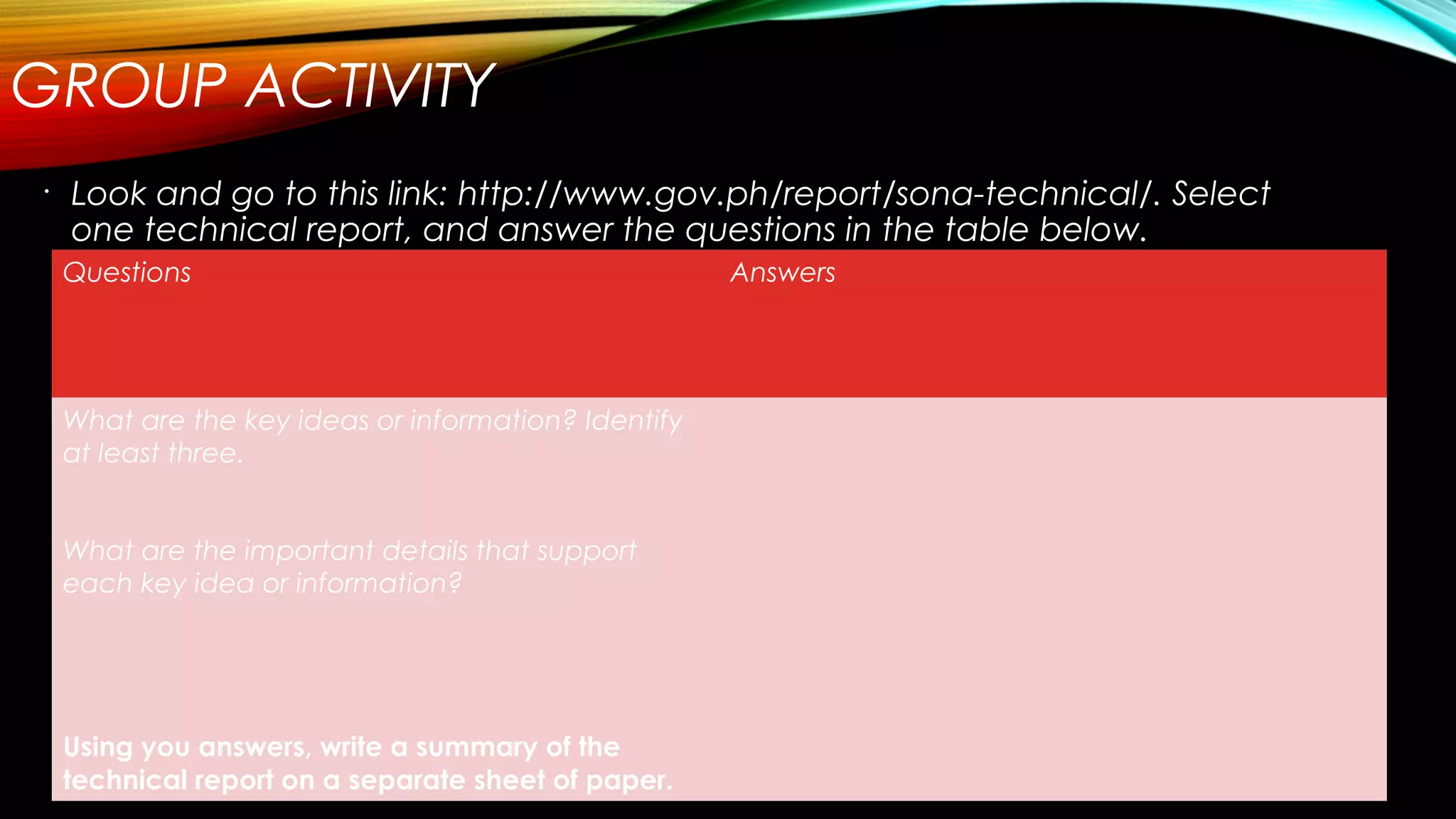
The document outlines the importance of summarizing as a critical reading skill, detailing effective strategies and guidelines for creating concise summaries. It emphasizes the need for understanding the text, identifying key ideas, and presenting them clearly while avoiding redundancy and personal comments. Additionally, it provides formats for summarizing and includes exercises to practice summarization skills.








![8. Ensure that do not copy a single sentence from
the original text.
9.Refrain from adding comments about the text.
Stick to the ideas it presents.
10.Edit the draft of your summary by eliminating
redundant ideas.
11.Compare your output with the original text to
ensure accuracy.
12.Record the details of the original source
(author’s name/s, date of publication, title,
publisher, place of publishing, and URL [if online]). It](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofsummarizing-171212094434/75/Basics-of-Summarizing-9-2048.jpg)