The document discusses data types in Microsoft SQL Server. It describes that SQL Server has system-defined data types organized into categories like exact numerics, approximate numerics, date/time, character strings, and binary. It also provides examples of common data types like int, varchar, datetime, image, and explains how to define user-defined data types and handle conversions between types.








![3/2/2014 1:58 PM
SQL Character String Data Types
Data Type
Storage Capacity
Range
Char [(n) ]
Varies
1 to 8,000 characters
Varchar [(n|max)]
Varies
8,000 characters
Text
Varies
231–1 (2,147,483,647) characters
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypeonmssqlserver-140302075820-phpapp01/85/Data-type-s-on-MS-SQL-Server-9-320.jpg)
![3/2/2014 1:58 PM
SQL Unicode Character String Data Types
Data Type
Storage Capacity
Range
nchar [(n)]
Varies
1 to 4,000 characters
nvarchar [(n|max)]
Varies
4,000 characters
ntext
Varies
230–1 (1,073,741,823) characters
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypeonmssqlserver-140302075820-phpapp01/85/Data-type-s-on-MS-SQL-Server-10-320.jpg)
![3/2/2014 1:58 PM
SQL Binary Data Types
Data Type
Storage Capacity
Range
binary [(n)]
Varies
8,000 bytes
varbinary [(n|max)]
Varies
8,000 bytes
Image
Varies
231–1 (2,147,483,647) bytes
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypeonmssqlserver-140302075820-phpapp01/85/Data-type-s-on-MS-SQL-Server-11-320.jpg)
![3/2/2014 1:58 PM
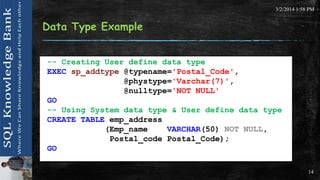
SQL User Define Data Types
▪ User define data type are based on system data type of MS
SQL Server.
▪ It is created when several table object use the same data in
terms of data type, length and null ability.
The syntax of creating user define data types are
mentioned bellow :
sp_addtype [
[
[
[
@typename = ] type,
@phystype = ] system_data_type
, [ @nulltype = ] 'null_type' ]
, [ @owner = ] 'owner_name' ]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypeonmssqlserver-140302075820-phpapp01/85/Data-type-s-on-MS-SQL-Server-13-320.jpg)