Embed presentation
Downloaded 54 times
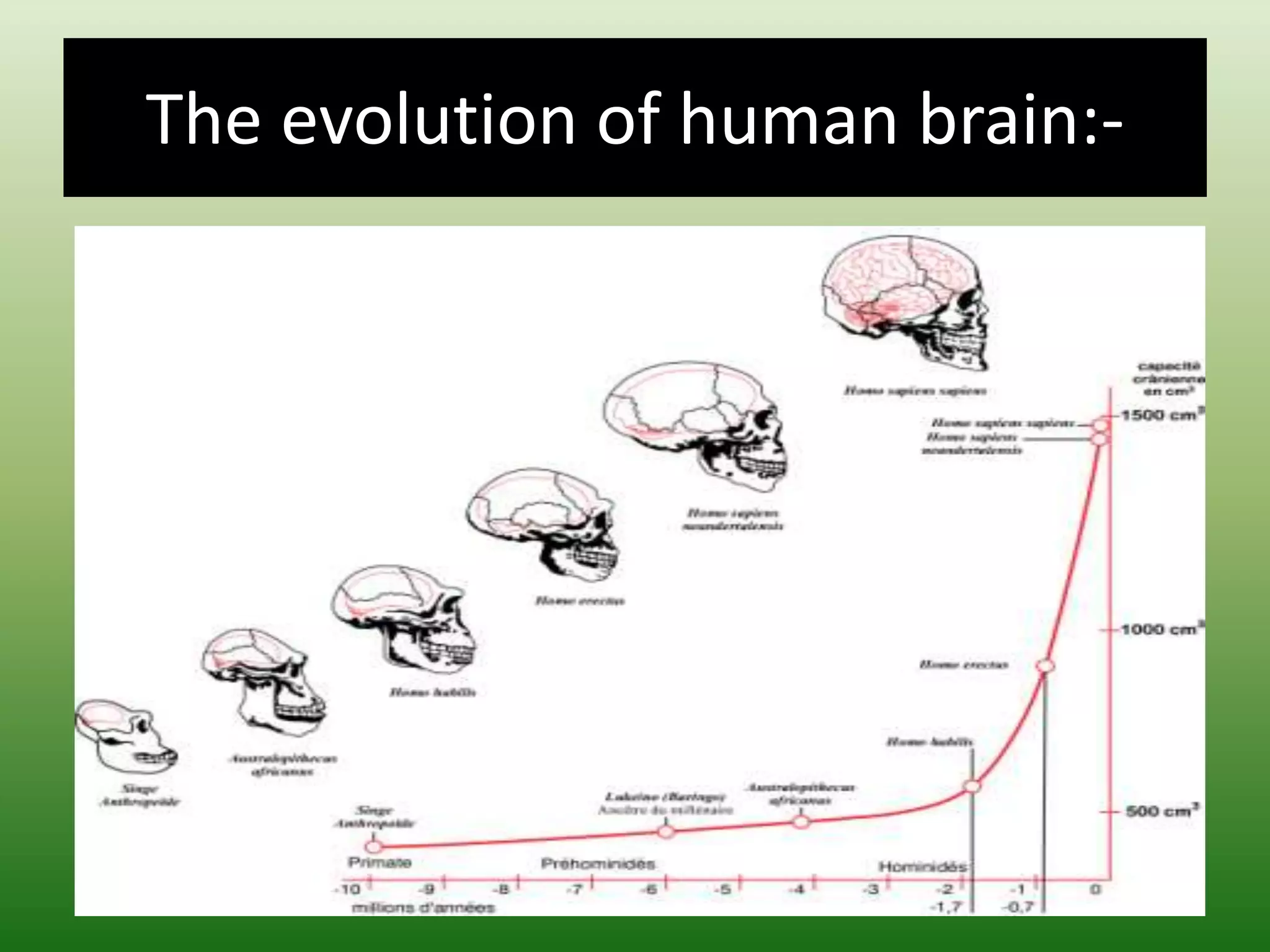


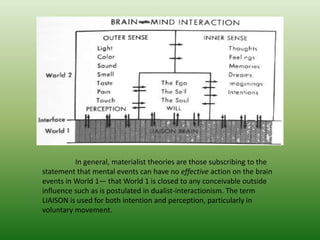


The document discusses three hypotheses for the evolution of the human brain: the epiphenomenal hypothesis which argues that brain size increases led to mental states but did not causally impact behavior; the ecological hypothesis which proposes that environmental conditions constrained brain evolution to better adapt to consuming leaves or fruits; and the social brain hypothesis, though not described in detail. The epiphenomenal hypothesis views behavior as solely caused by neural impulses and muscles, independent of mental states. The ecological hypothesis suggests fruit-eating animals evolved larger brains than leaf-eating animals to process resources.





