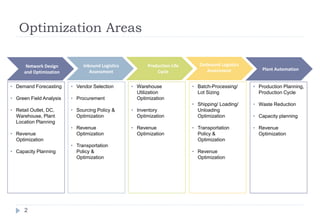
This document discusses optimization opportunities across the supply chain, including demand forecasting, location planning, capacity planning, vendor selection, transportation optimization, warehouse utilization, inventory optimization, production planning, and waste reduction. The key areas of focus are network design and optimization, production planning, and revenue optimization throughout the supply chain from inbound logistics to outbound logistics. Optimization aims to minimize costs while meeting customer requirements and maintaining quality and service levels.