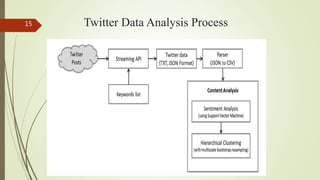
This document discusses supply chain analytics and how analyzing big data can help improve forecasting and decision making. It focuses on using social media data to analyze consumer sentiment regarding the beef supply chain. Key points include:
1. Supply chain analytics applies techniques like machine learning to patterns in data to improve forecasting and efficiency.
2. Analyzing social media, point-of-sale, and in-store data on topics like product choices and foot traffic can provide insights for forecasting sales.
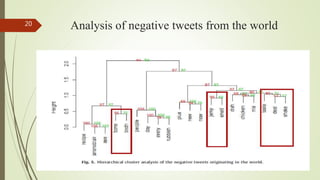
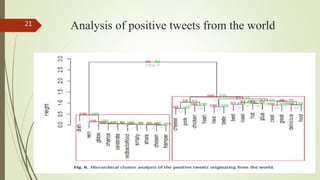
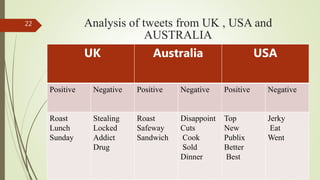
3. A case study analyzed tweets about beef/steak, finding issues around food safety, quality, and coordination between suppliers affected consumer satisfaction.
4. Recommendations include developing consumer-centric supply chains and