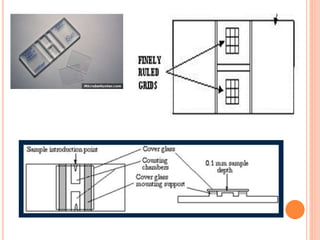
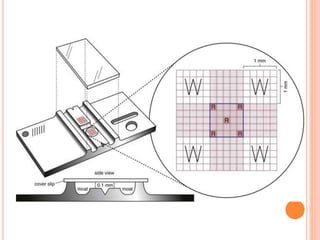
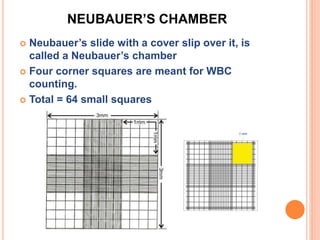
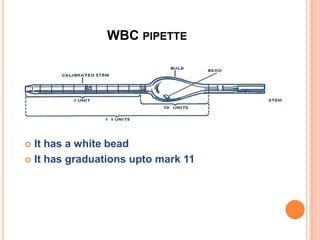
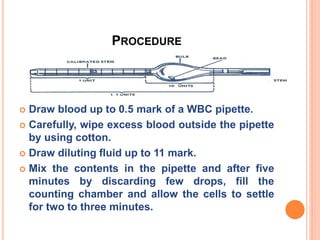
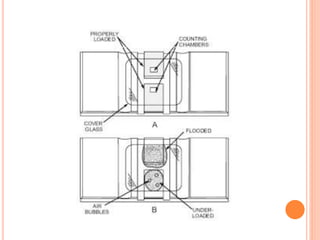
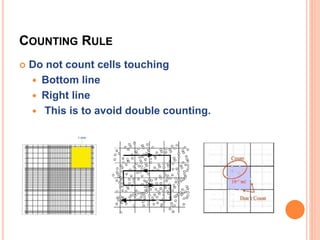
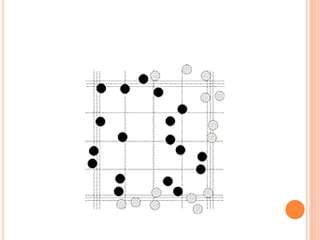
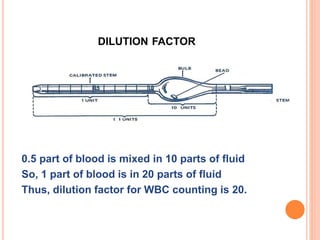
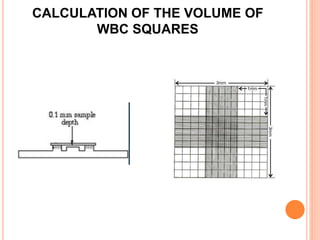
This document discusses total leukocyte count (TLC), also known as the total white blood cell count. It provides the normal ranges for TLC across different age groups. Leukocytosis is defined as a TLC over 11,000/mm3 and can occur due to physiological or pathological factors. Leukopenia is a TLC below 4,000 cells/cu.mm and can be caused by various infections, bone marrow depression, or drugs. The document then describes the manual hemocytometer method for counting white blood cells using a Neubauer chamber, as well as an electronic method using automated analyzers.