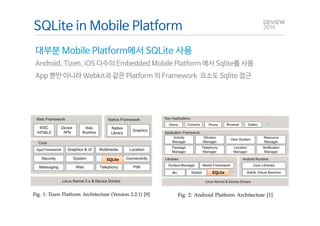
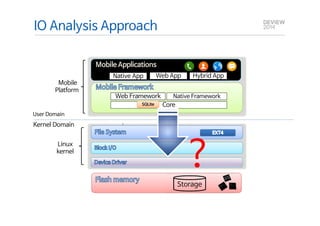
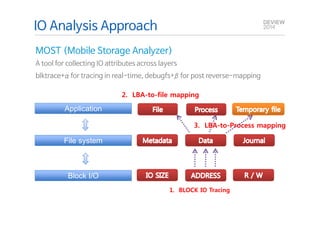
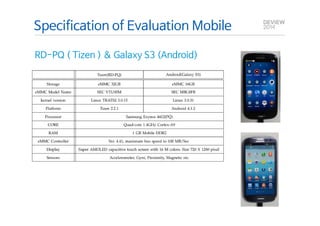
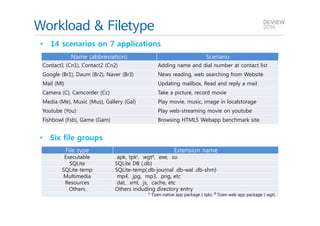
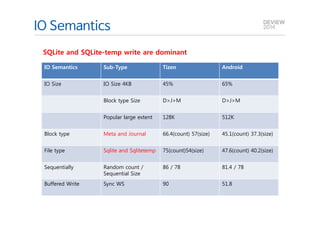
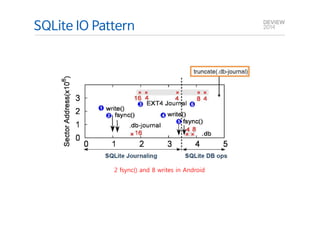
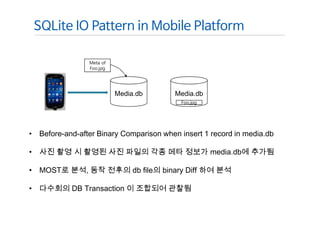
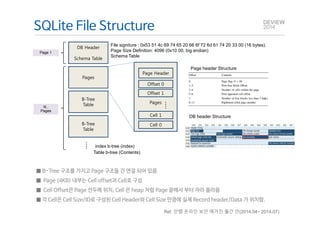
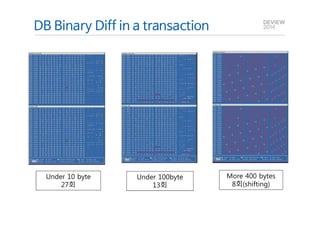
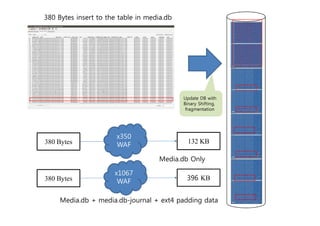
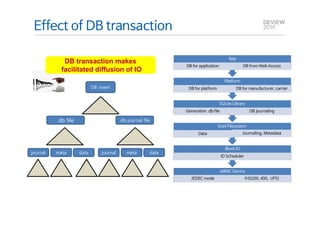
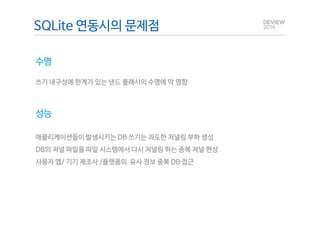
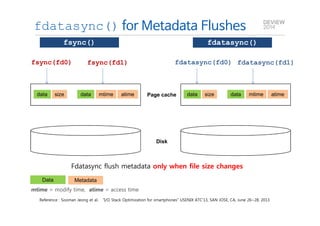
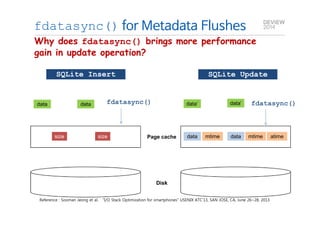
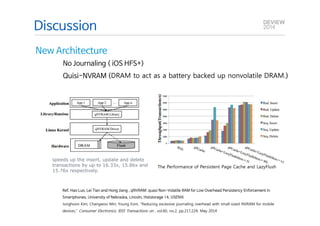
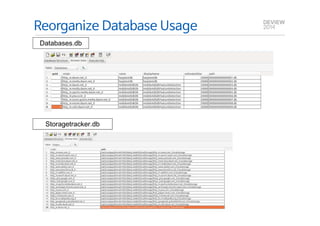
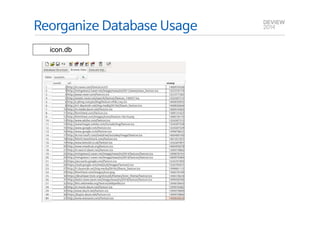
This document analyzes the I/O characteristics of SQLite databases in mobile platforms like Android and Tizen. It finds that SQLite database I/O is dominant, with small 4KB writes being common. SQLite journaling and Ext4 filesystem journaling together generate excessive I/O. Various optimizations are discussed, including using SQLite's WAL journal mode, filesystem mount options, fdatasync(), and reorganizing how databases are used by platforms and applications.