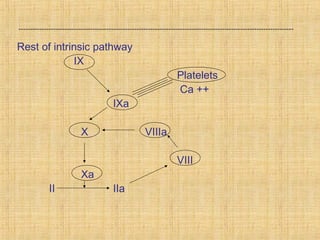
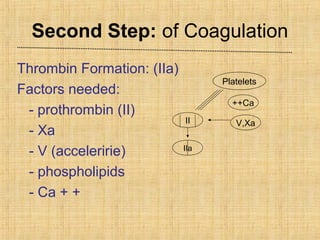
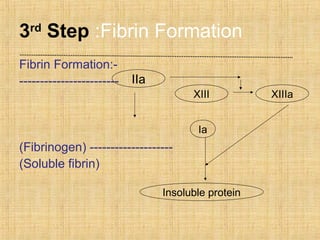
This document summarizes key information about platelets:
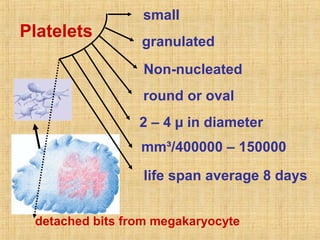
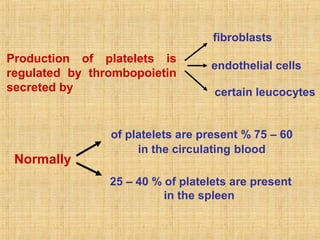
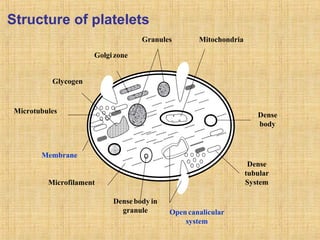
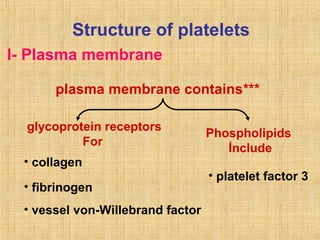
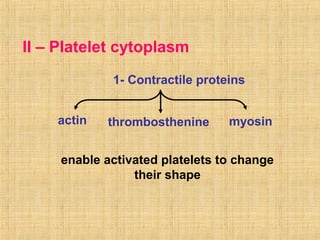
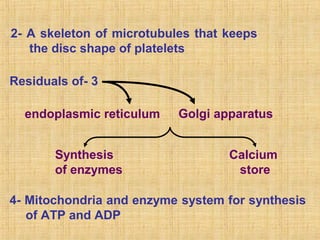
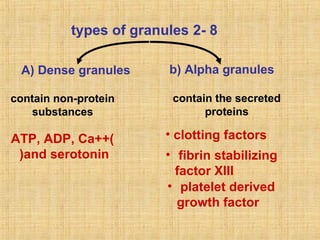
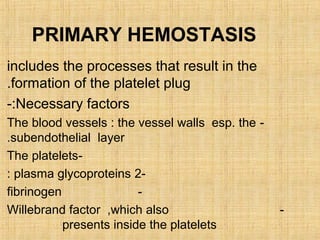
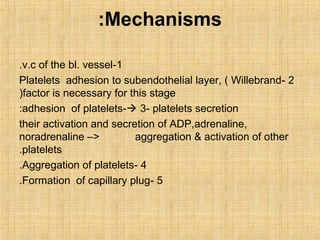
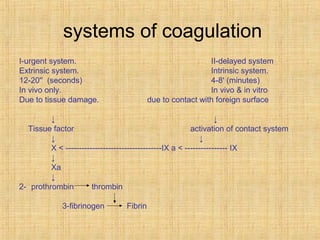
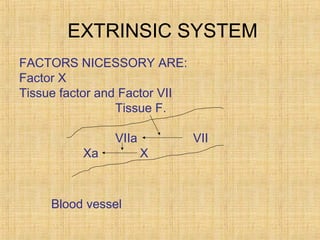
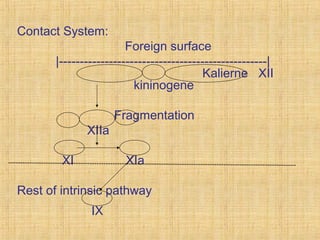
Platelets are small, granulated, and non-nucleated cell fragments that are 2-4 micrometers in diameter. They are produced from megakaryocytes at a rate of 400,000-150,000 per cubic millimeter of blood, and have an average lifespan of 8 days. Platelets play a critical role in hemostasis, the process of stopping bleeding, through adhesion, activation, aggregation, and formation of a platelet plug. Their cytoplasm contains various proteins, organelles, and granules that enable activation and responses to injury.