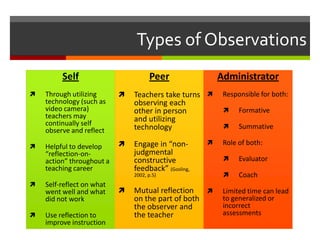
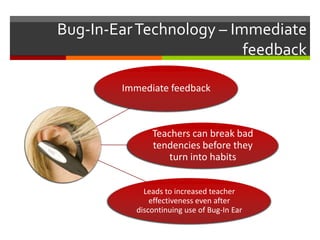
This document discusses various technologies that can be used to observe and provide feedback to teachers, including video cameras, bug-in-ear technology, Skype, and mobile devices. Video cameras allow for self-reflection and formative or summative evaluations by administrators, who can review footage to fully assess teachers. Bug-in-ear technology and Skype enable immediate feedback during lessons from supervisors observing remotely. Mobile devices let administrators digitally record observations and sync/share reports. These technologies aim to improve teacher reflection and supervision in more objective and timely ways compared to traditional post-lesson feedback alone.