The document discusses different types of numbers:
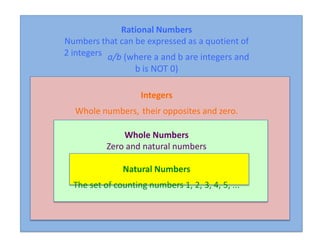
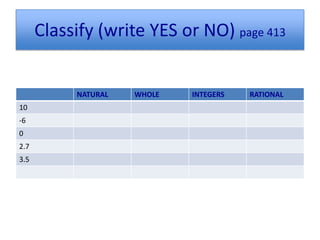
1) Natural numbers are whole numbers starting from 1. Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions or decimals.
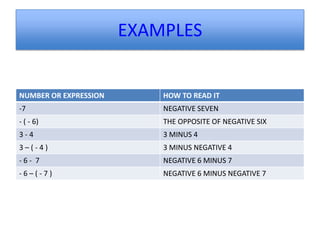
2) Integers include whole numbers and their opposites, as well as zero. They can be ordered and compared on a number line.
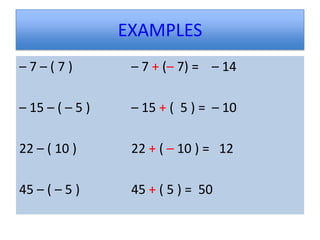
3) Rules for operating on integers include adding like signs and subtracting unlike signs, as well as products and quotients of the same or different signs being positive or negative.