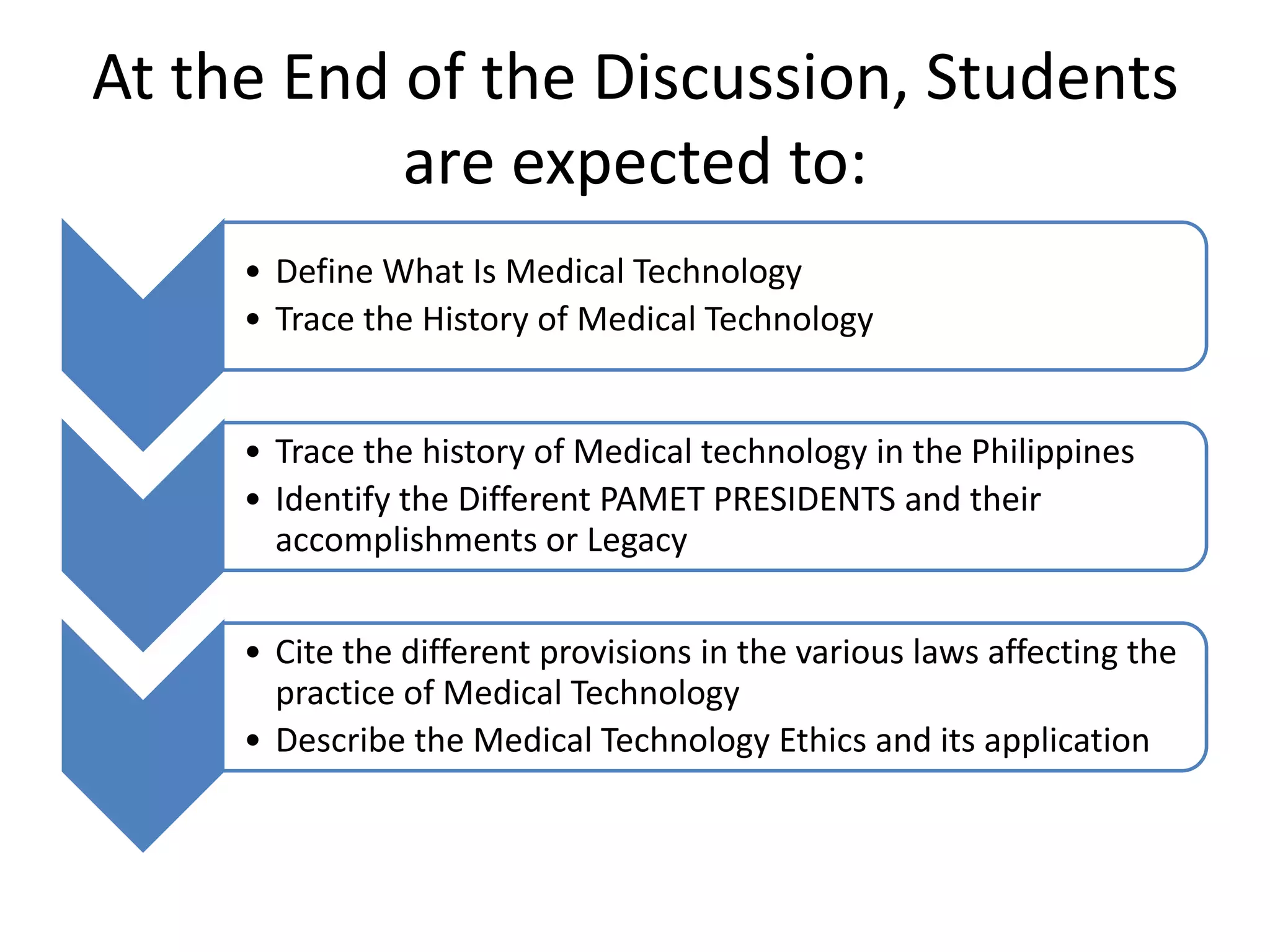
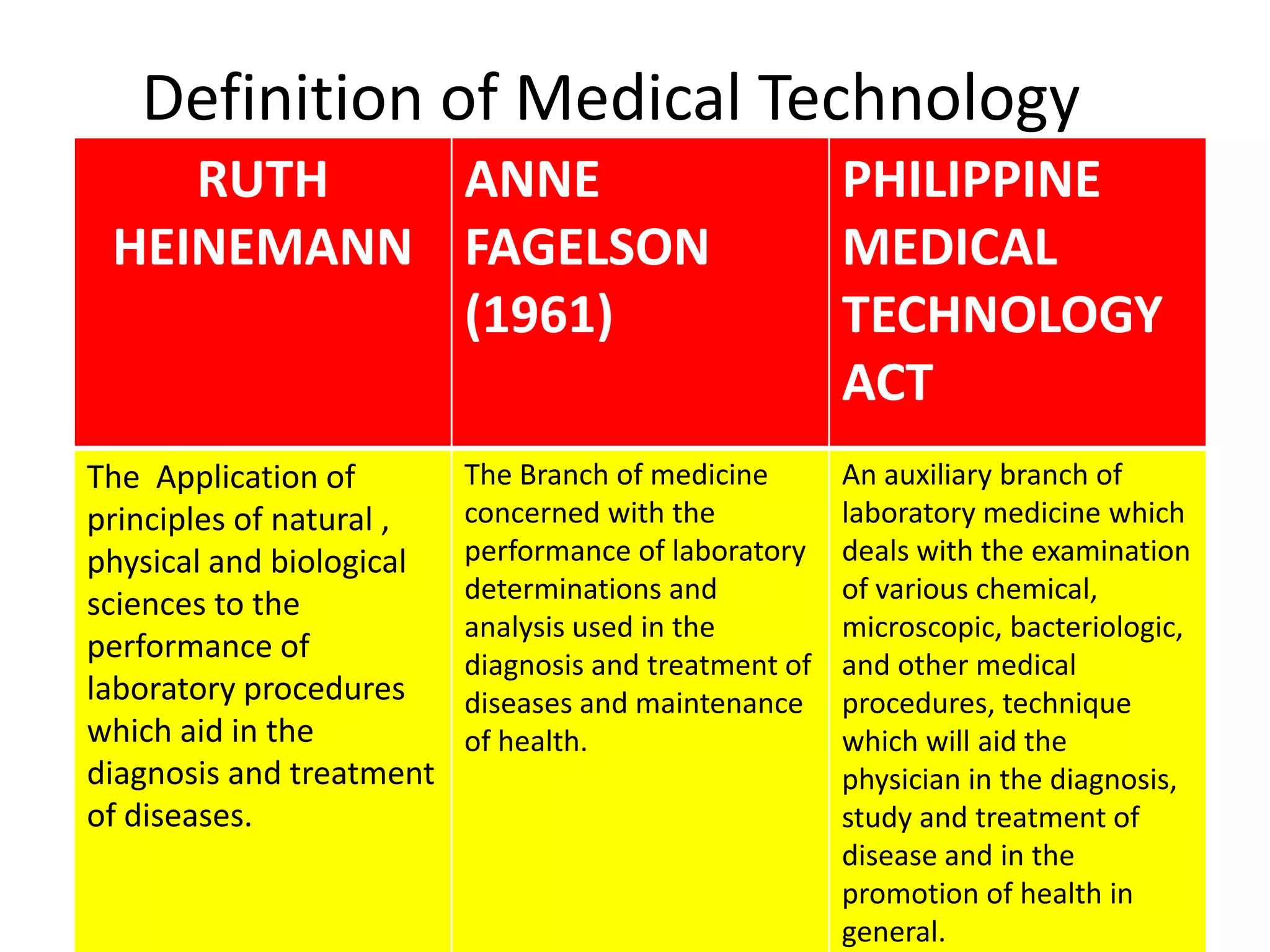
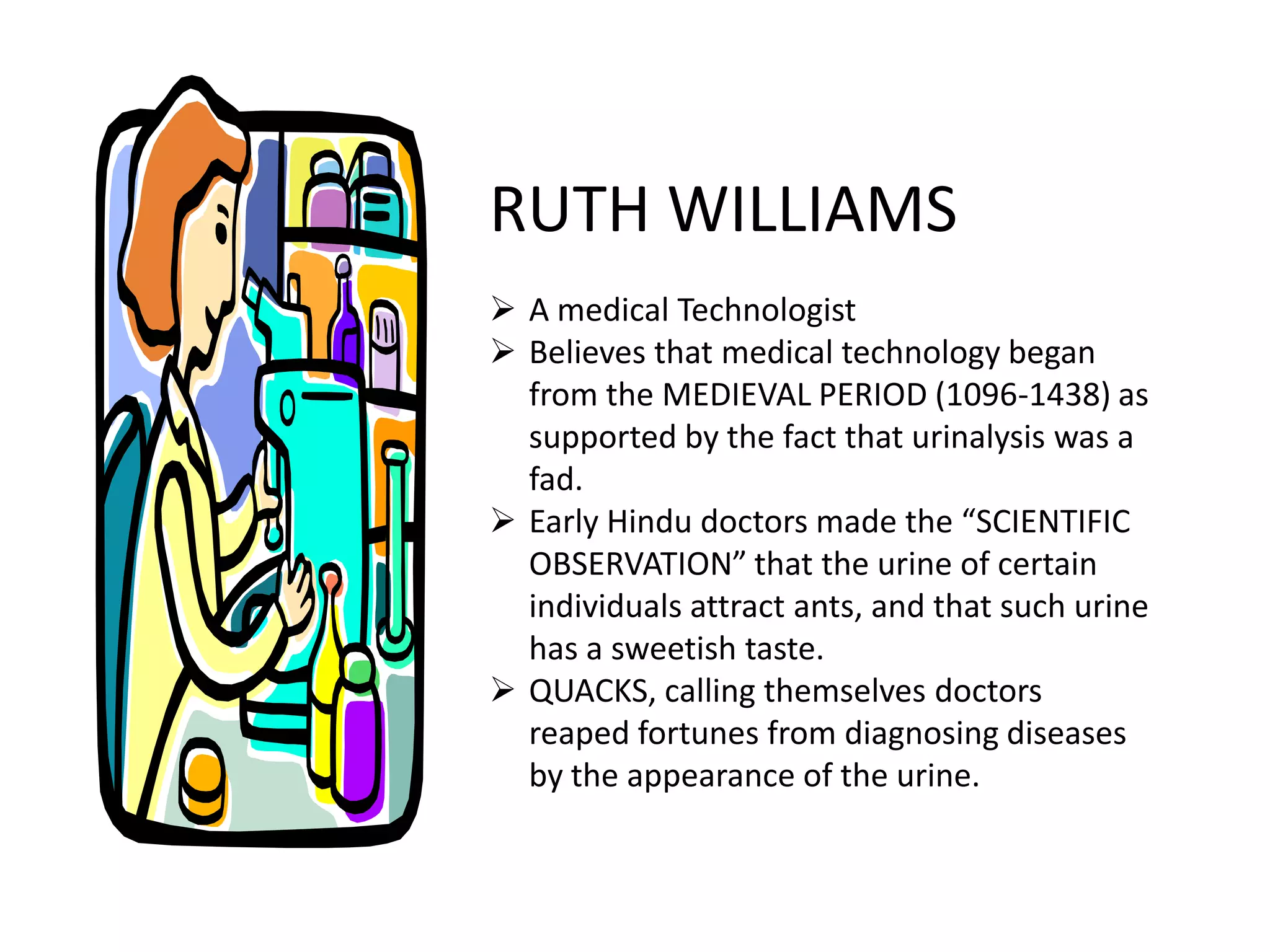
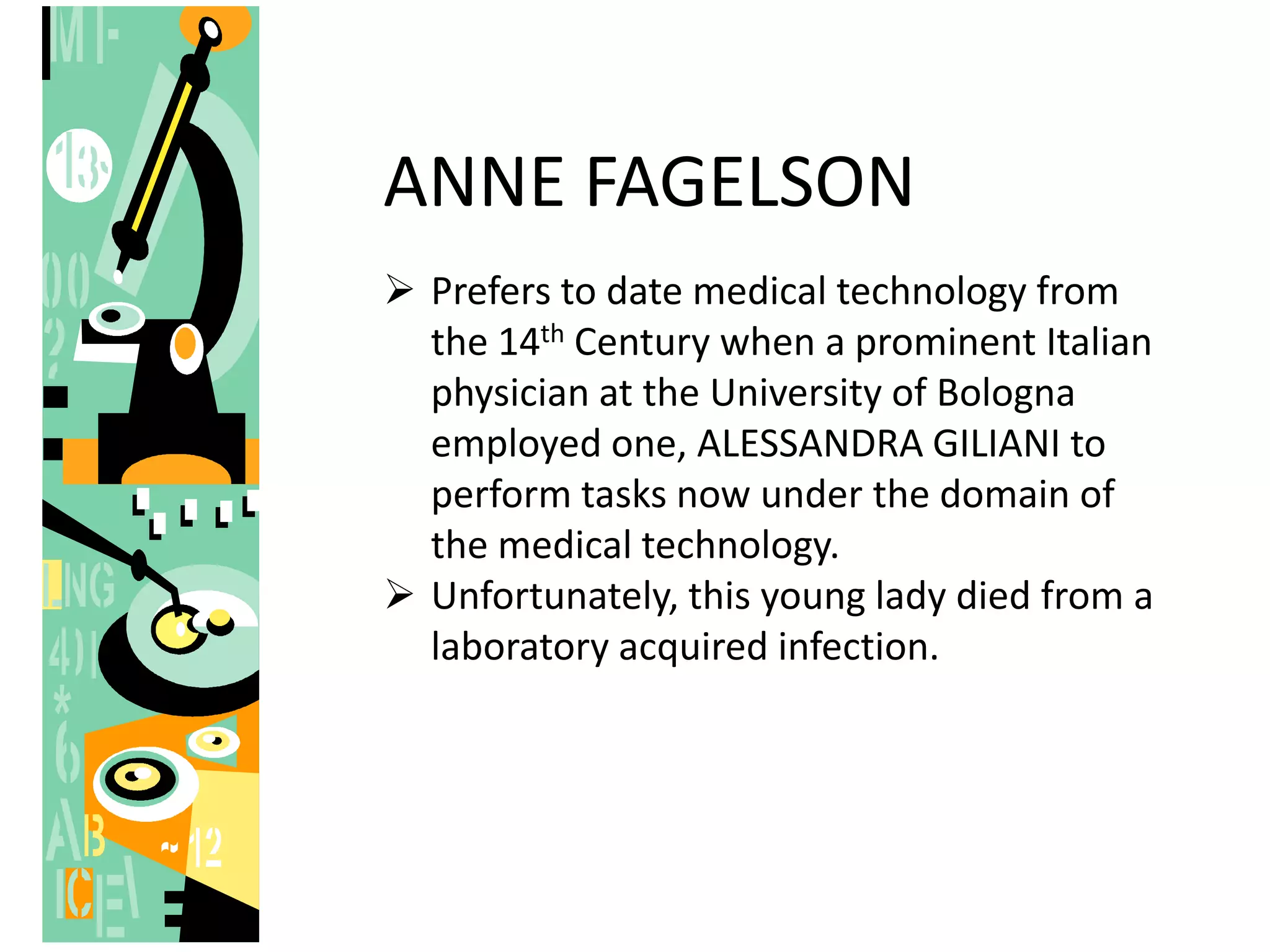
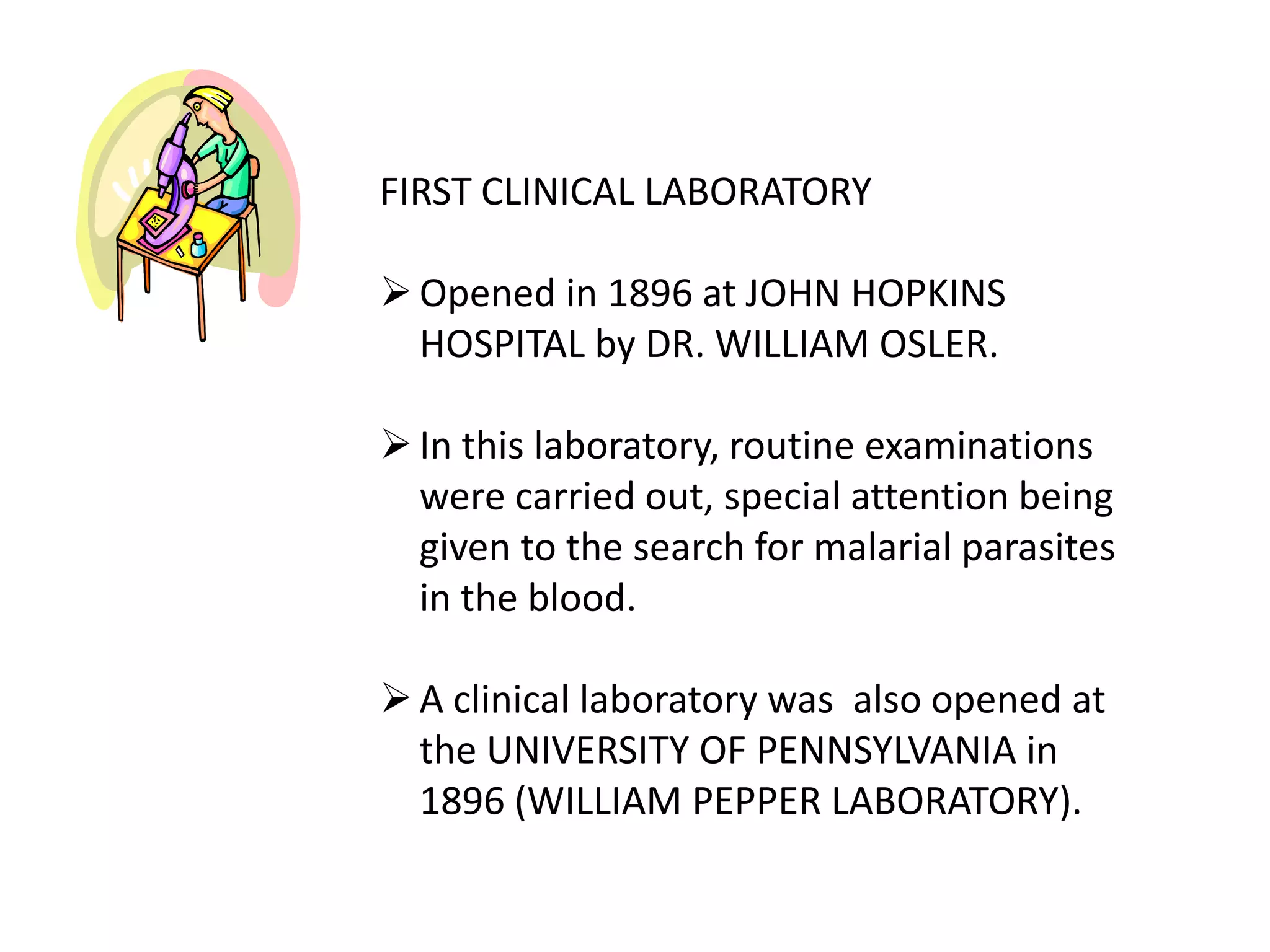
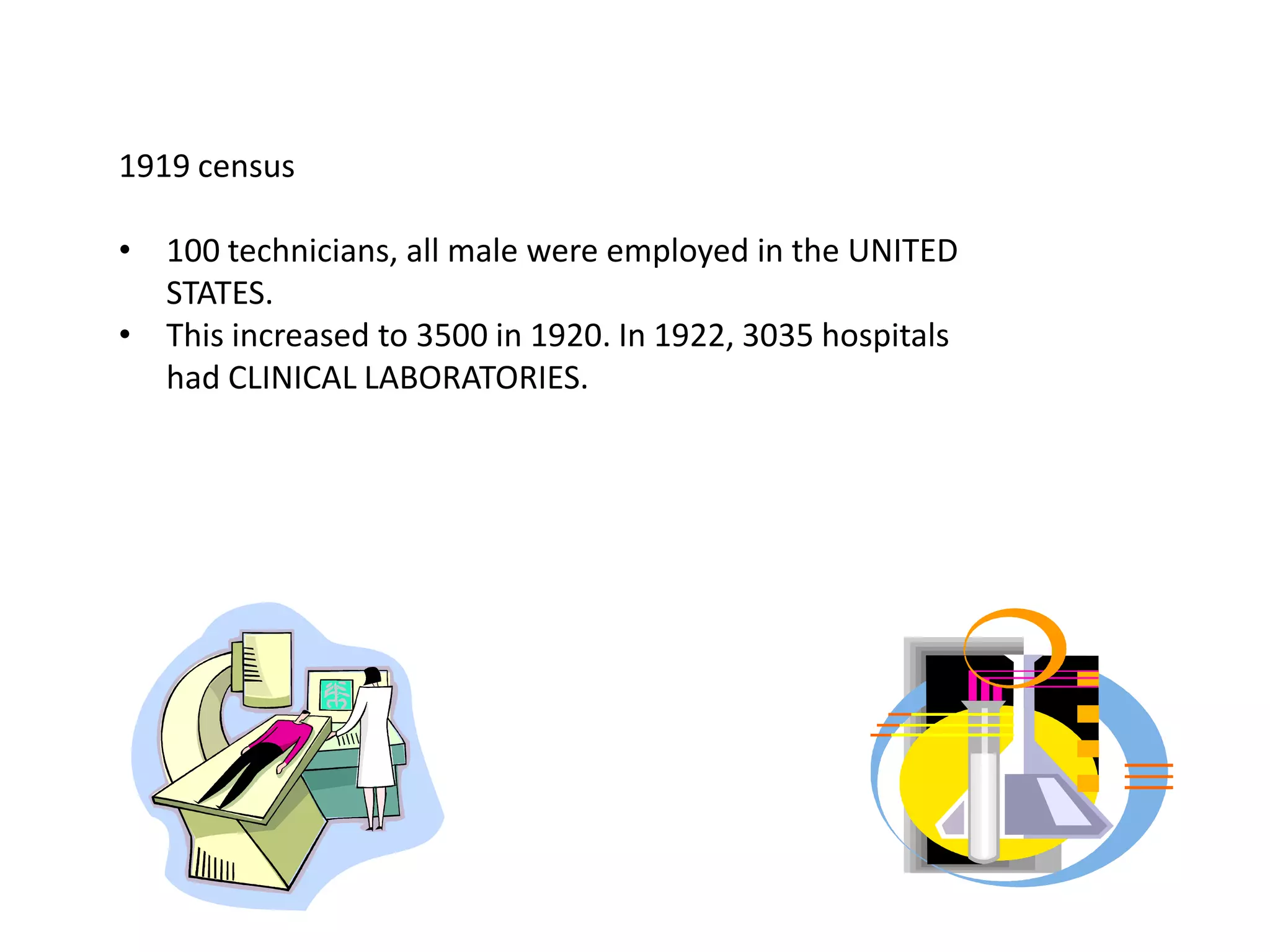
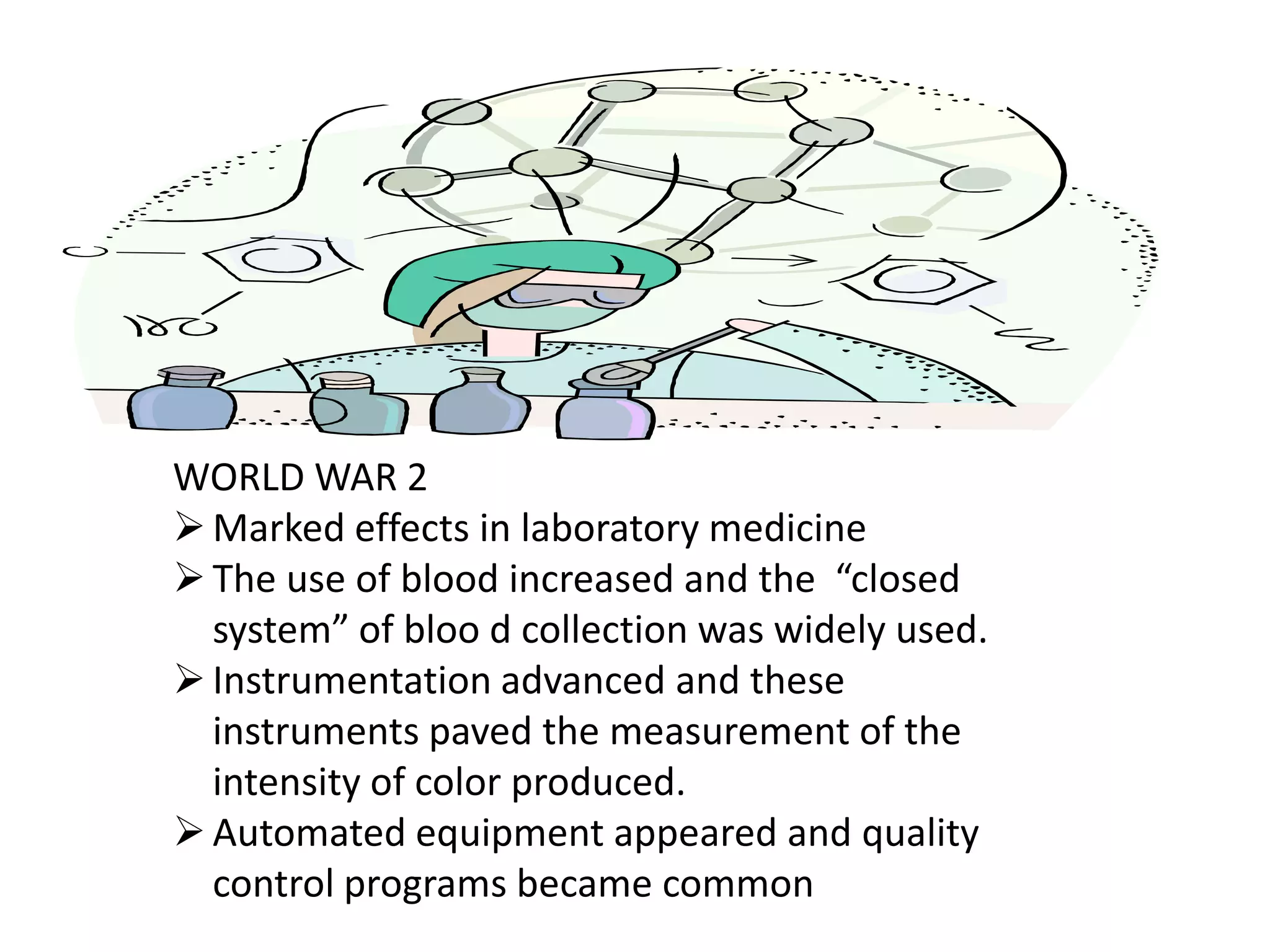
The history of medical technology began thousands of years ago with early observations and experiments, but the field grew rapidly in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Key developments included the invention of the microscope, which allowed early scientists like Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Malpighi to observe cells and pathogens. The first clinical laboratories opened in the 1890s at Johns Hopkins Hospital and the University of Pennsylvania. During World Wars I and II, demand increased for trained technicians. The practice of medical technology was introduced to the Philippines in 1944 and the first degree program began in 1957 at the University of Sto. Tomas. The profession continued to grow with more schools offering programs and opportunities for post-graduate study.