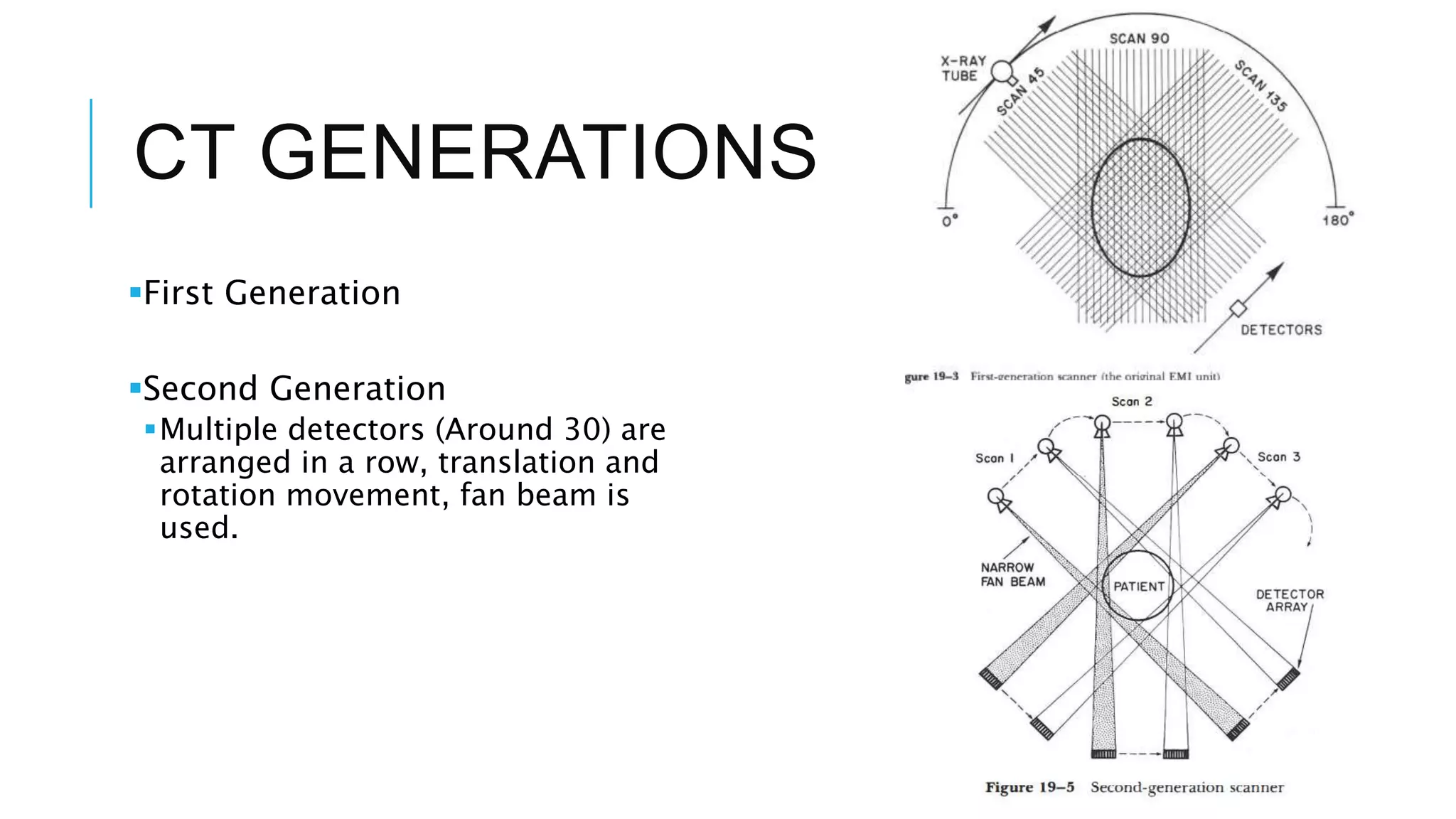
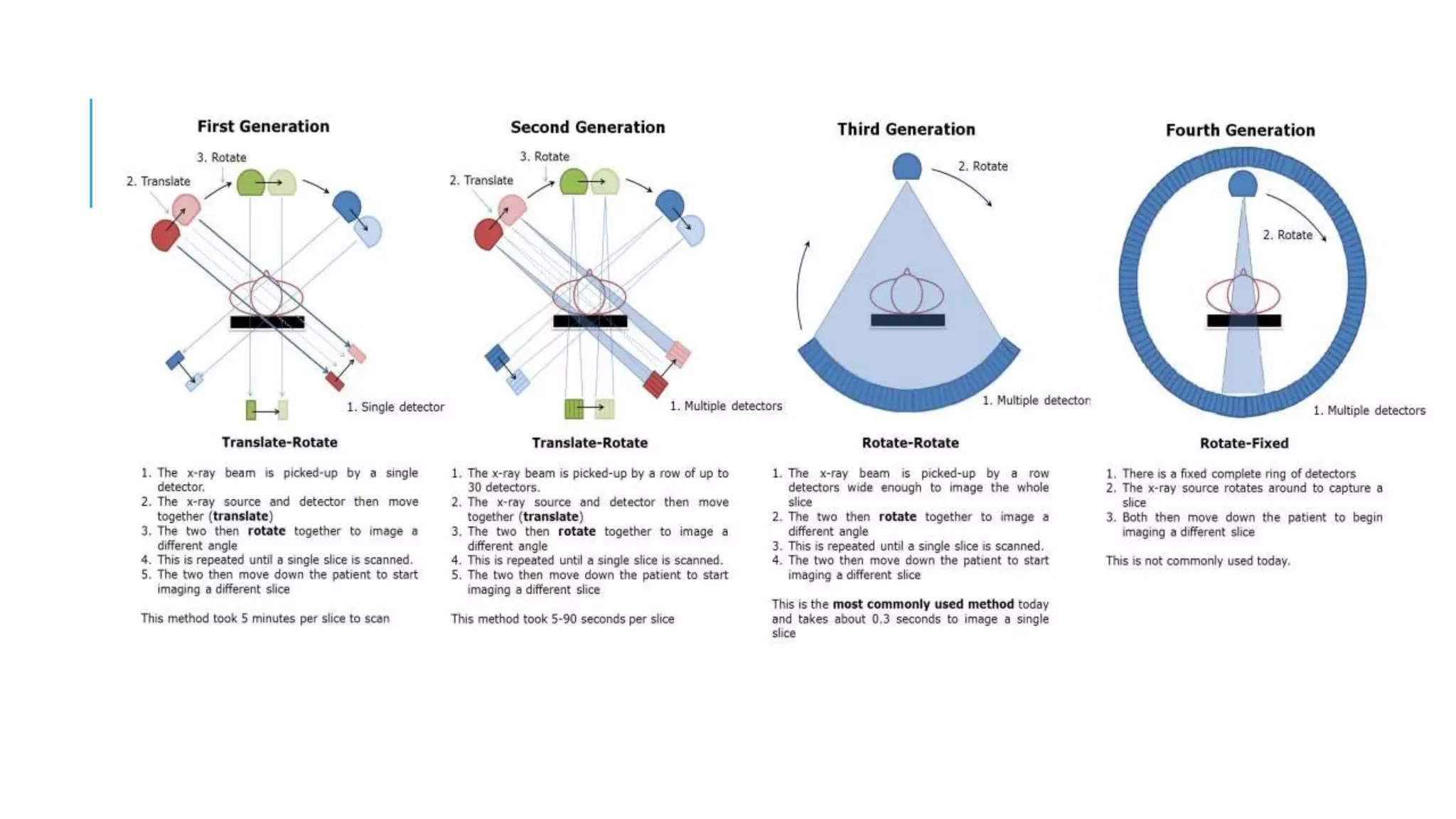
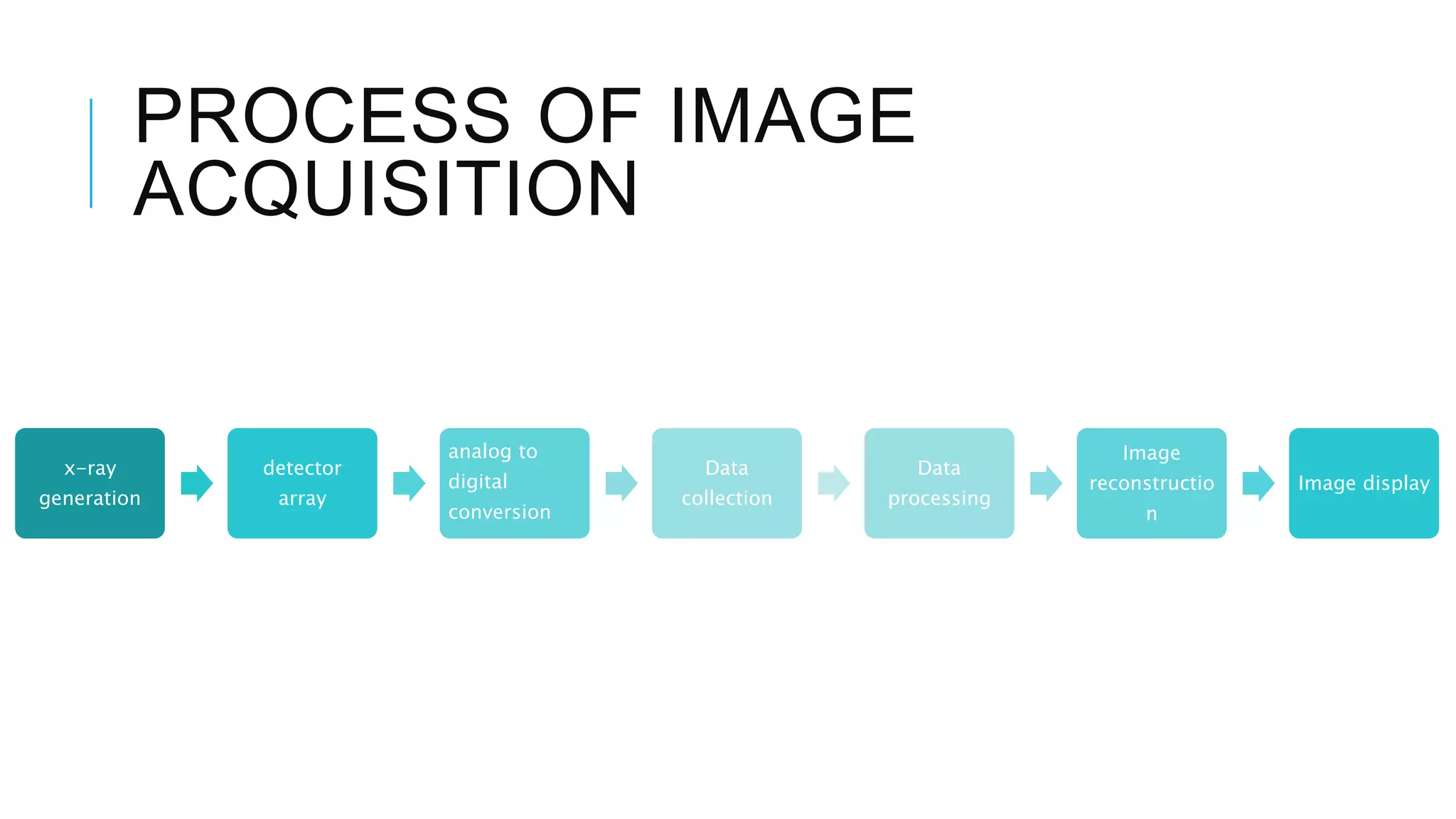
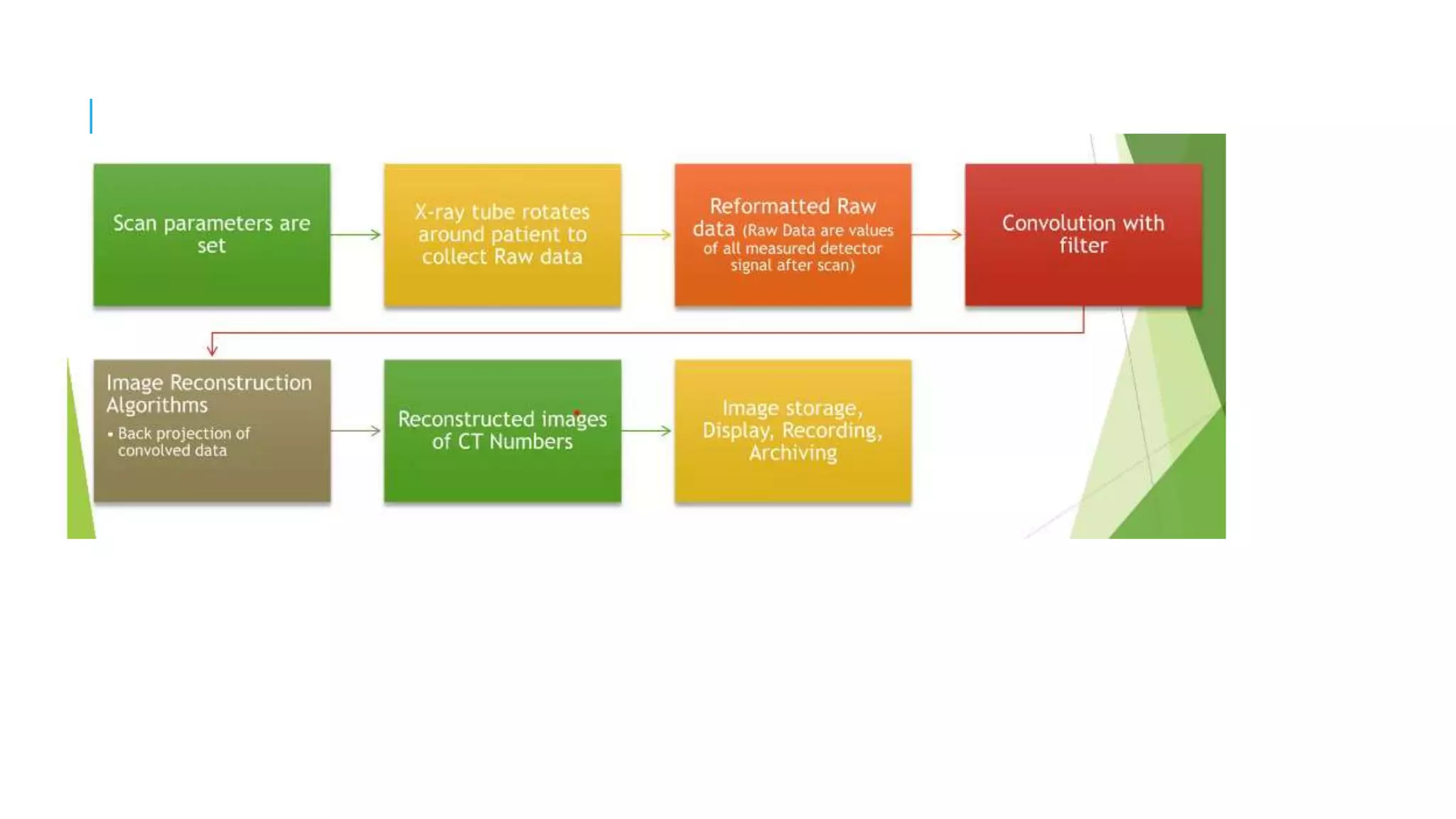
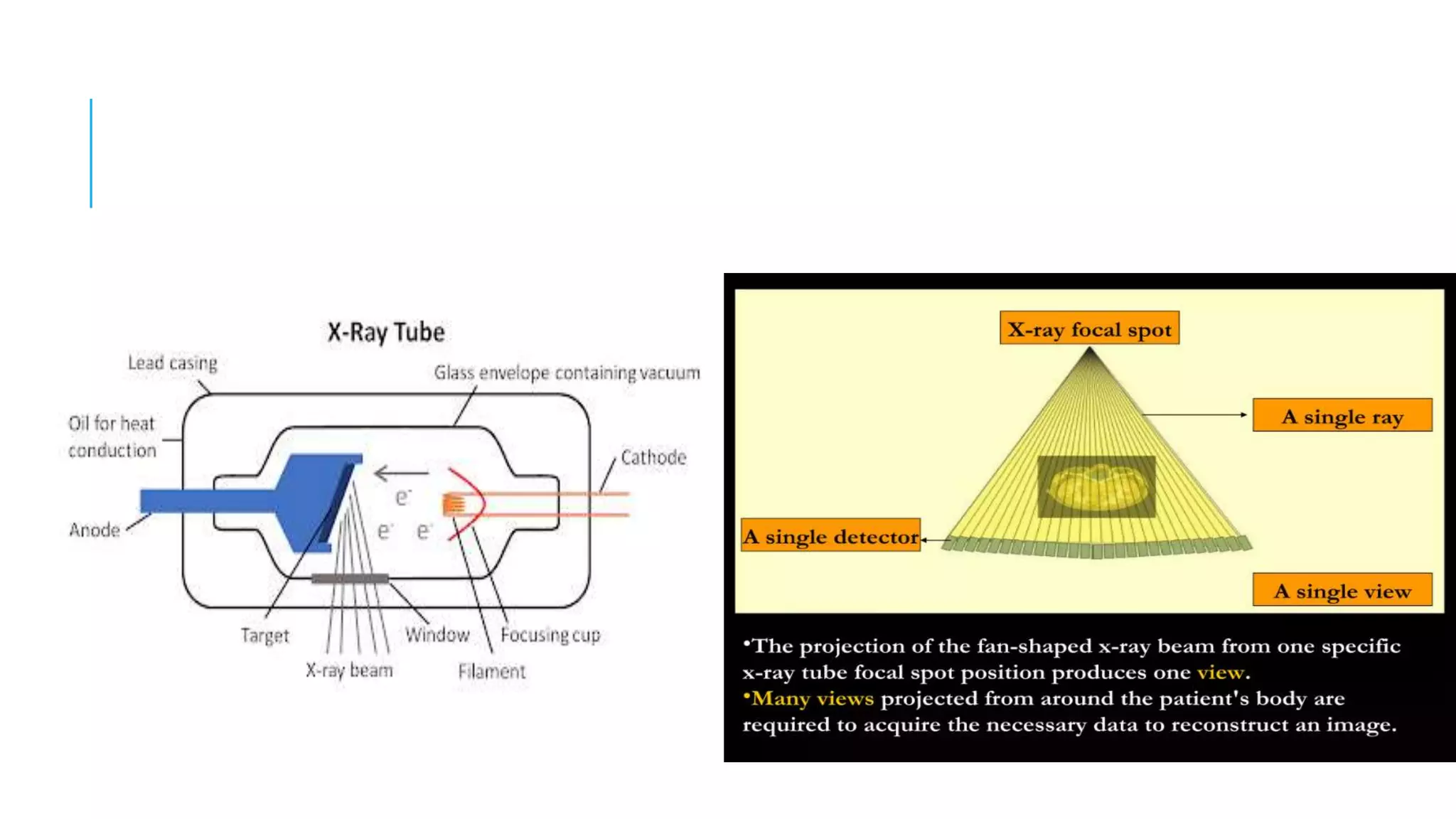
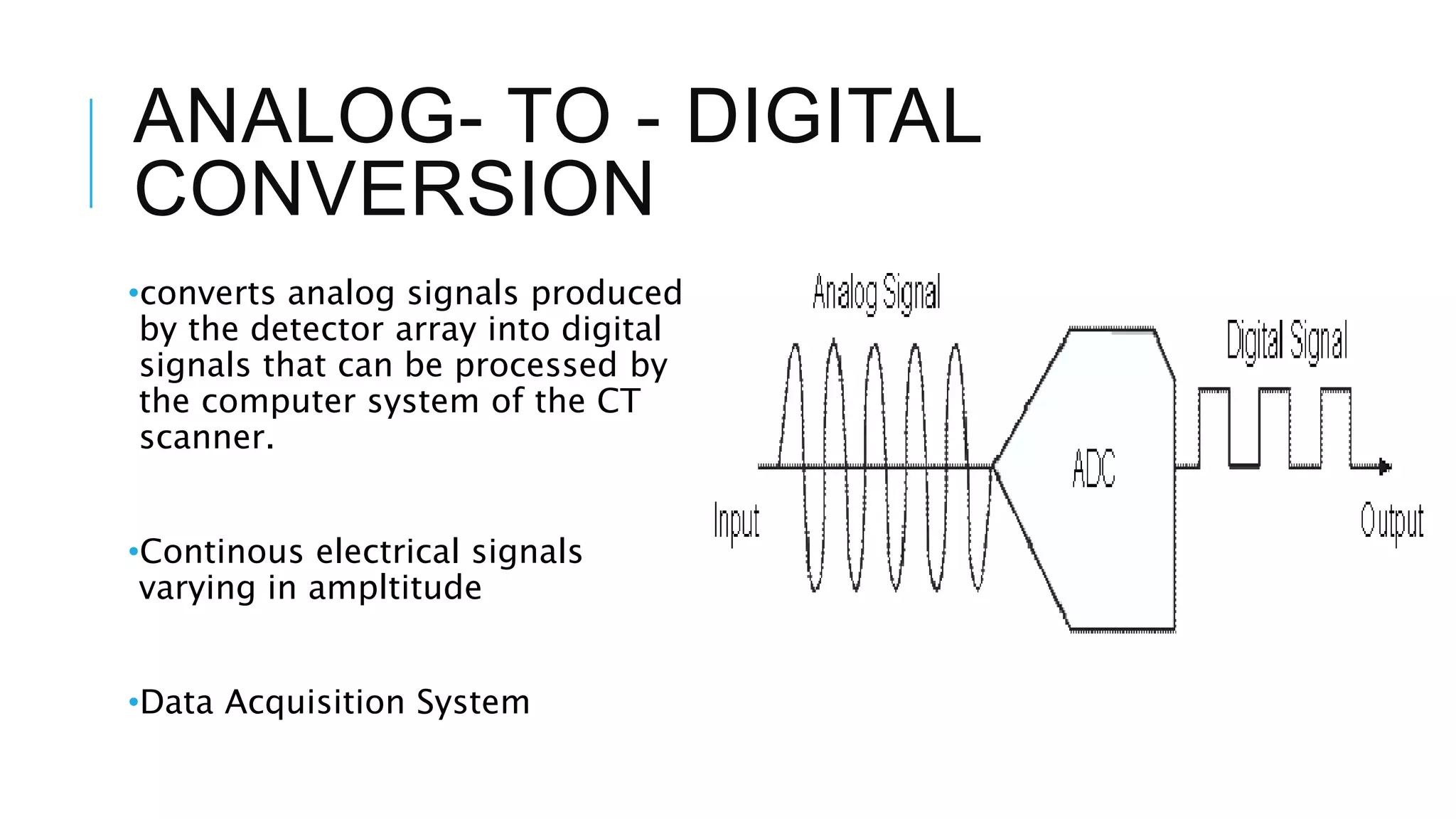
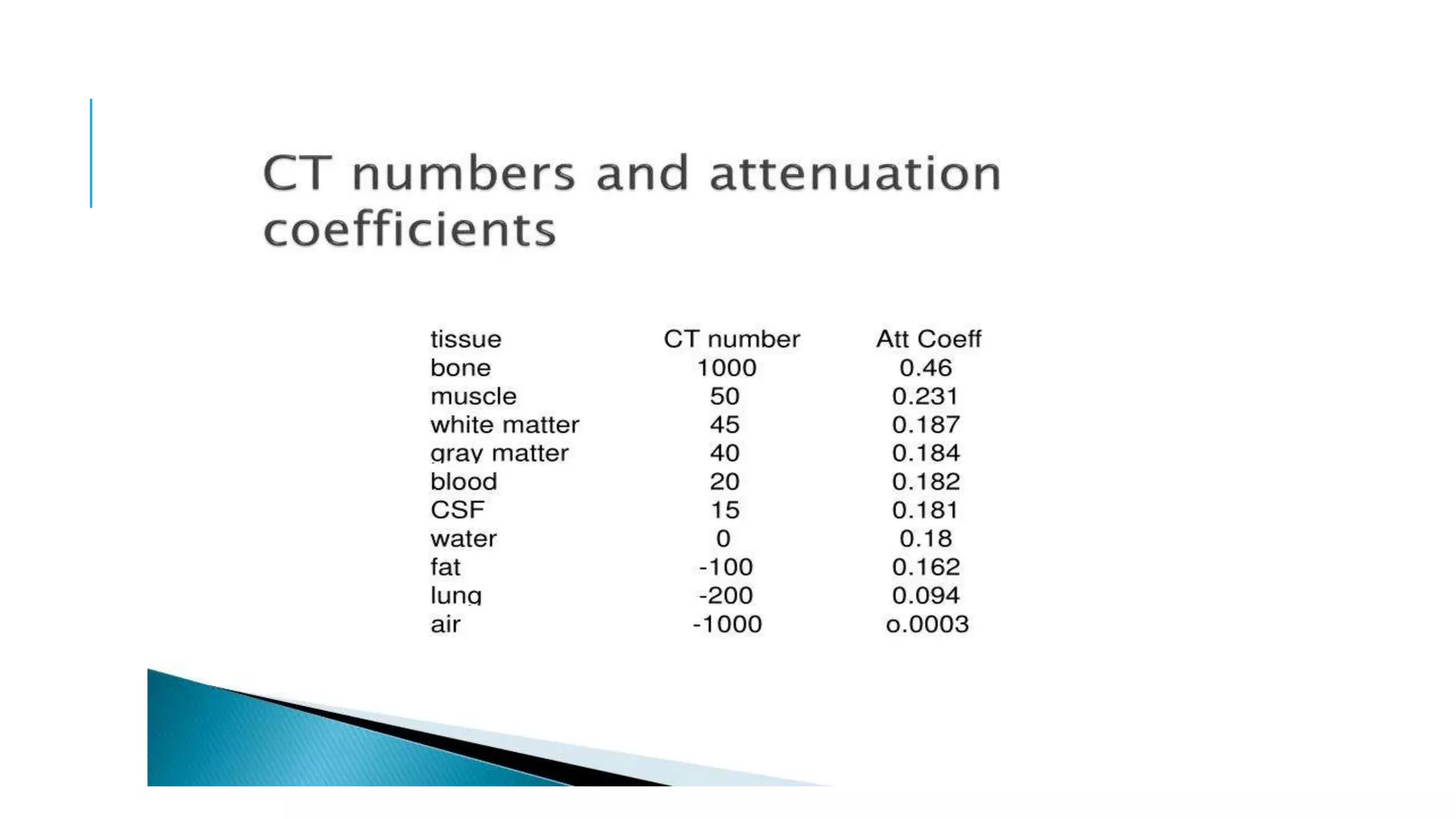
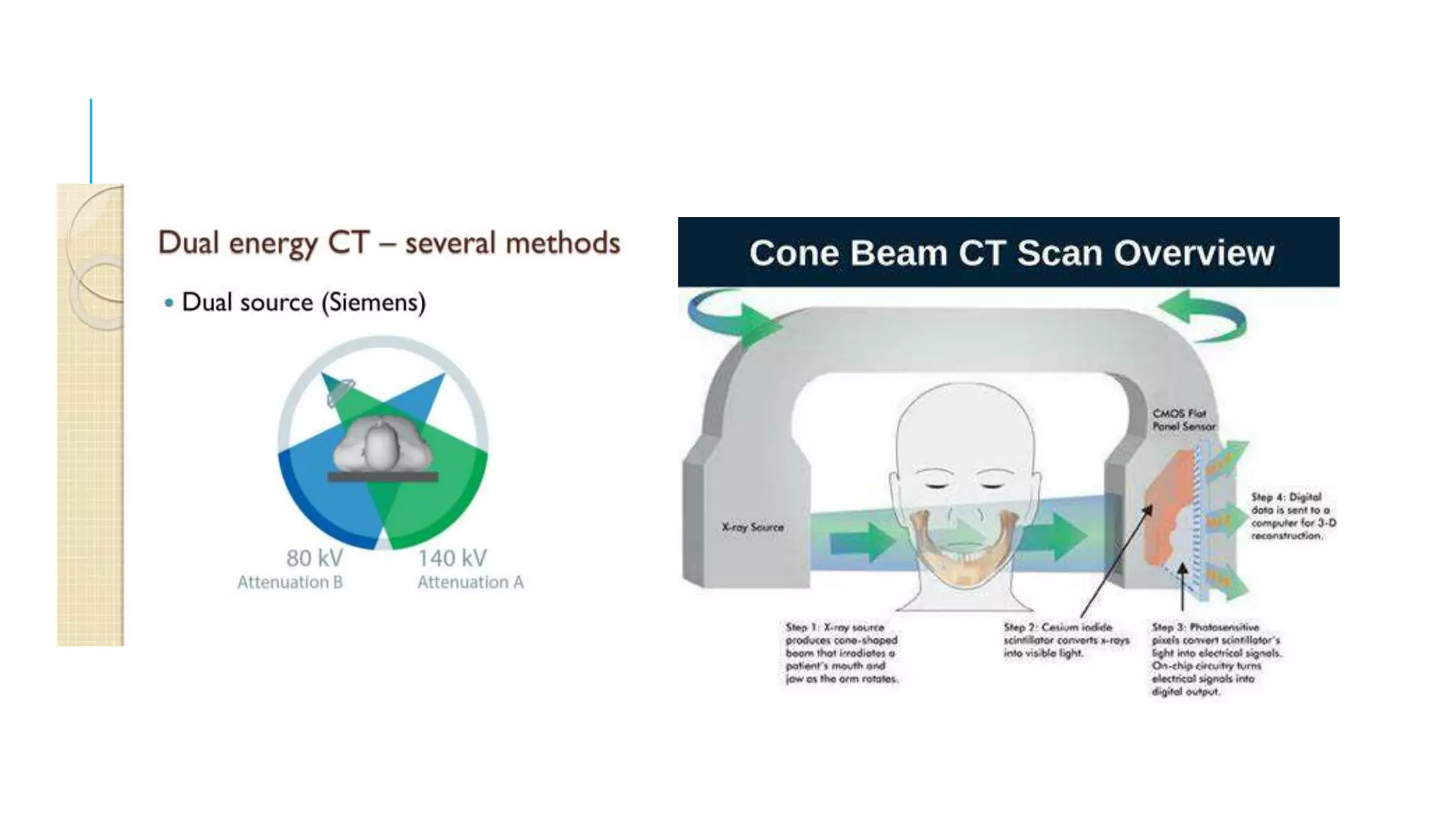
This document discusses CT image acquisition. It describes how CT scanners work, including the components of a CT scanner like the x-ray tube and detector array. It explains the image acquisition process, from x-ray generation to data collection and processing, and image reconstruction. Key steps include positioning the patient, rotating the x-ray tube, acquiring data projections from different angles, converting analog signals to digital, reconstructing images from the data using algorithms. The document provides an overview of the CT imaging process.