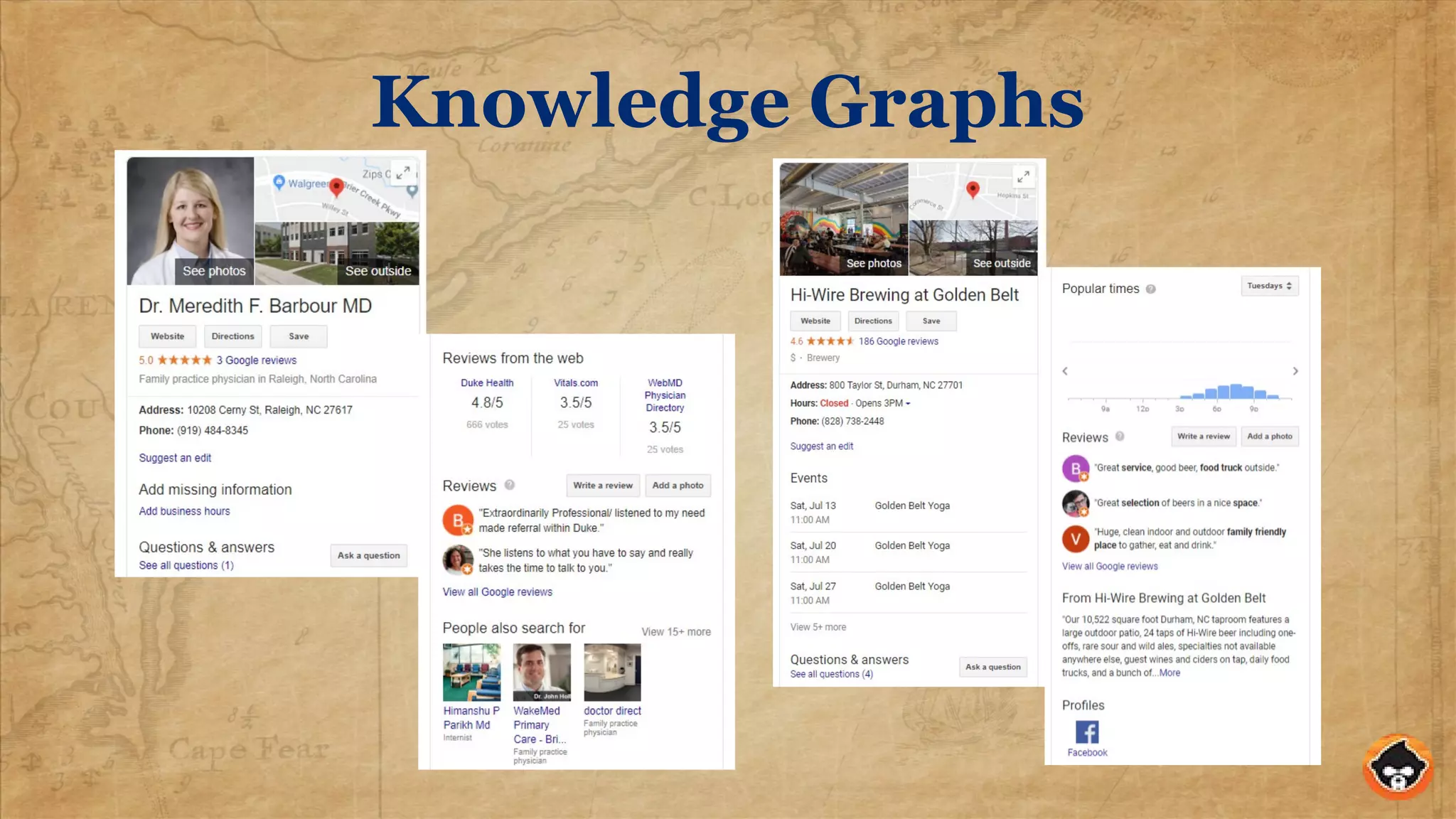
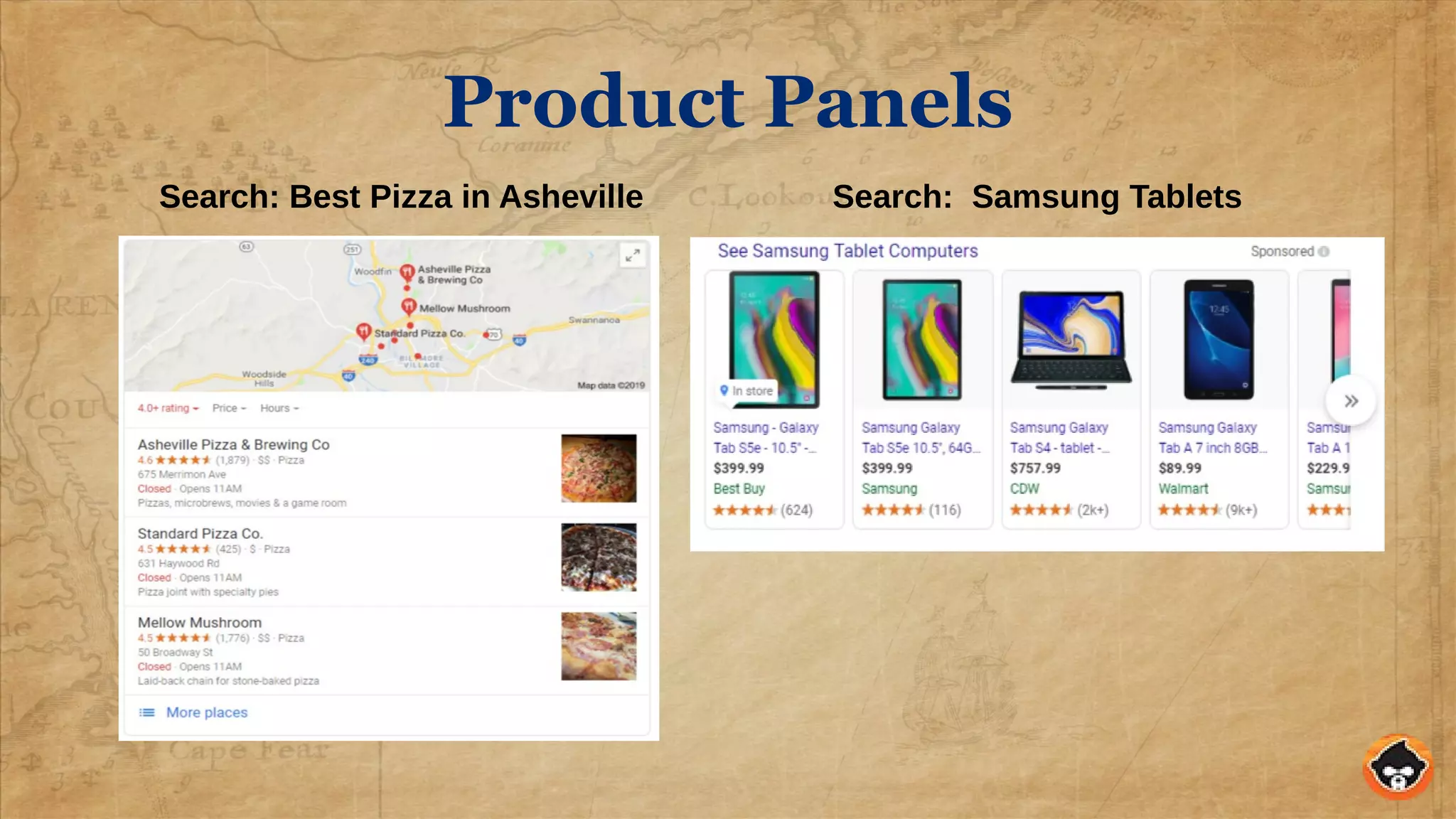
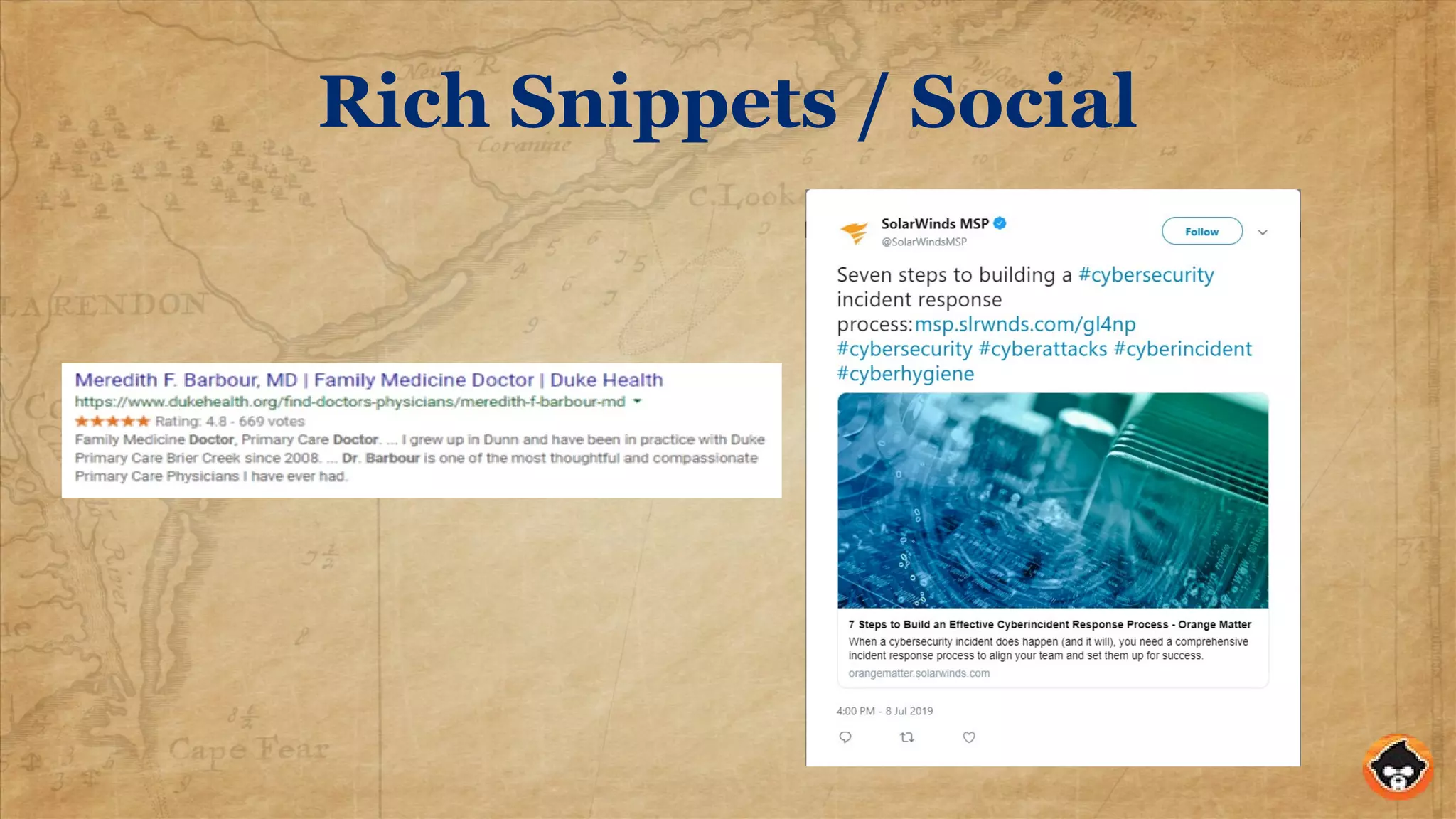
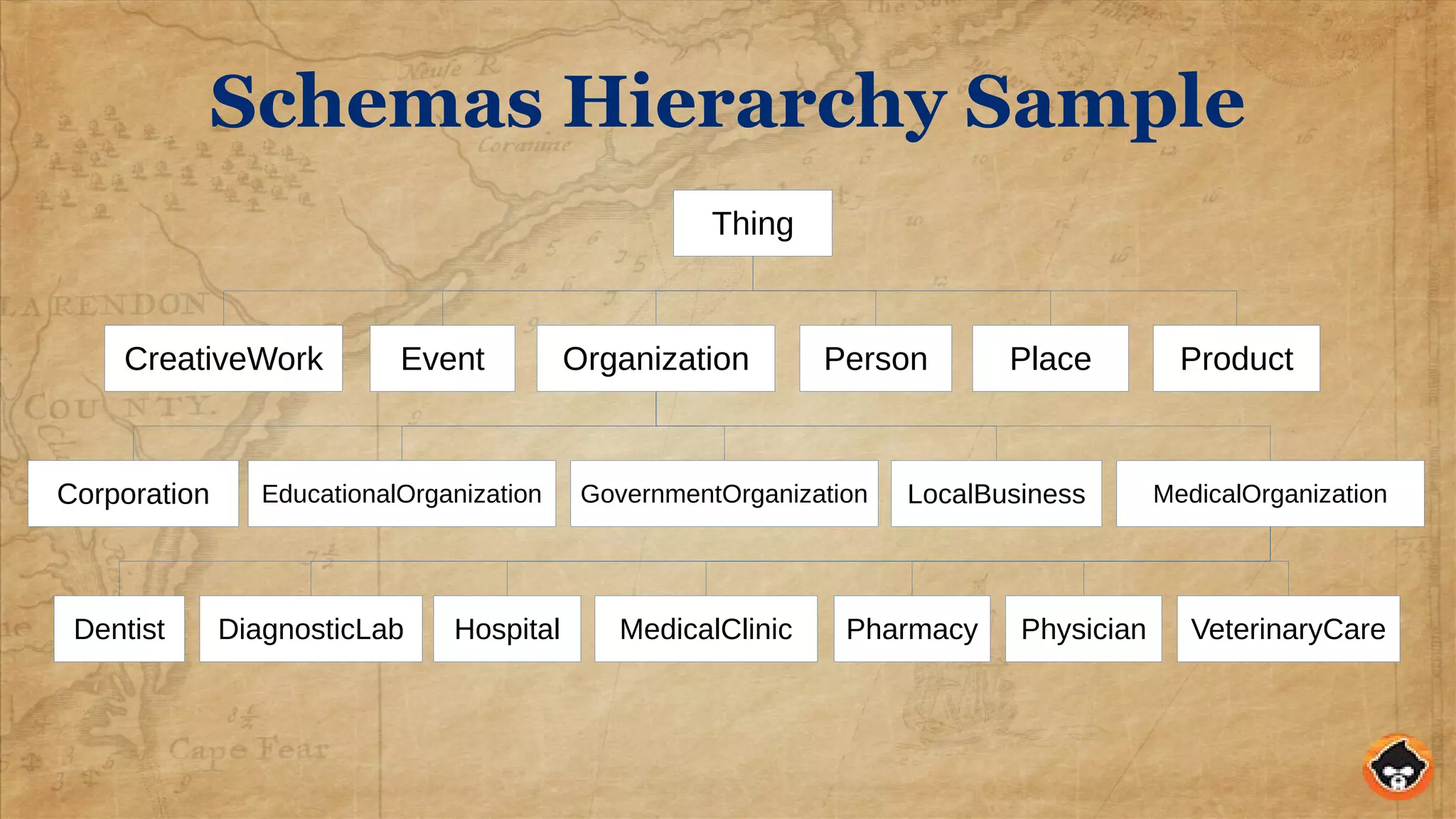
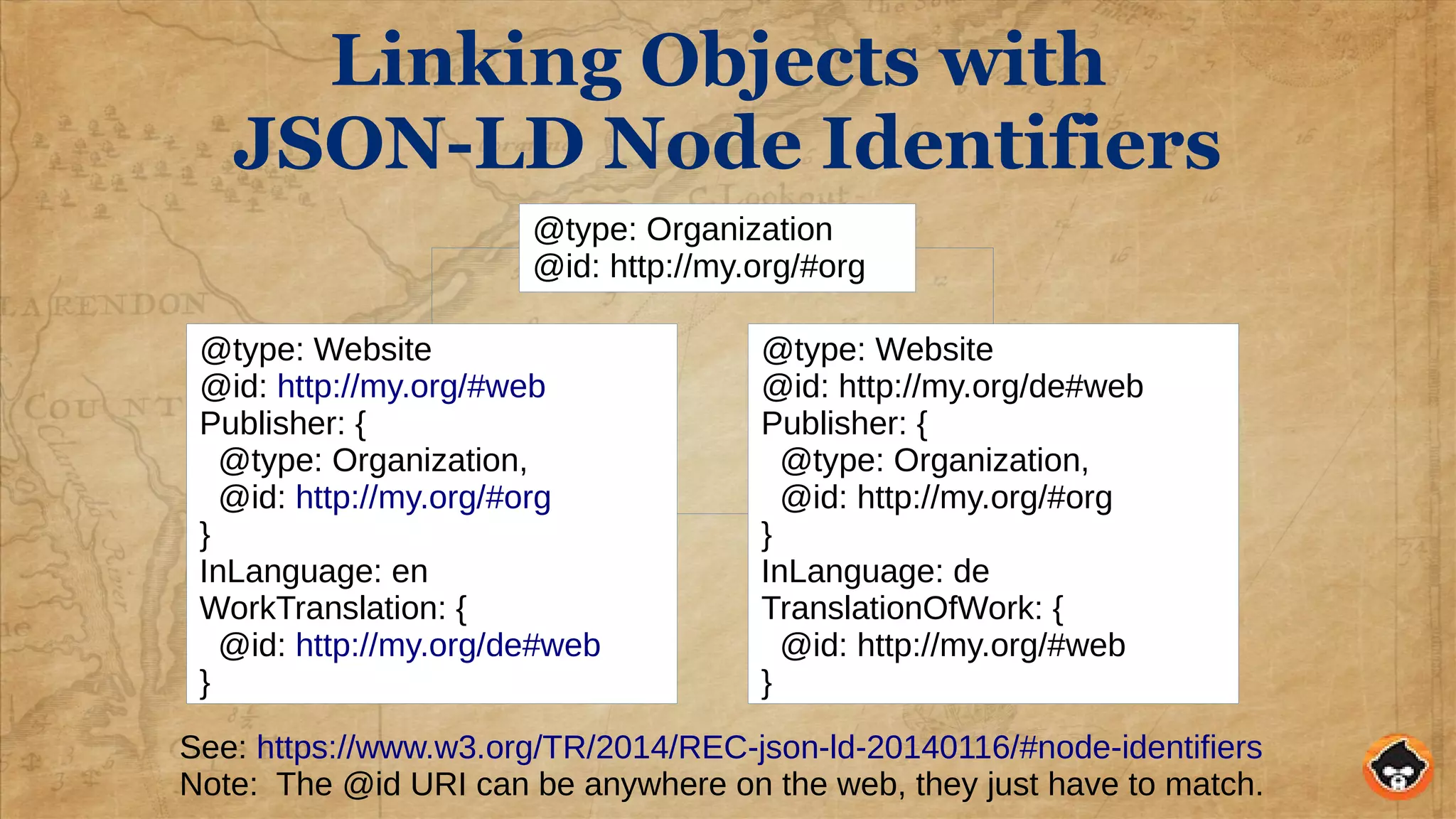
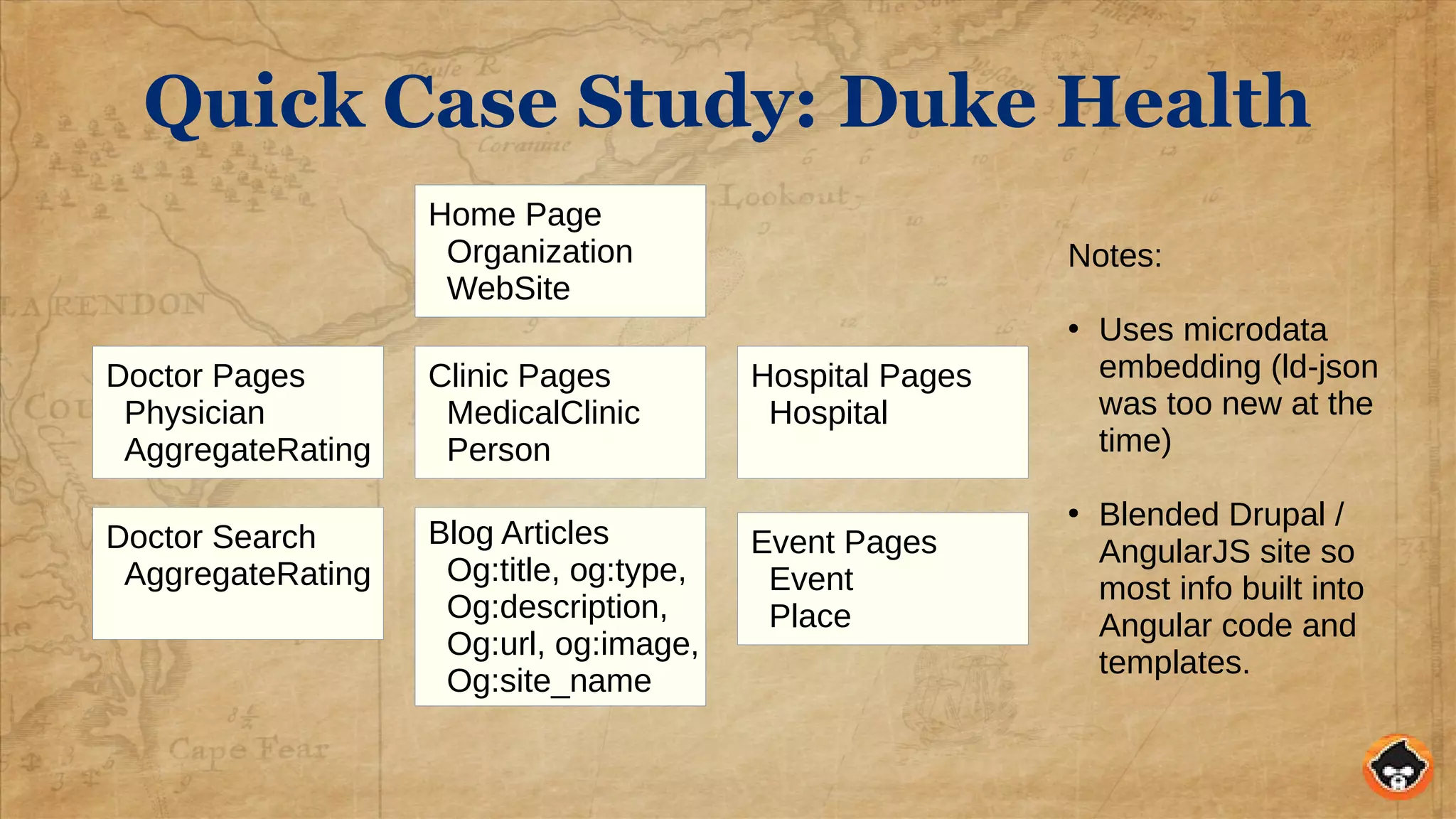
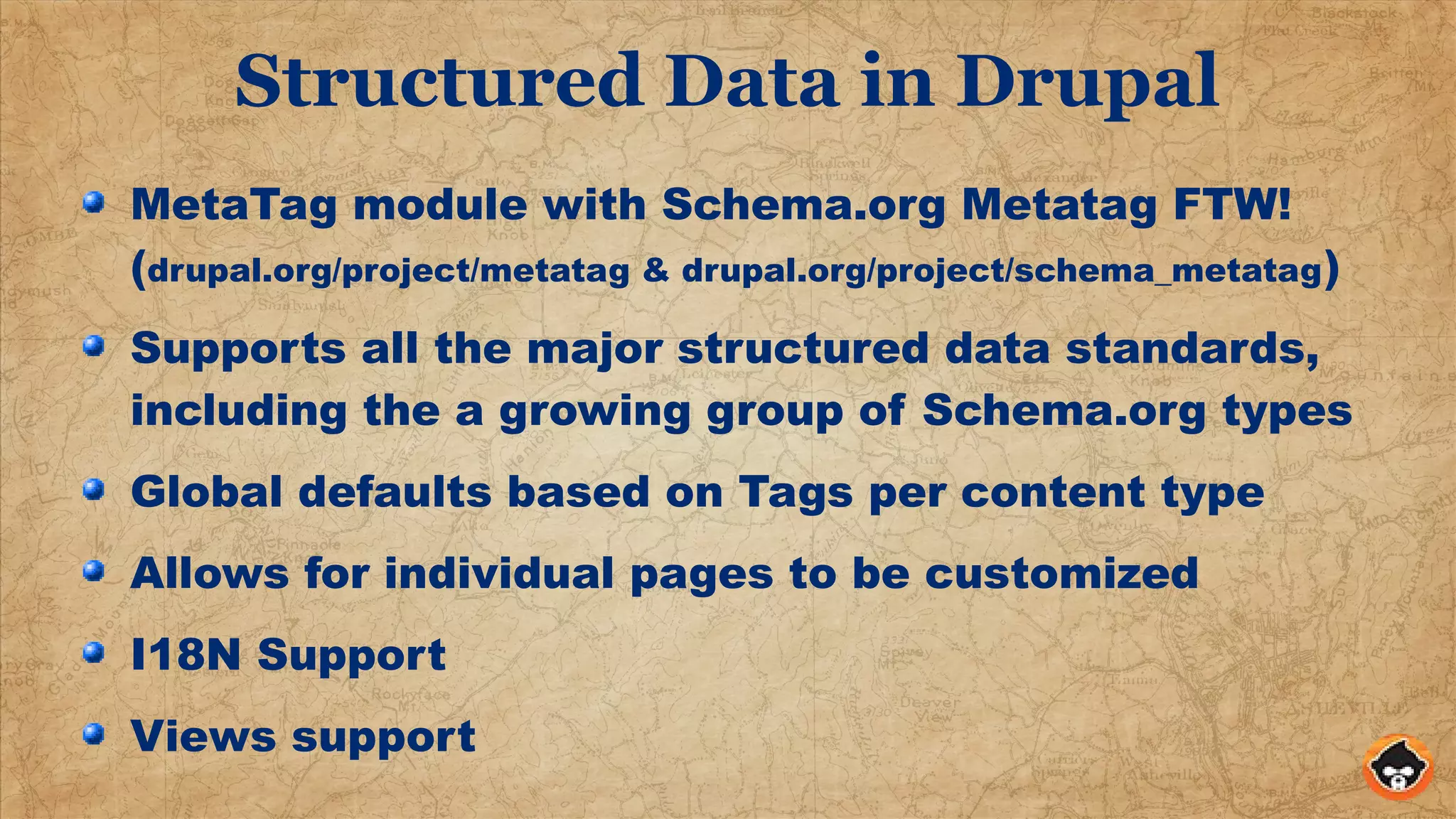
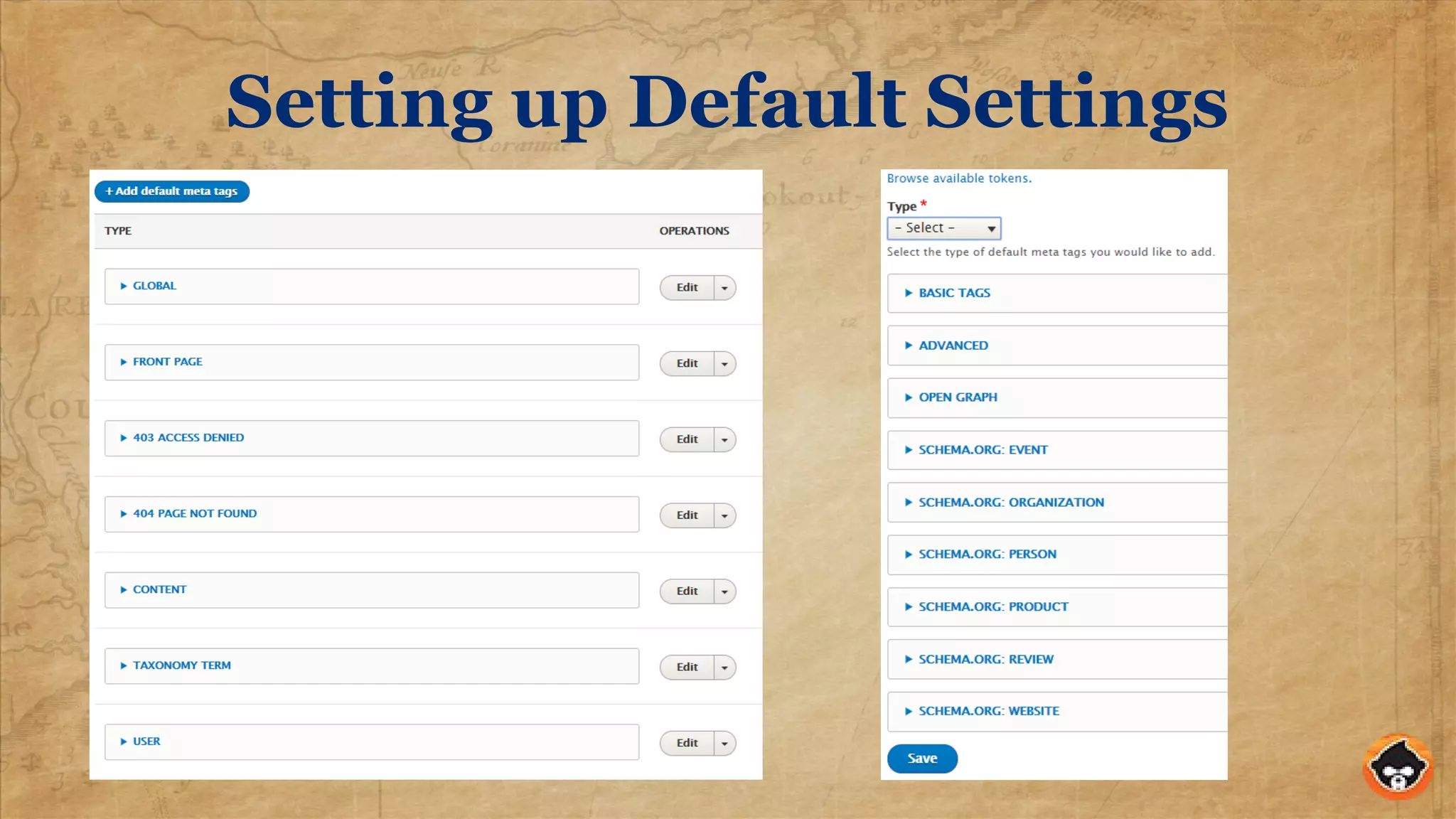
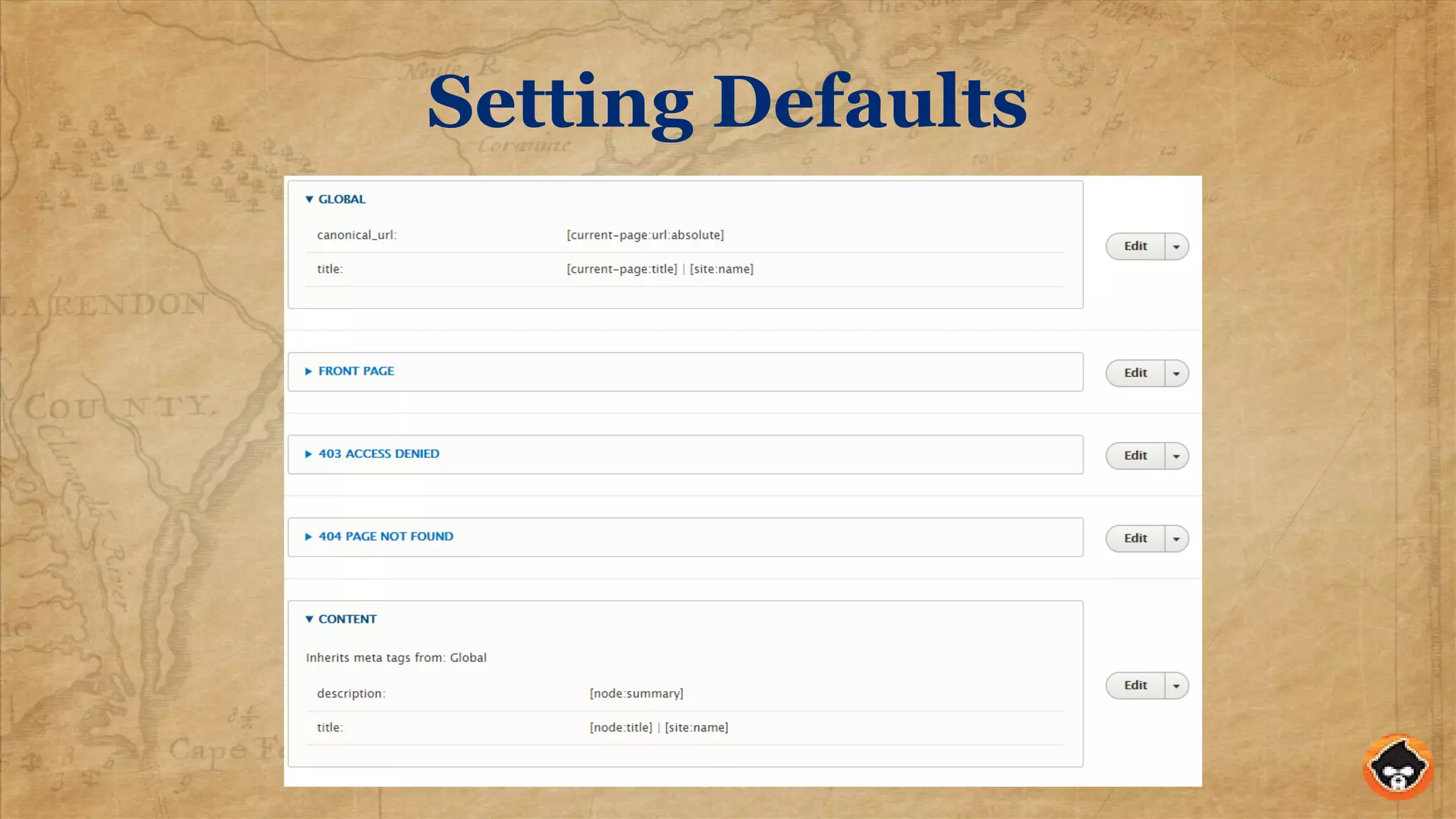
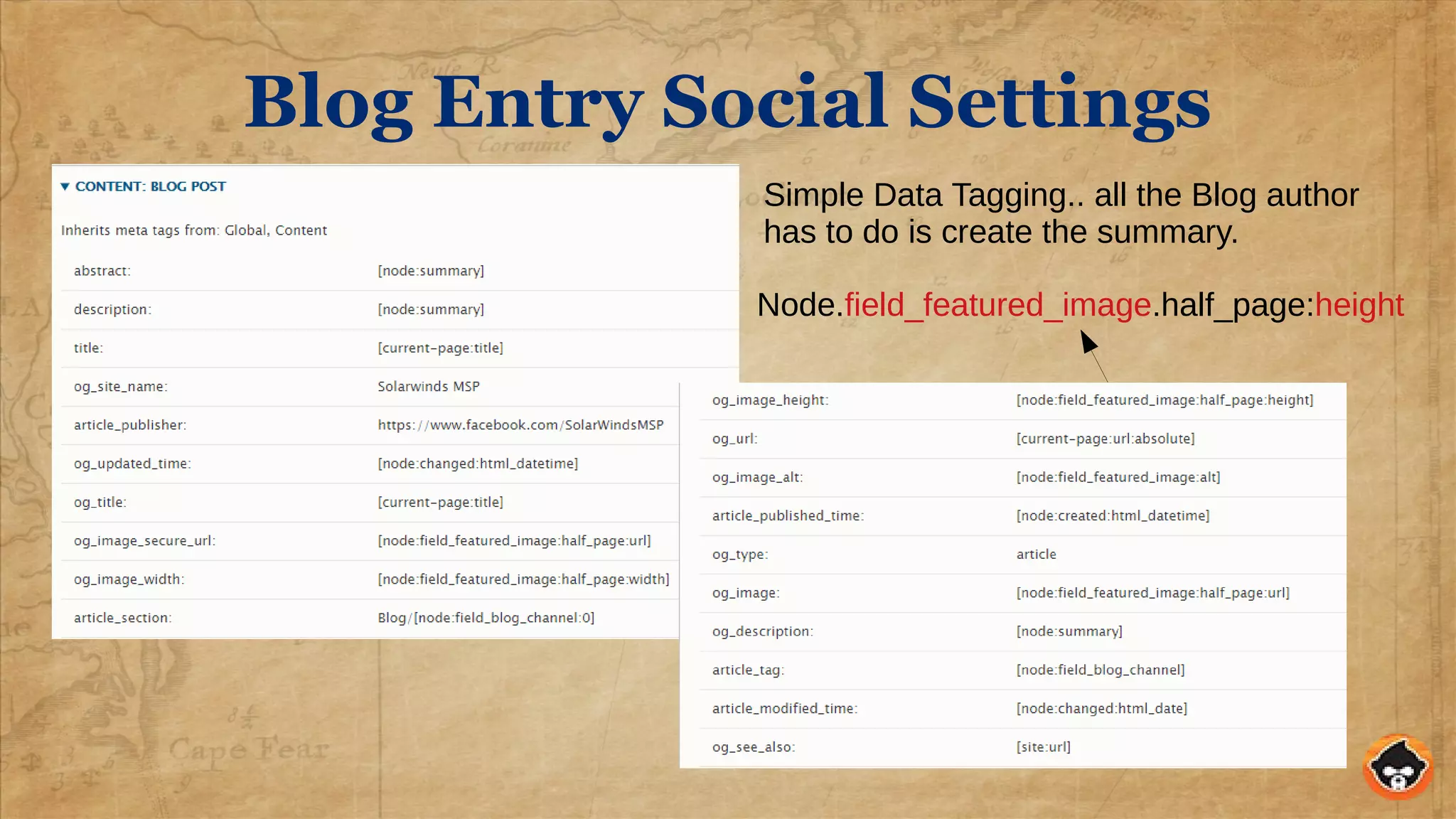
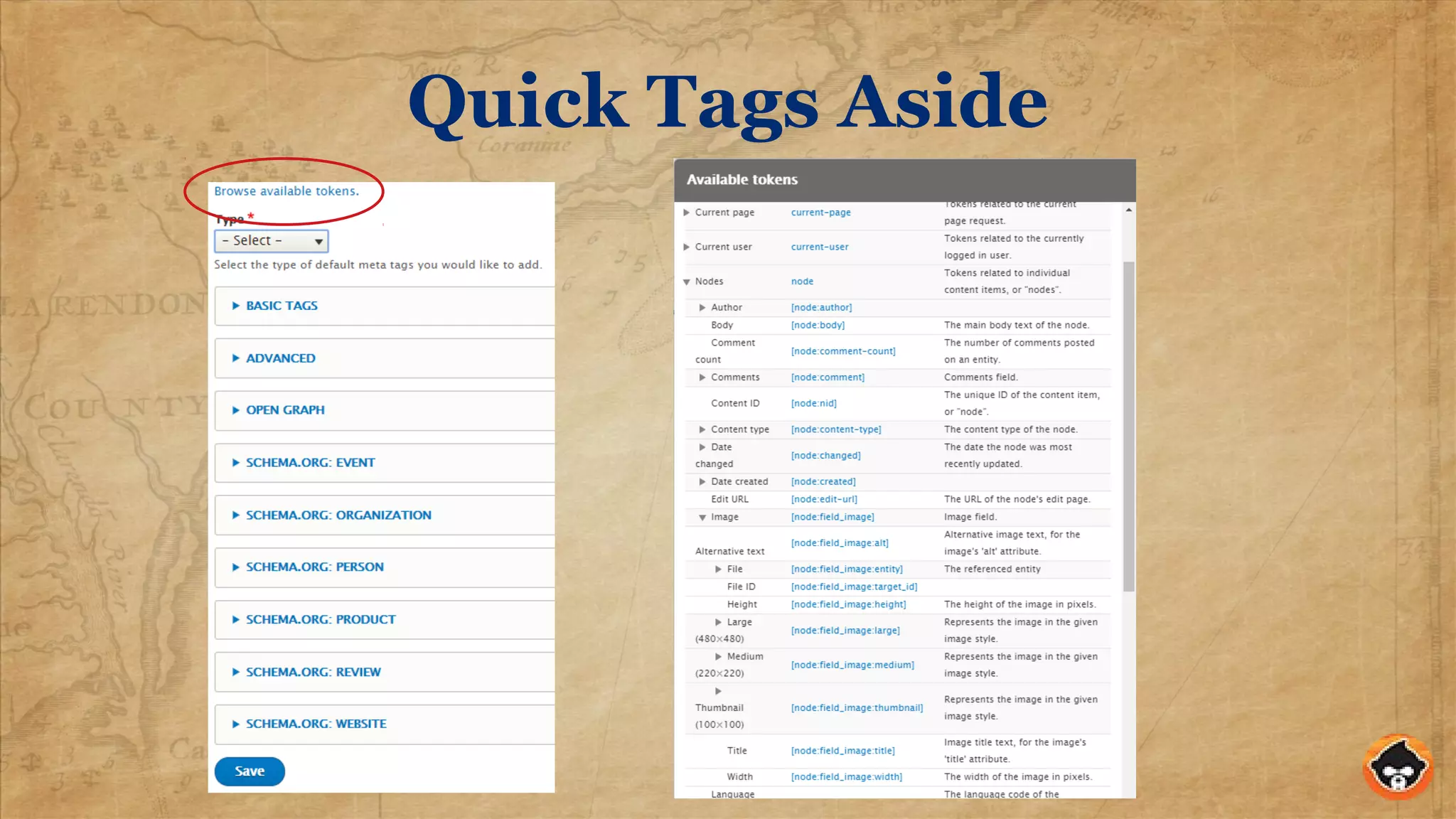
This document provides an overview of structured data and how to implement it in Drupal using the MetaTag and Schema Metatag modules. It discusses why structured data is useful for SEO, gives examples of rich snippets and knowledge graphs, and outlines how to set global and per-entity structured data defaults in Drupal. It also provides tips on validation and best practices for structured data implementation.









![JSON-LD Example
<script type="application/ld+json">
{"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@graph": [{
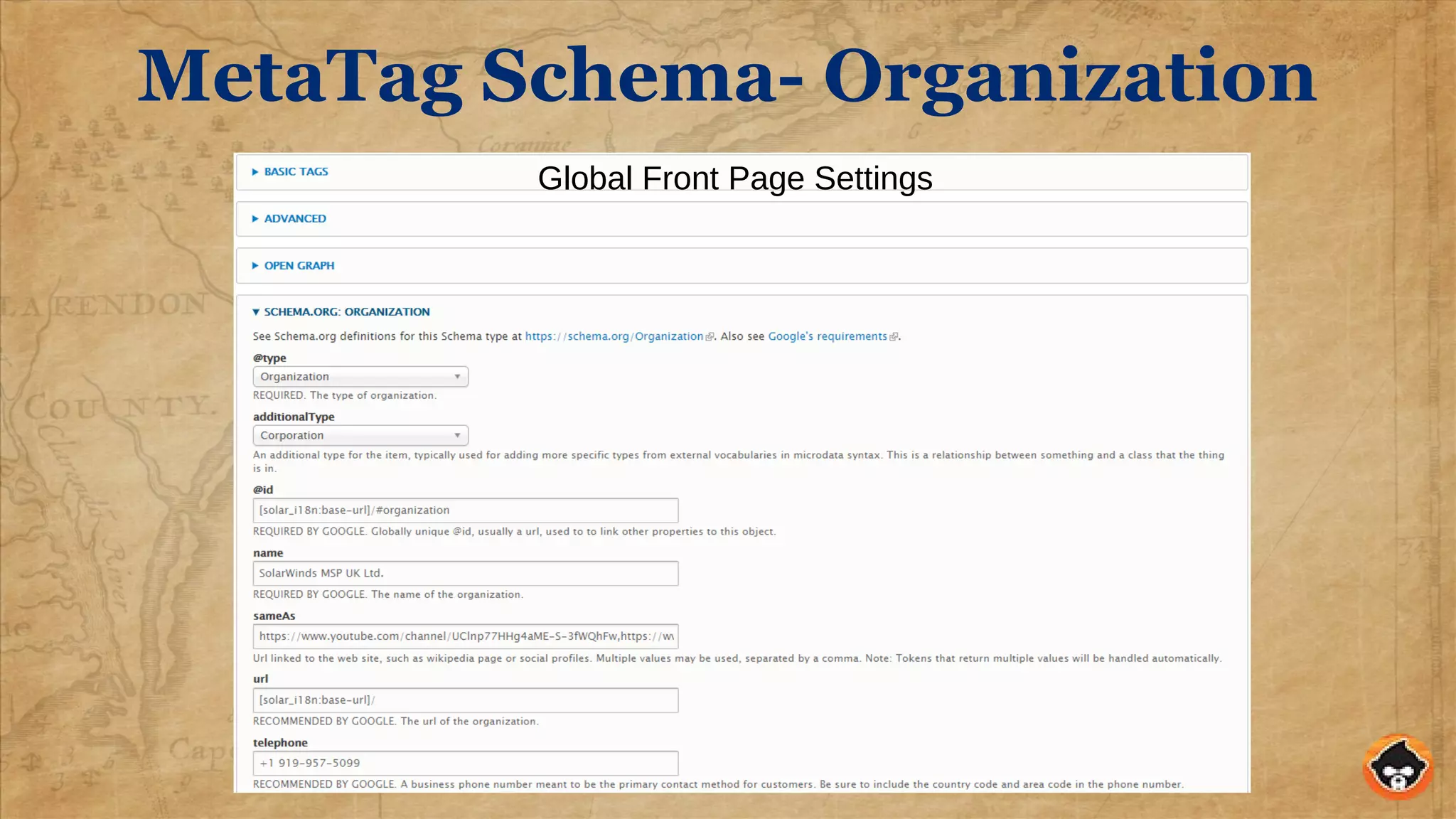
"@type": "Organization", "additionalType": "Corporation",
"@id": "https://www.solarwindsmsp.com/#organization",
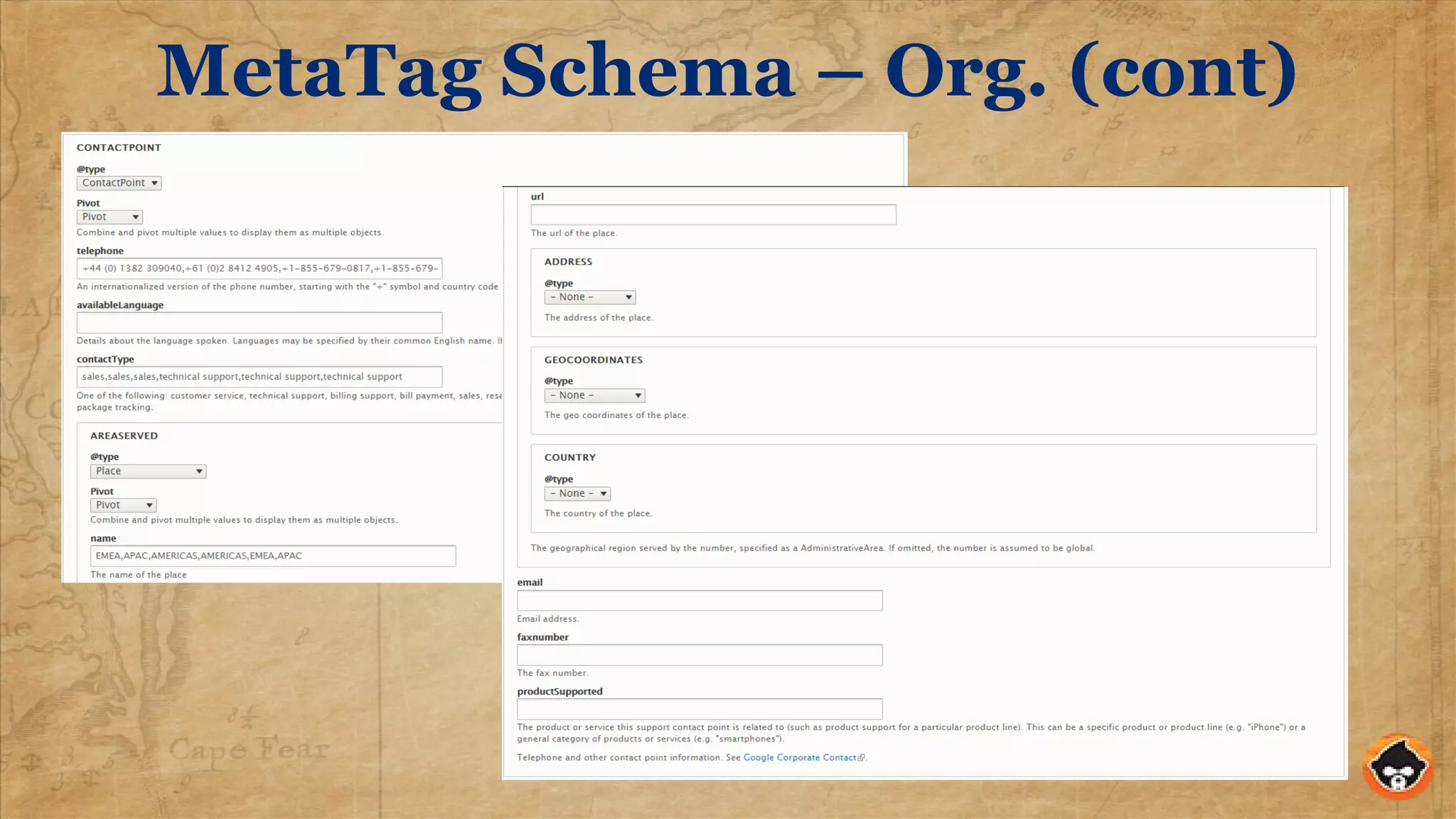
"sameAs": ["https://www.youtube.com/channel/UClnp77HHg4aME-S-3fWQhFw",
"https://twitter.com/solarwindsmsp", "https://www.facebook.com/SolarWindsMSP/"],
"name": "SolarWinds MSP UK Ltd.",
"url": "https://www.solarwindsmsp.com/",
"telephone": "+1 919-957-5099",
"logo": { "@type": "ImageObject", "url": "https://www.solarwindsmsp.com/msp-
logo.png",
"width": "649", "height": "256"},
"address": { "@type": "PostalAddress", "streetAddress": "3030 Slater Rd",
"addressLocality": "Morrisville", "addressRegion": "NC",
"postalCode": "27560", "addressCountry": "USA" }}]}
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structured-seo-data-overview-and-how-to-190713022207/75/Structured-SEO-Data-An-overview-and-how-to-for-Drupal-15-2048.jpg)





![Adding data via Code
Use the hook:
page_attachments_alter()
Add your JSON encoded
information to the
$attachments parameter.
$attachments['#attached']['html_head']
['my_custom_schema'] = [
[
'#type' => 'html_tag',
'#tag' => "script",
'#value' => theme_build_schema_elements(),
'#attributes' => [
'type' => 'application/ld+json',
],
],
];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structured-seo-data-overview-and-how-to-190713022207/75/Structured-SEO-Data-An-overview-and-how-to-for-Drupal-33-2048.jpg)
