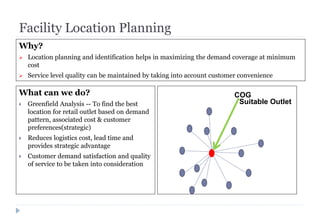
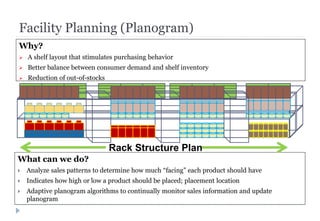
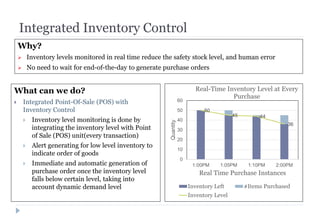
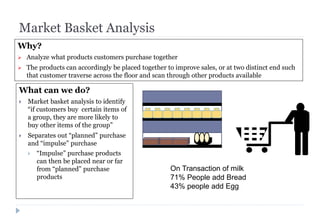
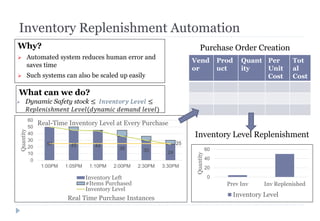
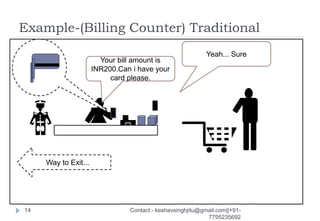
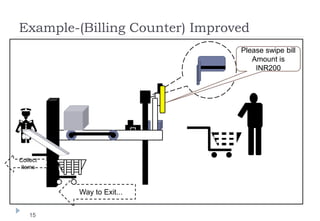
The document discusses various ways that intelligent process automation can optimize operations in the retail industry. It describes focusing on areas such as demand pattern identification, facility location planning, floor planning, sourcing automation, self-checkout counters, integrated inventory control, market basket analysis, inventory replenishment automation, stock clearance, and price optimization. Specific approaches and benefits are provided for each area. The overall goal is to reduce costs, improve inventory management and the customer experience through automation, data analysis, and optimization of retail operations and supply chain processes.