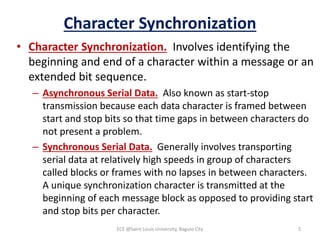
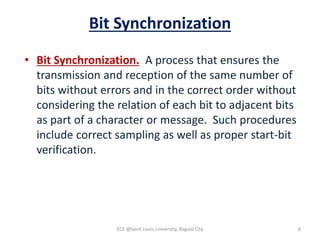
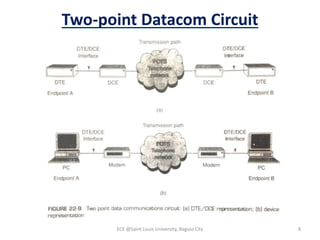
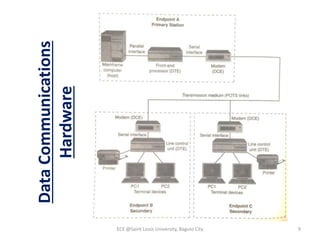
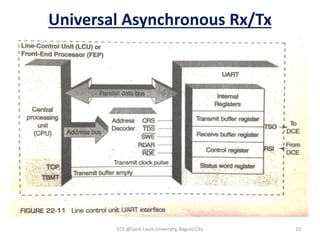
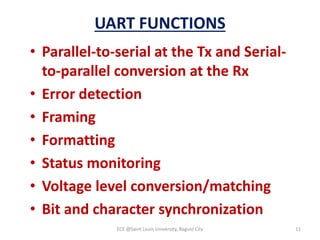
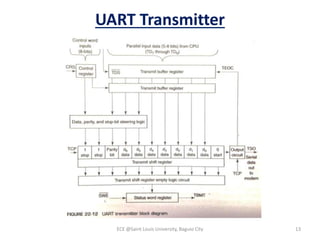
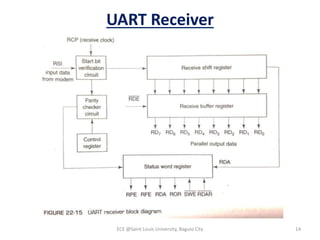
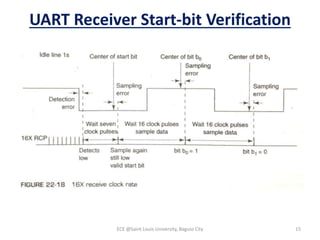
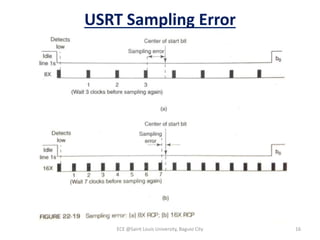
Module 4 covers fundamental concepts of data communications, focusing on data communication codes, error coding, and synchronization. It describes the hardware components involved, such as data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communication equipment (DCE), along with their functions. The chapter also includes an overview of UART and USRT functionalities, and provides a quiz on the discussed topics.