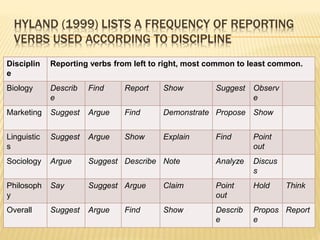
This document provides guidance on summarizing texts. It explains that a summary captures the essential ideas and key points while avoiding opinions, background knowledge, and personal information. The document outlines several guidelines for summarizing, including clarifying the purpose, understanding the text, identifying and underlining key ideas, writing ideas in bullet points, combining sentences into paragraphs, and ensuring accuracy by comparing to the original. It also discusses different formats for summaries such as including the idea before or after a citation and different heading styles that place the idea before the date or author. The document concludes by explaining the importance of using accurate reporting verbs when discussing another's work.