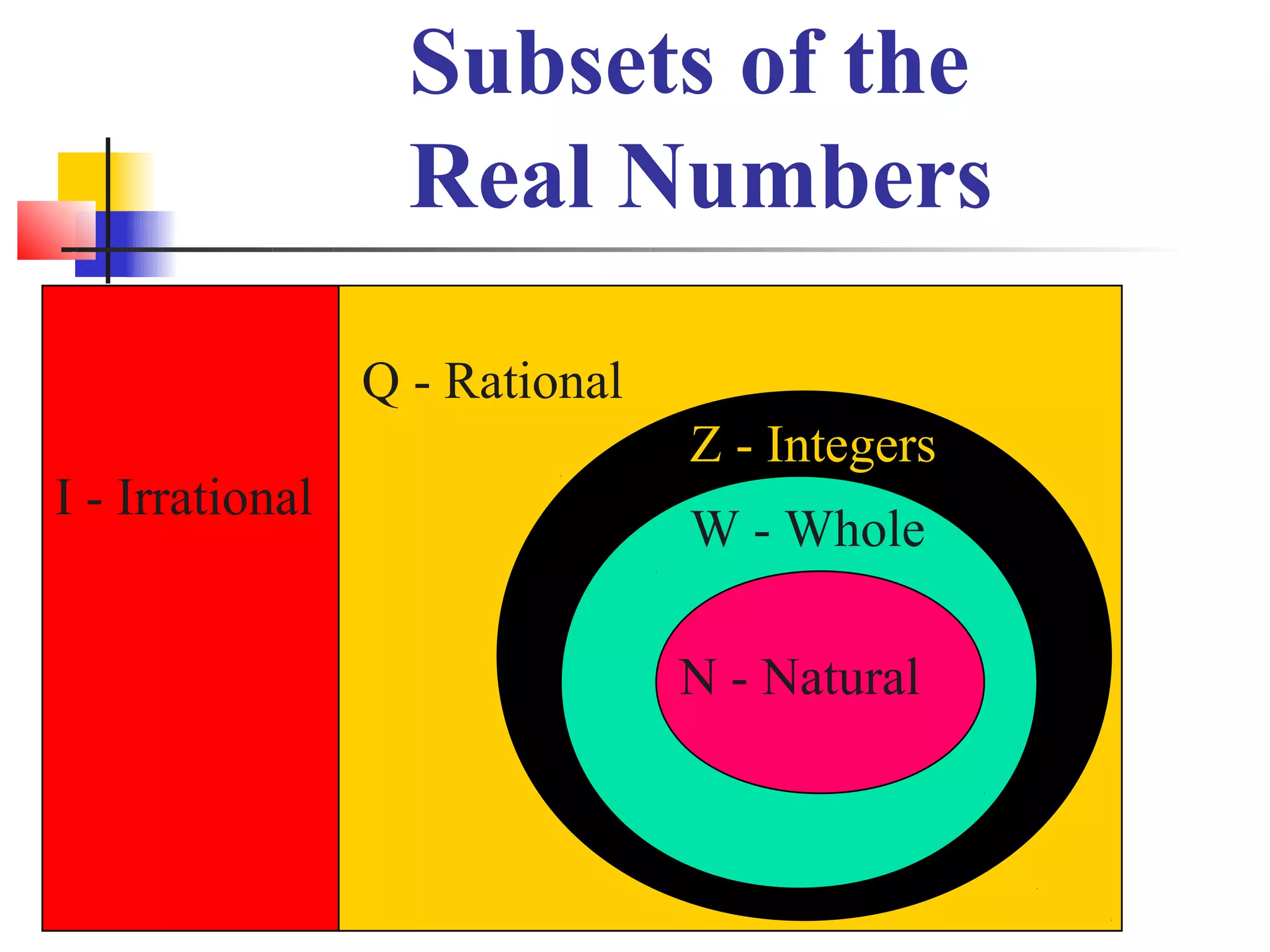
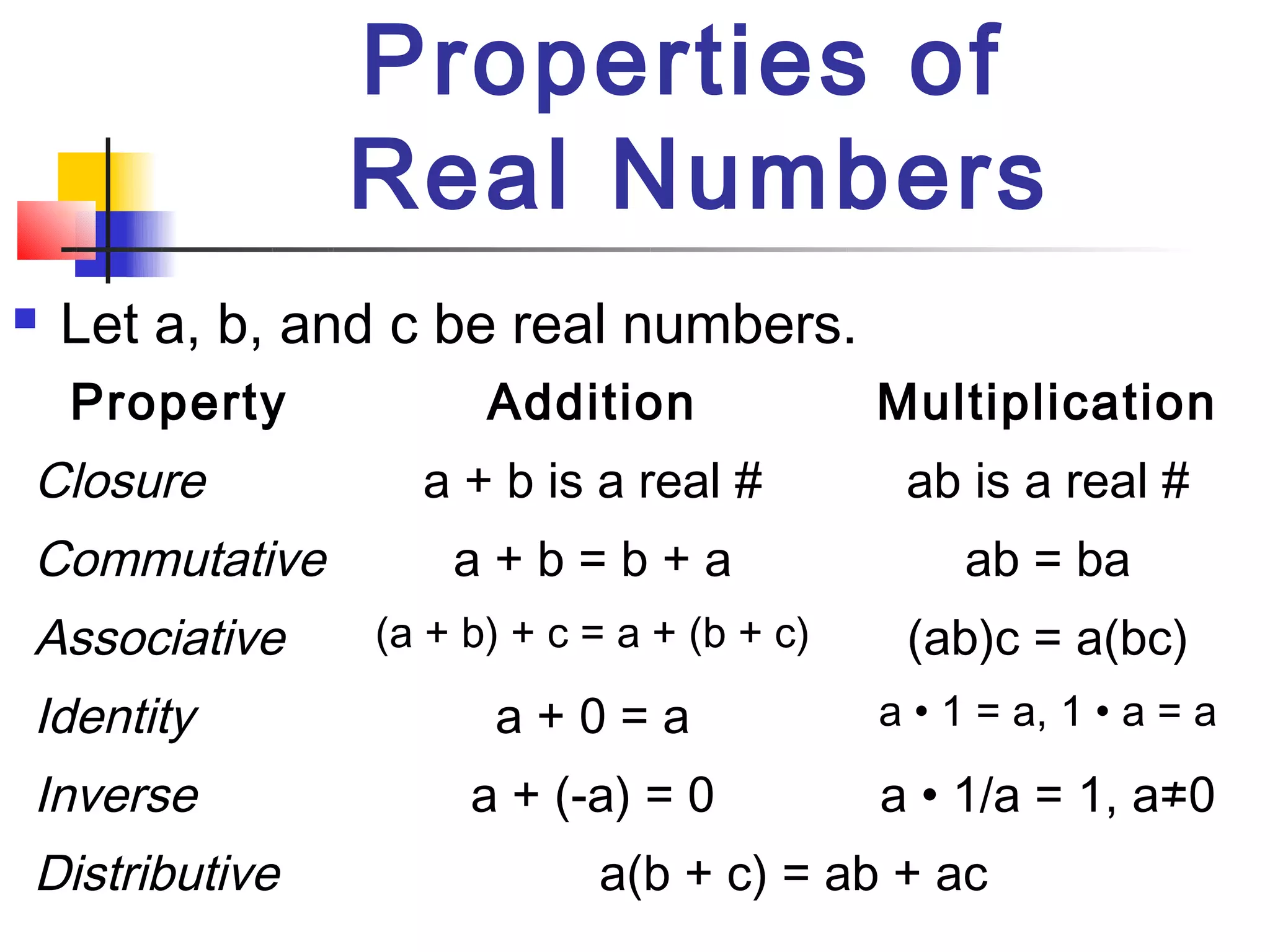
1. The document discusses real numbers and their properties, including subsets such as rational and irrational numbers.
2. Key topics covered include using a number line to graph and order real numbers, properties of number operations like closure and commutativity, and defining operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
3. Unit analysis is also introduced to check that units make sense when performing number operations for real-life applications.