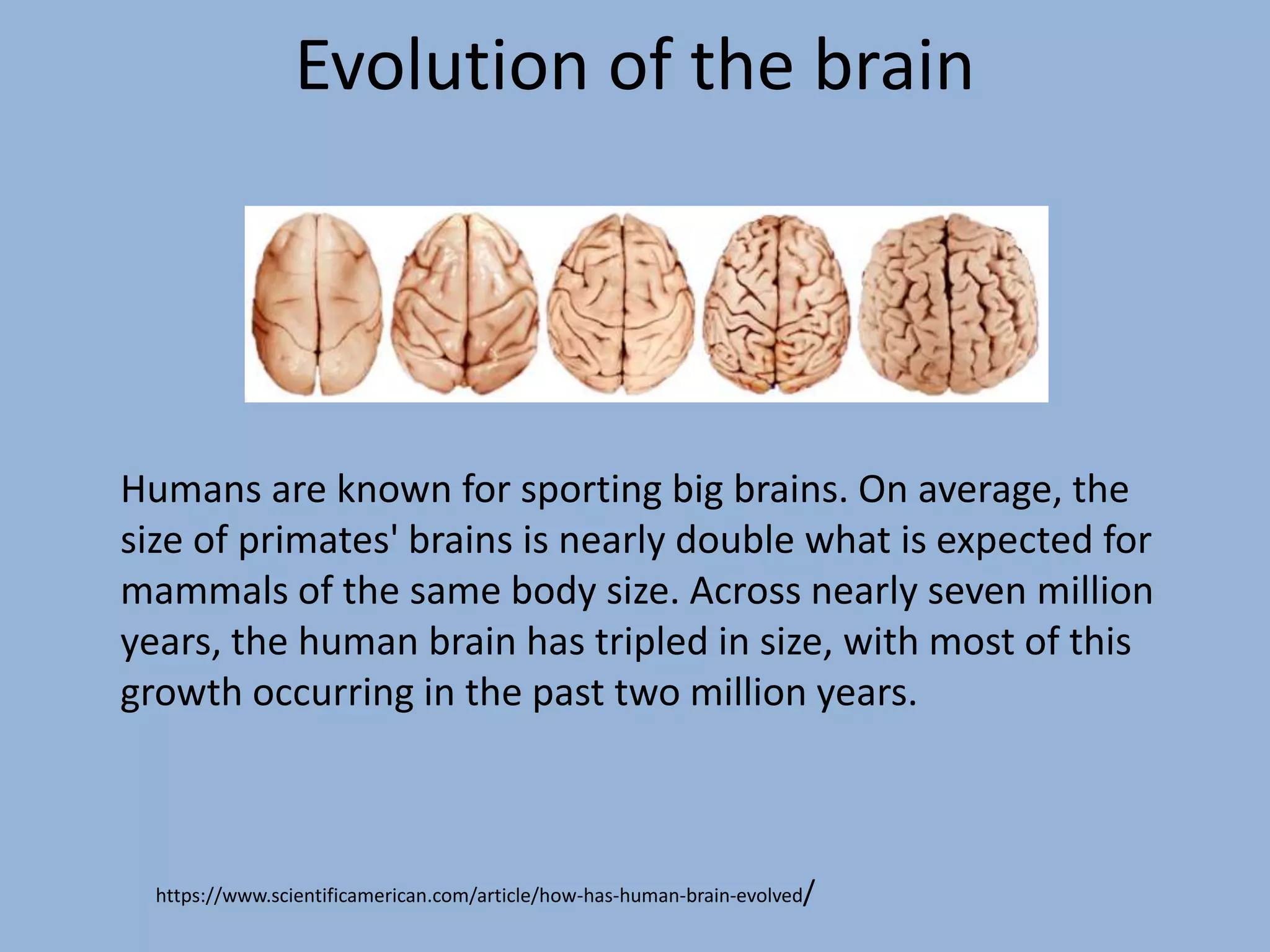
The document discusses several facts about the human brain, including that it cannot feel pain itself, is more active during dreaming than waking hours, and benefits from exercise like the body. It also notes that the visual areas are located in the back of the brain, brains were larger in ancestors, and contains more cell types than any other organ. The brain continues developing into early adulthood and decreases in size with age.