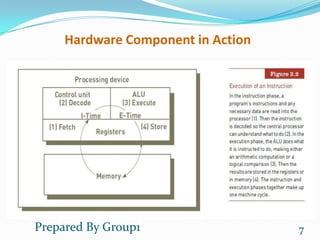
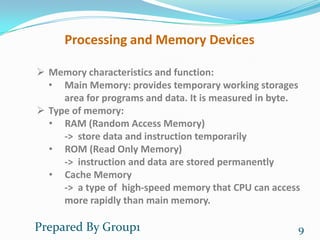
This document discusses hardware components of a computer system. It is presented by a group that includes Ben Piseth, Chin Putry, Chan Sopov, Chan Piseth, Chao Yorkchhive, and Duch Mony. The objectives are to define hardware, identify its advantages for organizations, and describe hardware components. It discusses the central processing unit, arithmetic logic unit, control unit, registers, primary storage, processing and memory devices, multiprocessing, parallel computing, secondary storage, input/output devices, computer systems, and green computing.