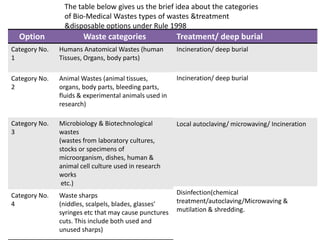
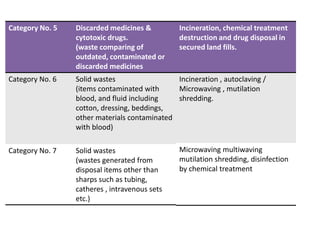
The document discusses the management of healthcare waste. It defines healthcare waste as any waste generated during diagnosis, treatment or immunization of humans or animals in healthcare facilities. It notes that healthcare waste requires safe handling due to its potential for infection and injury. It then outlines the types of healthcare waste and provides examples, as well as treatment and disposal options according to regulations. Finally, it discusses how healthcare waste is managed and treated in Pimpri Chinchwad, with waste being collected and transported daily to an incinerator facility.



![The institutions mainly involved in generation of Bio-Medical
wastes include:
~Government hospitals
~Nursing home
~Physicians office/clinics.
~Dentists office/clinics
~Dispensaries.
~Medical and research training center
~Mortuaries.
~Blood banks and Collection centers
~Slaughter houses
~Laboratories
~Bio-technology institutes and production units.
~Research organizations.
All these Health care establishments generate wastes and are therefore
covered under Bio-Medical wastes[BMW].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biomedicalwastedisposal-120423093526-phpapp02/85/Biomedical-waste-disposal-4-320.jpg)