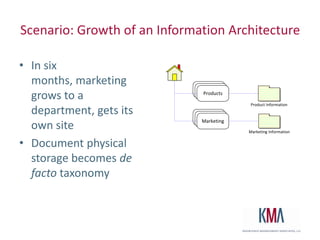
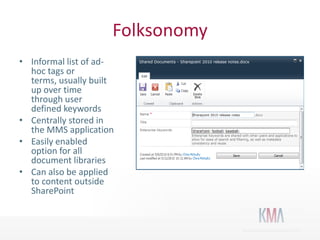
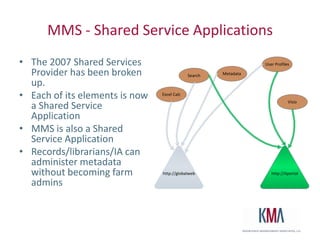
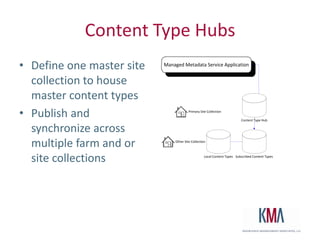
The document discusses the use of taxonomies and metadata in SharePoint 2010, emphasizing the significance of managed metadata services and content types for effective information management. It outlines the architecture of SharePoint, explains key metadata terminology, and offers practical guidance on taxonomy administration and design considerations. Additionally, the document highlights design best practices, security models, and resources for further learning.