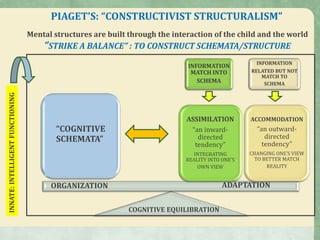
Jean Piaget's constructivist structuralism posits that knowledge is organized into changing cognitive structures as children interact with their environments. His theory emphasizes three main influences on cognitive development: maturation, active engagement, and learning from others. The process of knowledge construction involves assimilation, accommodation, and cognitive equilibration, allowing children to adapt their mental structures to better fit their experiences.