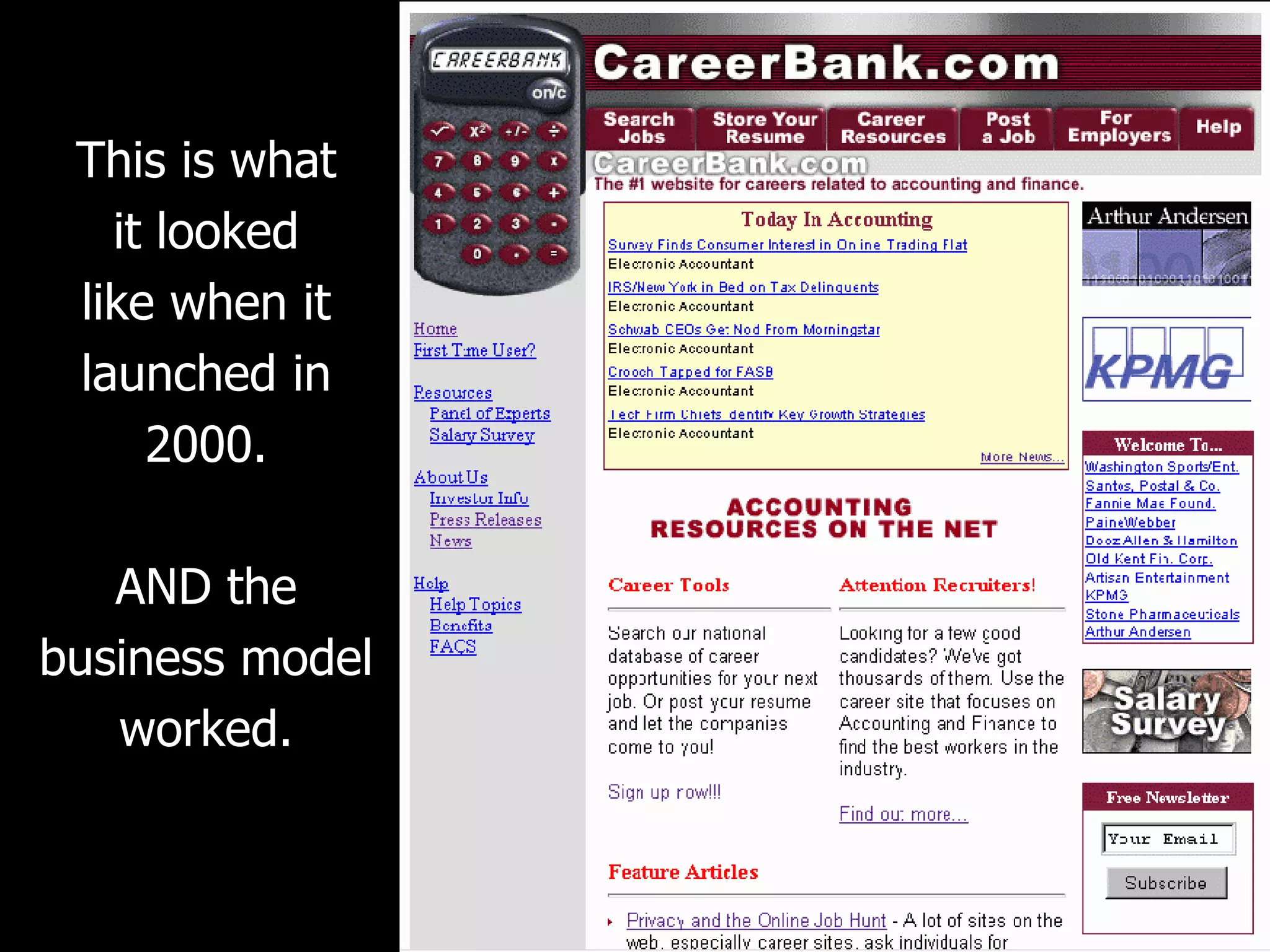
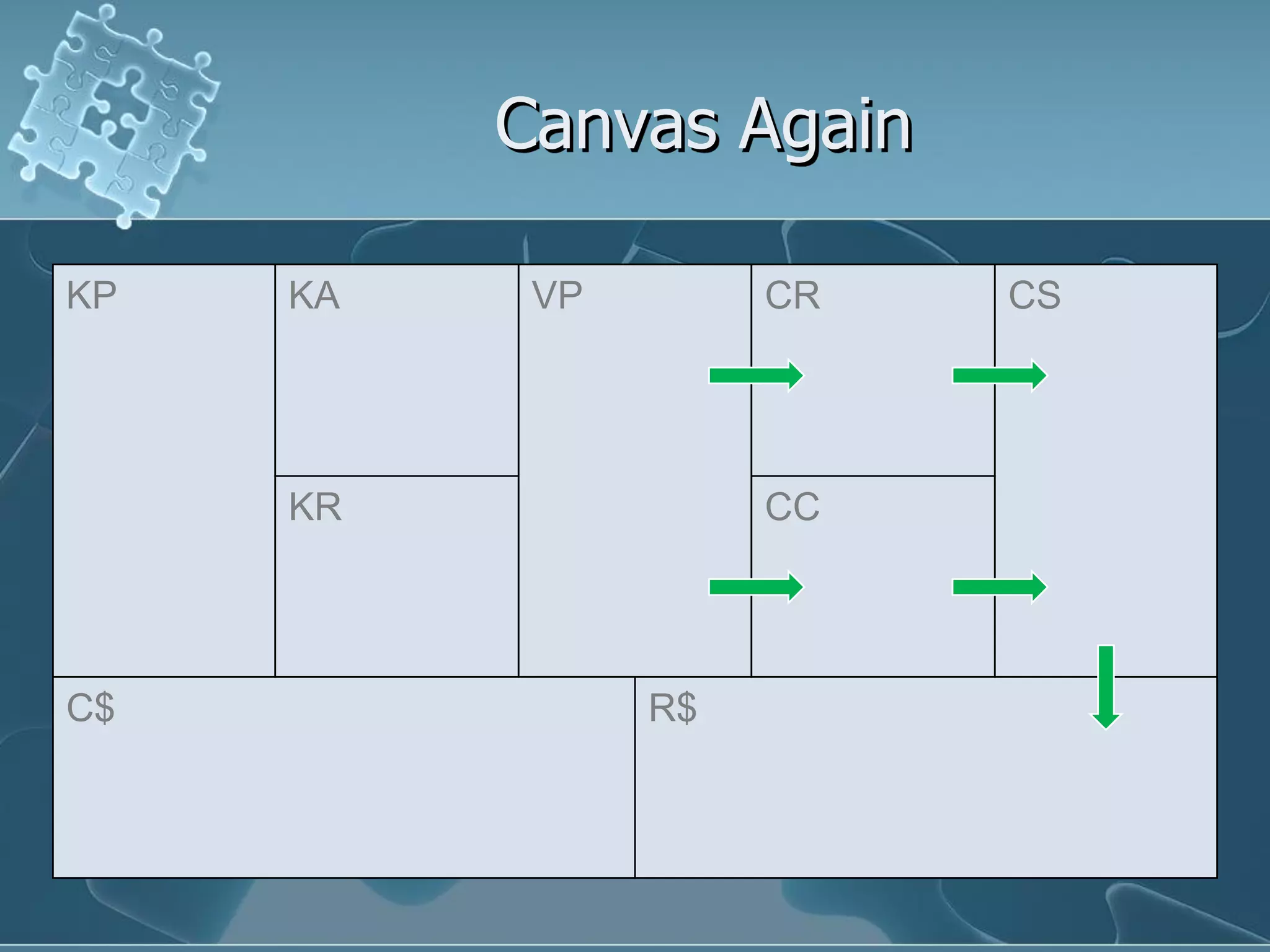
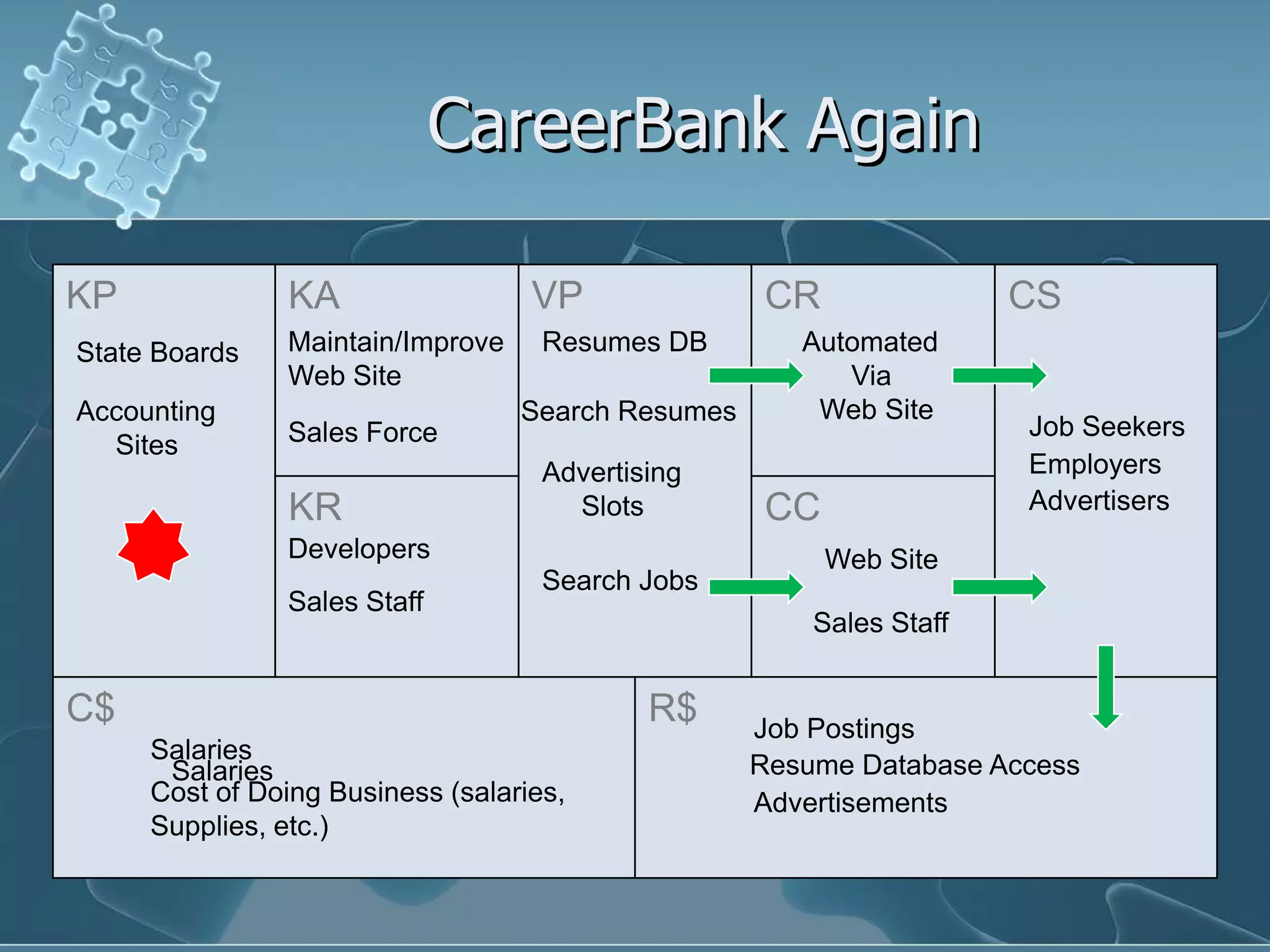
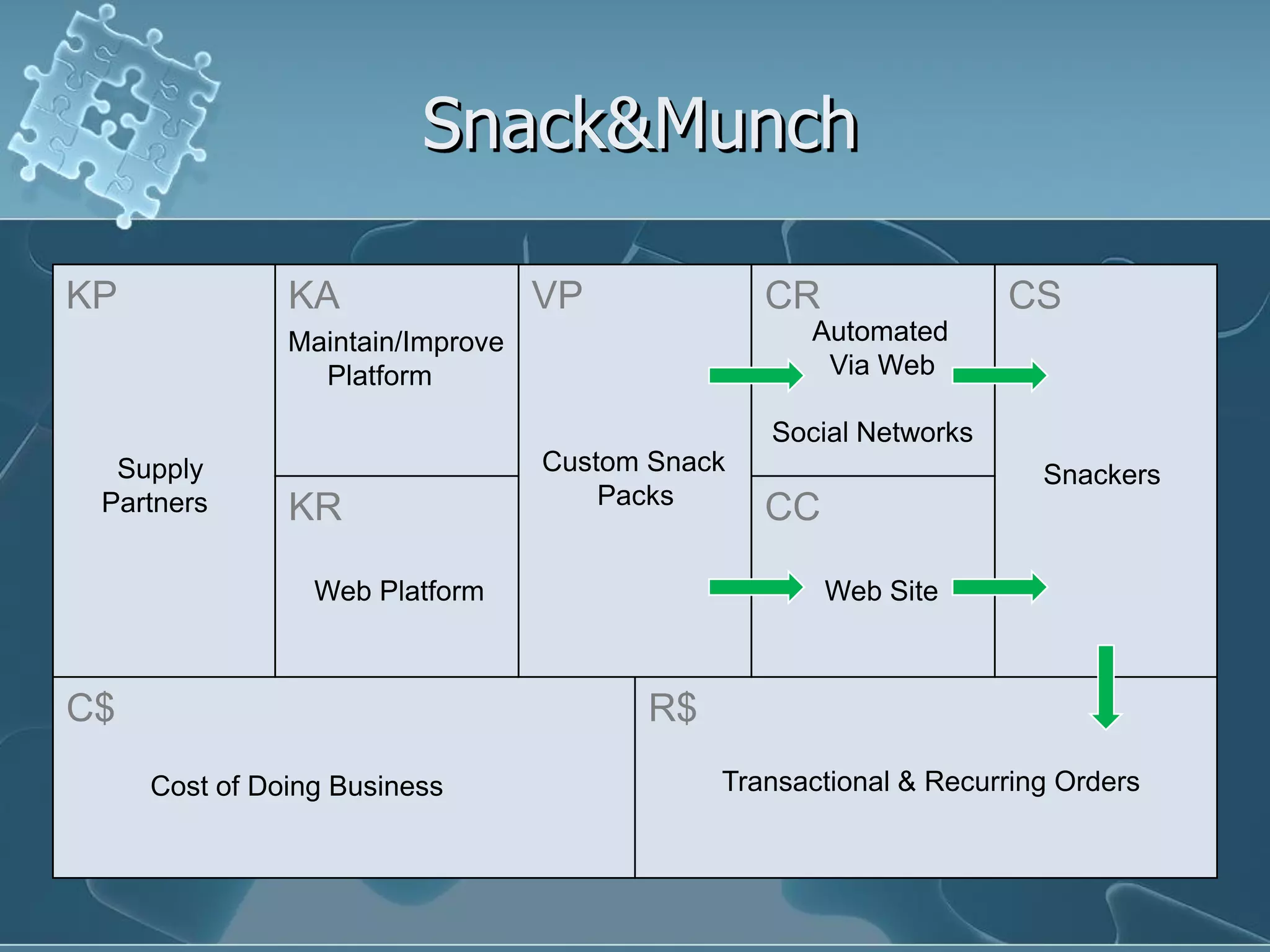
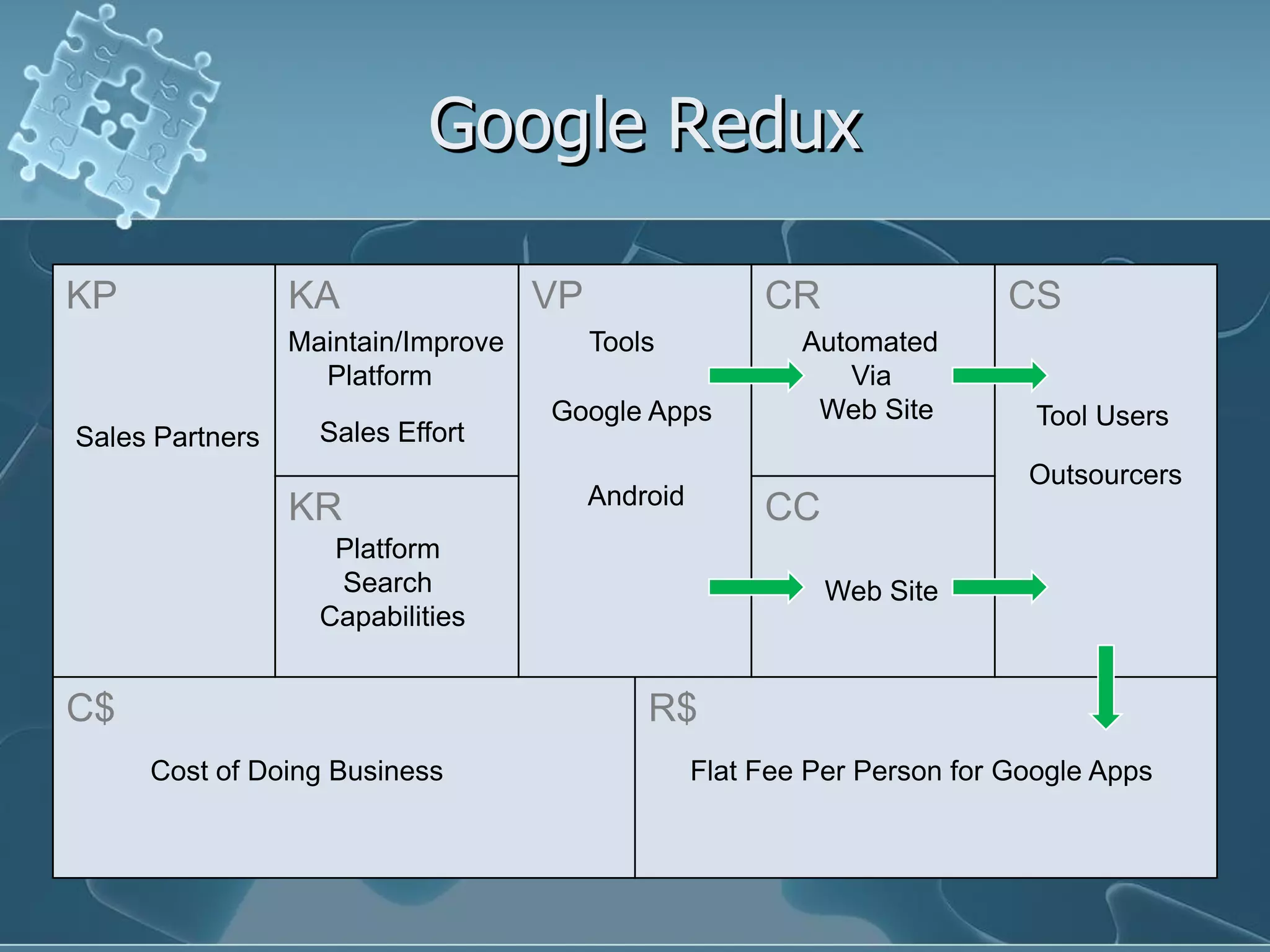
David Keener's talk on business models emphasizes the importance of understanding business models for Ruby developers and entrepreneurs. He introduces the 'business model canvas,' a tool for designing business models, and outlines key components such as value propositions, customer segments, and revenue streams. The presentation also discusses patterns in business models using real-world examples, highlighting how companies can leverage their strengths and partnerships to create value.