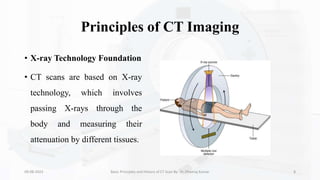
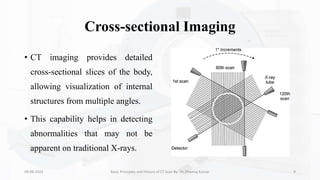
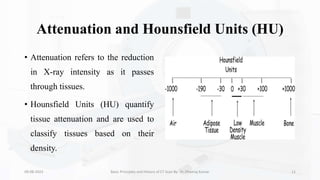
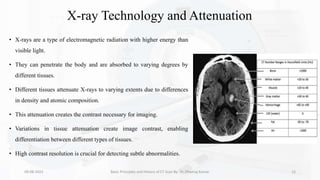
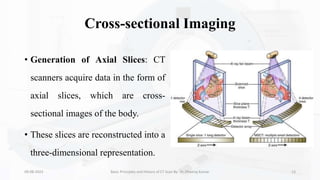
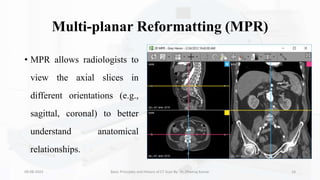
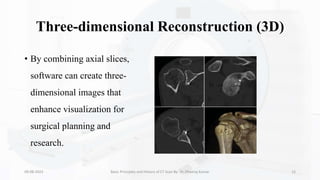
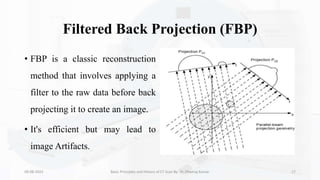
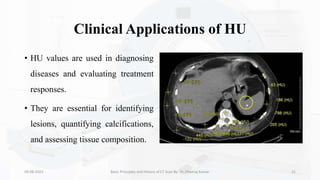
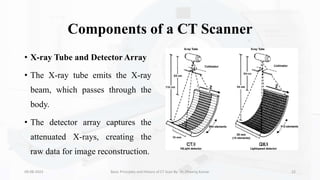
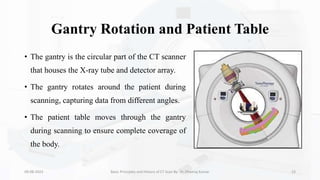
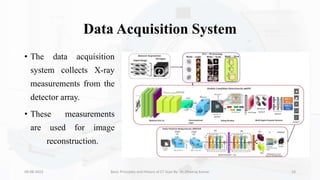
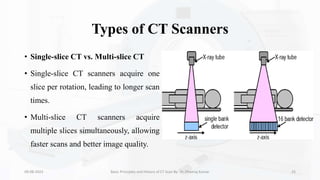
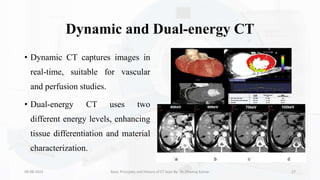
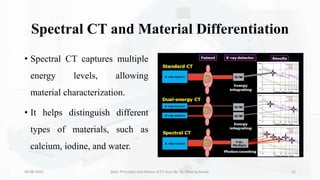
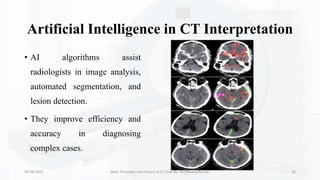
The document details the principles, history, and advancements of computed tomography (CT) scans, a vital medical imaging technique utilizing x-ray technology for producing detailed images of the body. It discusses the inception of CT scans in the 1970s by Sir Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack, their importance in diagnosis and disease monitoring, and the evolution of technology that has improved image quality and reduced scan times. Additionally, the document highlights safety considerations regarding radiation exposure and recent advancements like artificial intelligence integration in CT interpretation.